CCRN (Adult) - Direct Care Eligibility Pathway Questions and Answers
A nurse has responded to a rapid response call on a medical-surgical floor in the hospital. The nurse finds the patient with the following data:
BP72/30
HR132
RR24
T102.3° F (39.0° C)
SpO295%
Ph7.13
PaCO234 mm Hg
PaO288 mm Hg
HCO3 14 mEq/L
Na+ 142 mEq/L
The nurse should anticipate an order to administer which of the following?
When caring for a patient with septic shock secondary to osteomyelitis, which of the following laboratory tests will best monitor response to therapy?
A patient has been declared brain dead. A nurse would like the family to consider organ donation but has never requested this from a family before. The best initial action by the nurse is to
A patient with end-stage COPD who has failed multiple mechanical ventilation weaning trials communicates a desire to discontinue mechanical ventilation and be extubated. Which of the following is a nurse's best response?
Which of the following should the nurse expect in a patient with papillary muscle dysfunction?
The first priority in management of an acute GI hemorrhage is
A patient who sustained acute head trauma exhibited intermittent unconsciousness prior to admission. The patient is disoriented initially and exhibits rapid deterioration in neurological status shortly after admission. X-rays reveal a right temporal bone fracture, and a diagnosis of epidural hematoma is made. The deterioration in the patient's condition is most likely associated with
The primary pathophysiology underlying acute respiratory failure in a patient with head trauma involves
A patient who was admitted after an open aortofemoral bypass for claudication at rest has a hemoglobin A1C of 8.9. The patient admits having poor control of blood glucose levels and is scared to use insulin as directed because of a few episodes of hypoglycemia. Which of the following should the nurse initially request to be consulted?
A patient with history of hypothyroidism is admitted with severe confusion and nonpitting edema. The nurse should anticipate which order?
A patient is admitted with Gl bleeding. During the assessment, the nurse notes the patient to be tremulous, anxious, and startles every time he is touched by the nurse. Which of the following is the most pertinent part of the patient's history to obtain?
Examination of a patient exhibiting Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs indicates which of the following?
A consistent prolongation of the P-R interval beyond 0.20 sec indicates which of the following types of AV block?
Which of the following ECG changes is expected in a patient with a potassium concentration of 3.0 mEq/L?
The spouse of a critically ill patient is indecisive, withdrawn, and tells the nurse, "I feel so helpless." Appropriate nursing interventions include
A patient is admitted with hypotension, tachycardia, and intermittent confusion. Upon arrival, the patient asks to walk to the bathroom. Which of the
following is a nurse's best action?
A patient who is confused and dyspneic is admitted with ABG values that reveal hypoxemia. Results from insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter are:
PAP 38/18 mm Hg
PAOP10 mm Hg
CI 3.5 L/min/m2
These values are most indicative of
In a patient with a chest tube, an air leak in the pleural space is indicated by which of the following conditions in the water-seal chamber?
Patients in end-stage cardiomyopathy often exhibit which of the following symptoms of right-sided heart failure?
A patient with a history of asthma presents with acute onset of dyspnea, a non-productive cough, and tachypnea. He is very anxious, restless, and tachycardic. Which of the following is a first-line drug for these symptoms?
The underlying pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is best explained as
A patient is experiencing lower left quadrant pain with guarding, as well as abdominal distention and rigidity. KUB reveals free air in the abdominal
cavity. Vital signs are:
BP76/40
HR130
RR32
T101.7° F (38.7°C)
A nurse would suspect
A patient with a C5 spinal cord injury calls the nurse every 15 minutes with requests for juice, water, and repositioning. Which of the following is the nurse's best response?
For a patient who sustained blunt renal trauma and a crush injury to the leg, monitoring should include observing for
An older adult patient is admitted with acute exacerbation of congestive heart failure. An echocardiogram indicates that EF is unchanged at 50%. The patient is most likely experiencing
A nurse is precepting an experienced critical care nurse who is new to the facility. To develop the orientation plan, which of the following should the preceptor do first?
A patient with hypertension received tPA for an acute embolic stroke with complete resolution of symptoms. Twenty-four hours after tPA administration, the nurse should anticipate an order for
An unconscious patient in hepatic failure secondary to alcoholism becomes acutely hypoglycemic. Glucagon administration is contraindicated for this patient because glucagon
Which of the following is the most common prerenal cause of acute tubular necrosis?
A patient underwent bariatric surgery for weight loss 3 days ago. The patient appears anxious, restless, and reports increased abdominal pain over the last 24 hours. The nurse palpates mild subcutaneous crepitus over the neck. Vital signs are:
BP 106/64
HR 128
RR 27
T 100.4° F (38°C)
Which action should the nurse anticipate?
A nurse admits a patient awaiting surgery for an unstable pelvic fracture following a fall in which no other injuries were sustained. The nurse should prioritize
A patient with acute renal failure has a serum potassium level of 7.2 mEq/L. The most appropriate immediate intervention for this patient is
A patient is receiving therapeutic hypothermia post-cardiac arrest. Which of the following orders should a nurse clarify?
The goal of PEEP therapy in acute lung injury (ALI) is to
Following a splenectomy, a patient is most at risk for
Pulsus paradoxus is defined as
A terminally ill patient is deteriorating. The patient's family states, "We don't want him to suffer any more." The most appropriate response is
A 22-year-old trauma patient sustained multiple fractures after a fall. The patient fell 50 feet from a cliff while rock climbing without a harness. The patient is intubated and sedated with casts to bilateral lower extremities. The nurse should recognize that young adults are
Assessment of a patient with a head injury reveals increased muscle tone and contractured positioning of the upper extremities. A nurse should
A patient is admitted with an acute anterior wall MI. Initial hemodynamic readings are:

The nurse anticipates initiating a plan of care for
After the administration of haloperidol (Haldol), a nurse should monitor closely for
A patient develops the dysrhythmia shown below:
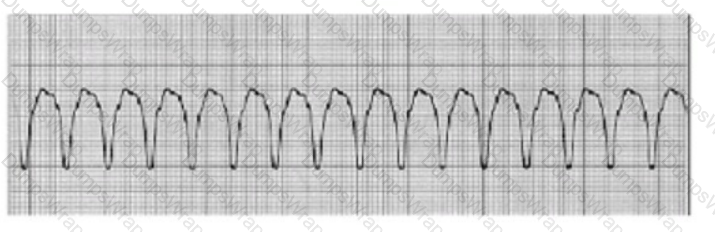
Blood pressure is 83/40. The patient is pale, diaphoretic, lethargic, and disoriented. The most appropriate treatment is
A patient in septic shock is treated with a dopamine (Intropin) infusion of 10 mcg/kg/min. Which of the following indicates that this intervention has been effective?
A nurse is performing medication reconciliation during a patient's admission. To determine the patient's current understanding of the medication furosemide (Lasix), which of the following is the best statement by the nurse?
A family member asks permission to visit a patient after work at 12:30 AM. On previous visits, the family member has been disruptive. To address the situation, a nurse should

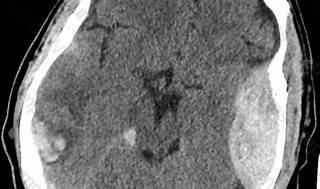 Epidural hematoma
Epidural hematoma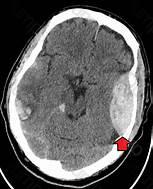
 Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome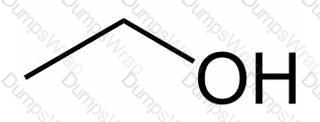
 Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia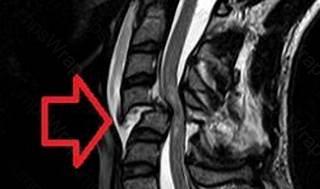 Spinal cord injury
Spinal cord injury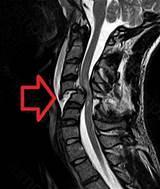
 Haloperidol
Haloperidol