Interior Design Fundamentals Exam Questions and Answers
What auxiliary equipment is required to make light-emitting diodes (LEDs) operate correctly?
Options:
Ballast
Meter
Driver
Relay
Answer:
CExplanation:
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are a type of lighting technology that requires specific auxiliary equipment to function properly. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and lighting design standards (e.g., from the Illuminating Engineering Society [IES]) provide guidance on the components needed for LED lighting systems.
A. Ballast: A ballast is used to regulate the current in fluorescent or high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, not LEDs. LEDs do not require a ballast because they operate on direct current (DC) and need a different type of regulation.
B. Meter: A meter is a device used to measure electrical usage or light output (e.g., a light meter), not to operate LEDs. It is not an auxiliary component for LED functionality.
C. Driver: An LED driver is a power supply that regulates the voltage and current supplied to an LED, converting alternating current (AC) from the building’s electrical system to the direct current (DC) required by LEDs. The driver ensures that the LED operates at the correct voltage and current, preventing damage and ensuring proper performance. This makes the driver the essential auxiliary equipment for LEDs.
D. Relay: A relay is an electrical switch used to control circuits, often in automation systems, but it is not required to make LEDs operate. It might be used in a larger lighting control system but is not specific to LED functionality.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual specifies that LEDs require a driver to function correctly, as the driver manages the electrical input to match the LED’s requirements. This is a fundamental aspect of lighting design for interior spaces.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 8: Environmental Control Systems): "LEDs require a driver as auxiliary equipment to regulate the voltage and current, converting AC power to the DC power needed for proper operation."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that an LED driver is necessary to ensure that LEDs receive the correct electrical input, protecting the diodes from damage and ensuring consistent performance. This distinguishes the driver from other components like ballasts (for fluorescent lights) or relays (for control systems).
Objectives:
Understand the technical requirements for LED lighting in interior design.
Identify the auxiliary equipment needed for different lighting technologies.
A designer notes that the travel distance from the remote point in a fitness center is greater than the maximum distance allowed by the building code. Which intervening spaces may be traveled through to reduce travel distance?
Options:
Office
Lockers
Storage
Reception
Answer:
DExplanation:
Travel distance is a key component of the means of egress, defined by the International Building Code (IBC) as the distance an occupant must travel from the most remote point in a space to reach an exit. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Chapter 10 (Means of Egress) specify maximum allowable travel distances based on occupancy type and whether the building is sprinklered. For a fitness center (likely classified as an Assembly occupancy, Group A-3), the maximum travel distance is typically 200 feet (61 meters) in a non-sprinklered building or 250 feet (76 meters) in a sprinklered building, per IBC Table 1017.2. The question asks which intervening spaces can be used to reduce travel distance, meaning the space must be part of the egress path and not pose additional hazards or restrictions.
A. Office: An office is a private space typically used by staff, not part of the public egress path. IBC Section 1006.2.1 states that egress paths must be through spaces that are accessible to all occupants, and private offices do not meet this requirement. Traveling through an office would not be a permissible part of the egress path.
B. Lockers: Locker rooms may be part of a fitness center, but they often contain obstacles like benches and lockers that can impede egress. Additionally, locker rooms may have dead-end corridors or limited exits, which could increase risk during an emergency. IBC Section 1018.4 limits dead-end corridors in egress paths, making locker rooms a less suitable option.
C. Storage: Storage rooms are not part of the egress path, as they are typically not accessible to the public and may contain hazards (e.g., clutter, locked doors). IBC Section 1006.2.2.3 prohibits egress through storage rooms due to the potential for obstruction and safety risks.
D. Reception: A reception area is a public, open space that is typically part of the main circulation path in a fitness center. It is designed to be accessible to all occupants and is often located near the main entrance/exit, making it a permissible and practical space to include in the egress path. Traveling through a reception area can reduce the overall travel distance by providing a direct route to an exit, as long as the path remains unobstructed and meets width requirements (per IBC Section 1005).
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC confirm that egress paths must be throughaccessible, public spaces like reception areas, which can help reduce travel distance while maintaining safety.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Chapter 10.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards): "Egress paths must be through accessible, public spaces such as reception areas, which can be used to reduce travel distance while ensuring a safe and unobstructed route to an exit."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that travel distance can be reduced by routing the egress path through public, accessible spaces like reception areas, which are designed for circulation and typically lead to exits. This aligns with IBC requirements that prohibit egress through private or hazardous spaces like offices, locker rooms, or storage areas.
Objectives:
Understand the components of the means of egress, including travel distance.
Identify permissible spaces for egress paths to ensure code compliance.
Which certification should the designer look for in the wood specifications if concerned about sustainable sourcing?
Options:
EPA
FSC
LEED
USGBC (CAGBC)
Answer:
BExplanation:
Sustainable sourcing of wood ensures that it comes from responsibly managed forests, reducing environmental impact. The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification is the most recognized standard for sustainable wood sourcing, verifying that the wood is harvested in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. Option A (EPA) is a regulatory agency, not a certification for wood. Option C (LEED) is a green building certification system that may credit FSC-certified wood but is not a wood certification itself. Option D (USGBC/CAGBC) is the organization behind LEED, not a certification for wood.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on sustainable design.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “When concerned about sustainable sourcing of wood, designers should look for FSC certification, which ensures responsible forest management.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes sustainable design principles, with FSC certification being the standard for verifying sustainable wood sourcing.
Objectives:
Specify sustainable materials in design (IDFX Objective: Material Selection andSpecification).
After completing programming research for a private residence, what is the BEST tool for summarizing the spatial requirements?
Options:
Criteria matrix
Rough floor plan
Stacking diagram
Orthographic diagram
Answer:
AExplanation:
After completing programming research, the designer needs to summarize the spatial requirements (e.g., square footage, adjacencies, and functional needs) in a clear, organized format. A criteria matrix is the best tool for this purpose, as it condenses the programming data into a tabular format, listing each space, its required area, and adjacency needs. This is particularly useful for a private residence, where spaces like bedrooms, kitchens, and living areas have specific requirements. Option B (rough floor plan) is a schematic design tool, not a programming summary. Option C (stacking diagram) is used for multi-story buildings to show vertical relationships, less relevant for a single residence. Option D (orthographic diagram) refers to technical drawings like elevations, not a summary tool.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on programming tools.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “A criteria matrix is the best tool for summarizing spatial requirements after programming, listing each space’s area and adjacency needs in a clear format.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the use of a criteria matrix to organize programming data, making it an effective tool for summarizing spatial needs in any project, including a private residence.
Objectives:
Use programming tools to summarize spatial requirements (IDFX Objective: Programming and Site Analysis).
Which item is BEST to specify for a universal workstation?
Options:
Adjustable task light
Overhead storage shelving
Under counter filing cabinets
Adjustable height work surface
Answer:
DExplanation:
A universal workstation is designed to accommodate a wide range of users, including those with disabilities, by incorporating principles of universal design. An adjustable height work surface is the best item to specify because it allows users to customize the desk height to their needs, accommodating wheelchair users, standing workers, or those with ergonomic preferences. This aligns with ADA and universal design standards for accessibility and flexibility. Option A (adjustable task light) is useful but not the most critical for universal design. Option B (overheadstorage shelving) may be inaccessible to some users. Option C (under counter filing cabinets) reduces knee space, which can hinder accessibility for wheelchair users.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on universal design and accessibility.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “For a universal workstation, an adjustable height work surface is the best specification to ensure accessibility and flexibility for all users, including those with disabilities.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes universal design principles, with adjustable height surfaces being a key feature to accommodate diverse users in workstations.
Objectives:
Apply universal design principles to workstations (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
What is the minimum clear width for two wheelchairs to pass according to ADA accessibility guidelines?
Options:
36" [914 mm]
48" [1219 mm]
60" [1524 mm]
72" [1829 mm]
Answer:
CExplanation:
ADA accessibility guidelines specify the minimum clear width required for two wheelchairs to pass each other, ensuring safe and accessible circulation in public spaces. The standard width for a single wheelchair is 32 inches (813 mm), but for two wheelchairs to pass, the ADA requires a minimum clear width of 60 inches (1524 mm). This accounts for the width of two wheelchairs (approximately 30 inches each) plus additional space for maneuvering. Option A (36 inches) is the minimum for a single wheelchair to pass through a doorway. Option B (48 inches) is the minimum for a wheelchair to make a 180-degree turn, not for passing. Option D (72 inches) exceeds the minimum requirement.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on accessibility standards.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualreferences ADA standards, stating, “The minimum clear width for two wheelchairs to pass is 60 inches (1524 mm), ensuring accessible circulation in public spaces.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum requires designers to apply ADA standards for circulation, with 60 inches being the minimum for two wheelchairs to pass safely.
Objectives:
Apply accessibility standards to circulation spaces (IDFX Objective: Codes and Standards).
Hot spots from cove lighting are created when
Options:
The lamps are improperly ventilated
White paint is used to reflect the light
The light source is too close to the ceiling
The light transformer interrupts the lamp configuration
Answer:
CExplanation:
Cove lighting is an indirect lighting technique where light sources are hidden in a recessed ledge or cove, typically along the perimeter of a ceiling, to create a soft, diffused glow. Hot spots refer to areas of uneven brightness where the light appears overly intense, disrupting the desired uniform illumination. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and lighting design standards (e.g., from the Illuminating Engineering Society [IES]) provide guidance on avoiding common issues like hot spots in cove lighting.
A. The lamps are improperly ventilated: Improper ventilation can cause lamps to overheat, potentially leading to reduced lifespan or safety hazards, but it does not directly cause hot spots. Hot spots are a visual issue related to light distribution, not heat dissipation.
B. White paint is used to reflect the light: White paint in a cove is often recommended because it reflects light evenly, helping to diffuse the illumination and reduce hot spots. Using a reflective surface like white paint is a standard practice in cove lighting design, nota cause of hot spots.
C. The light source is too close to the ceiling: Hot spots occur when the light source (e.g., LED strip, fluorescent tube) is positioned too close to the ceiling surface, causing the light to reflect directly off the ceiling without proper diffusion. This creates bright spots where the light hits the ceiling most intensely, rather than a smooth, even glow. The IES recommends maintaining a minimum distance (typically 6-12 inches, depending on the fixture) between the light source and the ceiling to allow for proper light spread and diffusion, avoiding hot spots.
D. The light transformer interrupts the lamp configuration: A transformer (or driver for LEDs) might cause issues with power supply or flickering, but it does not directly affect the distribution of light to create hot spots. This option is more related to electrical configuration than light placement.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual specifies that hot spots in cove lighting are caused by improper placement of the light source, particularly when it is too close to the ceiling, preventing even light distribution.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 8: Environmental Control Systems): "Hot spots in cove lighting are created when the light source is too close to the ceiling, causing uneven reflection and bright spots rather than a diffused glow."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that the distance between the light source and the ceiling is critical in cove lighting design. When the light source is too close, the light reflects directly off the ceiling, creating hot spots instead of the desired even illumination. Proper spacing ensures the light can spread and diffuse, achieving a uniform effect.
Objectives:
Understand the principles of cove lighting design in interior spaces.
Identify common issues like hot spots and their causes in lighting applications.
What standard should be referenced when specifying upholstered furniture to maintain air quality?
Options:
NSF
LEED
BOMA
BIFMA
Answer:
DExplanation:
When specifying upholstered furniture to maintain air quality, the designer must consider standards that address indoor environmental quality, particularly emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from furniture. The Business and Institutional Furniture Manufacturers Association (BIFMA) provides standards like BIFMA e3, which includes criteria for low-emission furniture to ensure good indoor air quality. Option A (NSF) focuses on food safety and water quality, not furniture. Option B (LEED) is a green building certification that includes air quality credits but is not specific to furniture standards. Option C (BOMA) deals with building measurement standards, not air quality.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on sustainable design and material specifications.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “BIFMA standards, such as BIFMA e3, should be referenced when specifying upholstered furniture to ensure low emissions and maintain indoor air quality.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes sustainable design principles, with BIFMA standards being a key reference for furniture specifications to support indoor air quality.
Objectives:
Specify materials for indoor air quality (IDFX Objective: Material Selection and Specification).
What are blocking and stacking diagrams used to determine?
Options:
Private office locations
Client organizational structure
Key departmental adjacencies
Square footage [m²] requirements
Answer:
CExplanation:
Blocking and stacking diagrams are tools used during the programming and schematic design phases to plan the layout of a multi-story building. Blocking diagrams show the horizontal arrangement of departments or functions on each floor, while stacking diagrams show the vertical arrangement across floors. Together, they are used to determine key departmental adjacencies, ensuring that related departments are placed near each other, either on the same floor or on adjacent floors, to support workflow and efficiency. Option A (private office locations) is too specific for these diagrams, which focus on larger zones. Option B (client organizational structure) is determined during programming, not through these diagrams. Option D (square footage requirements) is part of programming but not the primary purpose of blocking and stacking diagrams.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on space planning tools.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Blocking and stacking diagrams are used to determine key departmental adjacencies, showing the horizontal and vertical arrangement of functions in a multi-story building.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes blocking and stacking diagrams as tools for organizing space in complex projects, focusing on adjacencies to enhance functionality.
Objectives:
Use space planning tools to determine adjacencies (IDFX Objective: Programming and Site Analysis).
A designer is designing the interiors of a major medical center. Federal, state, and local jurisdiction codes apply. All the codes have conflicting requirements. What should the designer do?
Options:
Seek code variances for the conflicting codes
Comply with the least restrictive code that applies
Comply with the most restrictive code that applies
Seek a code source that has restrictions that conform to the design solution
Answer:
CExplanation:
When designing a major medical center, the designer must adhere to federal, state, and local codes, which may include the International Building Code (IBC), ADA standards, and healthcare-specific regulations like those from the Facility Guidelines Institute (FGI). When codes conflict, the standard practice is to comply with the most restrictive code to ensure the highest level of safety and compliance, especially in a healthcare setting where life safety is paramount. Option A (seeking code variances) is a last resort and not always feasible or timely. Option B (least restrictive code) compromises safety and is not acceptable. Option D (seeking a code source that conforms to the design) is unethical and violates code compliance principles.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on codes and standards.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “When multiple codes apply and conflict, the designer must comply with the most restrictive code to ensure safety and legal compliance.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum requires designers to understand and apply building codes, prioritizing the most stringent requirements to protect occupants, especially in high-risk settings like medical centers.
Objectives:
Understand the application of multiple codes in design (IDFX Objective: Codes andStandards).
Which of the following symbols would BEST indicate a pendant in a reflected ceiling plan?
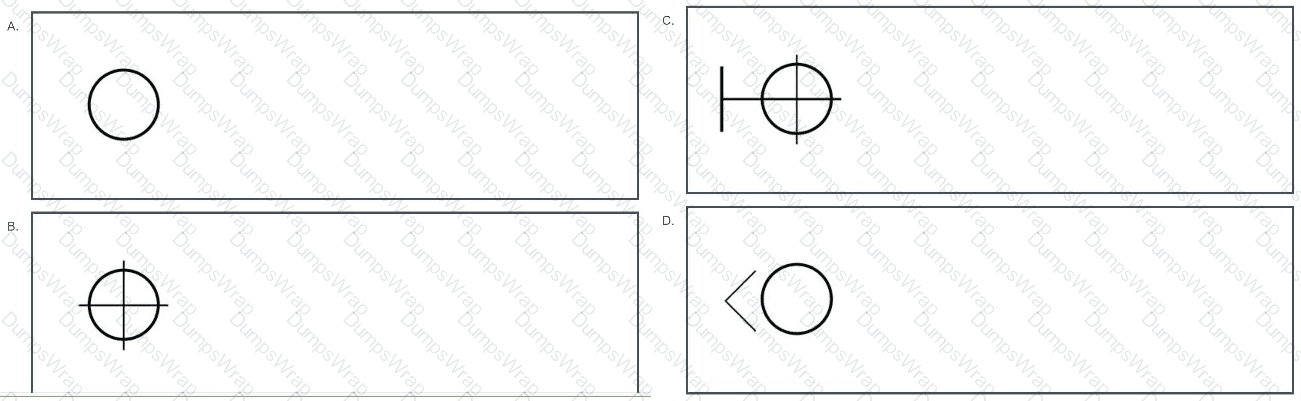
Options:
A plain circle
A circle with crosshairs
A circle with crosshairs and a vertical line
A circle with an arrow
Answer:
BExplanation:
A reflected ceiling plan (RCP) is a drawing that shows the ceiling of a space as if it were reflected onto the floor, typically used in architectural and interior design to indicate the placement of ceiling elements such as lighting fixtures, sprinklers, and other features. The question asks for the symbol that best indicates a pendant light, which is a type of lighting fixture that hangs from the ceiling, often suspended by a cord, chain, or rod, and is commonly used for ambient or task lighting in spaces like dining areas, kitchens, or lobbies.
To determine the correct symbol, we need to evaluate each option based on standard architectural and interior design drafting conventions, particularly those used in RCPs as outlined in NCIDQ Interior Design Fundamentals.
Option A: A simple circleA simple circle in an RCP typically represents a recessed light or a ceiling-mounted fixture, such as a can light or a flush-mounted light. Pendant lights, however, are not flush with the ceiling; they hang down, and their symbol should reflect this characteristic. A plain circle does not convey the hanging nature of a pendant light, so Option A is not the best choice for a pendant.
Option B: A circle with a crosshair (plus sign) insideIn architectural and interior design drafting standards, a circle with a crosshair (a plus sign) inside is a common symbol for a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan. The circle represents the fixture itself, and the crosshair indicates that the light is suspended from the ceiling, distinguishing it from recessed or surface-mounted fixtures. This symbol aligns with standard conventions for representing pendant lights in RCPs, making Option B a strong candidate for the correct answer.
Option C: A circle with a crosshair and a small perpendicular line at the topThis symbol is similar to Option B but includes an additional small line at the top of the circle. In some drafting standards, this extra line might indicate a specific type of ceiling fixture, such as a sprinkler head or a ceiling fan, where the line could represent a connection point or a blade. For pendant lights, however, the extra line is not a standard feature in most RCP symbols. The additional line makes this symbol less clear for a pendant light, so Option C is not the best choice.
Option D: A circle with an arrow pointing to the leftThis symbol is not a standard representation for a pendant light. In RCPs, an arrow might be used to indicate direction (e.g., for an exit sign or a directional light), but it is not typically associated with pendant lights. The arrow suggests movement or orientation, which does not align with the static, hanging nature of a pendant light. Therefore, Option D is not appropriate for a pendant light in an RCP.
Based on this analysis, the symbol that best indicates a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan isa circle with a crosshair inside (Option B), as it aligns with standard drafting conventions for pendant lights in RCPs. The crosshair effectively communicates that the fixture is suspended, which is a key characteristic of a pendant light.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using principles from the NCIDQ Interior Design Fundamentals and standard architectural drafting conventions, which are part of the NCIDQ exam preparation materials.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (a common resource for NCIDQ candidates):
"In a reflected ceiling plan, pendant lights are typically represented by a circle with a crosshair (plus sign) inside to indicate that the fixture is suspended from the ceiling, distinguishing it from recessed or surface-mounted lights."
The NCIDQ guidelines and standard architectural drafting practices specify that a pendant light in a reflected ceiling plan is represented by a circle with a crosshair inside. The circle denotes the fixture, and the crosshair indicates its suspended nature, which is a defining feature of a pendant light. This symbol ensures clarity in the RCP, allowing contractors and designers to understand the type of lighting fixture being specified. Options A, C, and D do not align with this standard convention for pendant lights, as they either lack the crosshair (Option A), include unnecessary elements (Option C), or use an unrelated symbol (Option D).
Objectives:
Understand the purpose and components of a reflected ceiling plan (RCP).
Identify and apply standard architectural symbols for lighting fixtures in RCPs.
Differentiate between symbols for various types of ceiling fixtures (e.g., recessed lights, pendants, sprinklers).
A designer visits a client and observes employee working relationships as well as how they utilize their work area. What part of the design process is this?
Options:
Programming
Space planning
Design development
Construction administration
Answer:
AExplanation:
The design process in interior design consists of several distinct phases, each with specific goals and activities. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual outlines these phases, including programming, space planning, design development, and construction administration, and describes the tasks associated with each.
A. Programming: Programming is the initial phase of the design process where the designer gathers and analyzes information about the client’s needs, goals, and requirements. This includes observing how users interact with the space, such as employee working relationships and how they utilize their work area. These observations help the designer understand the functional and spatial needs of the project, which are then translated into design solutions. The designer’s visit to observe employees is a classic programming activity, as it involves data collection to inform the design.
B. Space planning: Space planning involves creating layouts and arranging spaces based on the information gathered during programming. While observations might inform space planning, the act of observing is part of programming, not space planning itself.
C. Design development: Design development involves refining the design concept, selecting materials, and creating detailed drawings. This phase occurs after programming and space planning, so the observation of employees is not part of this stage.
D. Construction administration: Construction administration occurs during the construction phase, where the designer oversees the implementation of the design, addresses issues, and ensures the project is built as intended. Observing employees in their work area is not part of this phase, as it focuses on construction oversight rather than data collection.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual specifies that observing users and their interactions with a space is a key activity in the programming phase, as it helps the designer define the project’s requirements.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 3: Programming and Space Planning): "Programming includes observing users in their environment, such as employee working relationships and space utilization, to gather data on the project’s functional and spatial needs."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that programming involves collecting data through methods like observation to understand how users interact with their space. Observing employee working relationships and space utilization directly contributes to defining the project’s requirements, making this a programming activity.
Objectives:
Understand the phases of the interior design process.
Identify the role of observation in the programming phase.
A client notes that they have insufficient tiling and storage in their newly completed space. This could have been avoided if the designer had
Options:
Researched precedents
Conducted programming
Completed code research
Developed a punch [deficiency] list
Answer:
BExplanation:
The issue of insufficient tiling and storage in a completed space points to a failure in understanding the client’s needs and requirements during the design process. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual outlines the steps of the design process, emphasizing the importance of each phase in ensuring a successful project outcome.
A. Researched precedents: Researching precedents involves studying similar projects to inform design decisions. While this can provide inspiration, it does not directly address the client’s specific needs for tiling and storage, which are unique to their project.
B. Conducted programming: Programming is the phase of the design process where the designer gathers and analyzes the client’s needs, goals, and requirements. This includes determining the amount of storage needed, the types of spaces required, and specific material needs like tiling. If the designer had conducted thorough programming, they would have identified the client’s need for sufficient tiling (e.g., in wet areas) and storage (e.g., cabinets, shelving) early in the process, ensuring these elements were incorporated into the design. This makes programming the most relevant step to avoid the issue.
C. Completed code research: Code research ensures compliance with building codes, such as egress, accessibility, and fire safety. While important, it is not directly related to the quantity of tiling or storage, which are functional and client-specific requirements rather than code-driven.
D. Developed a punch [deficiency] list: A punch list is created at the end of a project to identify deficiencies or incomplete work (e.g., missing tiles, unfinished storage installation). While a punch list might catch installation errors, it does not address the root cause of insufficient tiling and storage, which is a failure to plan for these elements during the design phase.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual emphasizes that programming is the foundation of a successful design, as it ensures that the client’s needs are fully understood and addressed in the design solution. Insufficient tiling and storage indicate a lack of proper programming.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 3: Programming and Space Planning):"Programming involves gathering and analyzing the client’s needs and requirements, such as storage and material specifications, to ensure the design meets their functional and aesthetic goals."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that programming is the process of identifying the client’s specific needs, such as the amount of storage or the extent of tiling required for a space. By conducting thorough programming, the designer can incorporate these requirements into the design, preventing issues like insufficient tiling or storage in the completed project.
Objectives:
Understand the role of programming in the interior design process.
Identify how programming prevents design deficiencies related to client needs.
What would be the proxemics zone between 18" [457 mm] and 4'-0" [1219 mm]?
Options:
Public space
Intimate space
Personal space
Social informal space
Answer:
CExplanation:
Proxemics is the study of how people use and perceive space in relation to others, particularly in terms of physical distance during interactions. Developed by anthropologist Edward T. Hall, proxemics defines four spatial zones based on distance, which are widely used in interior design to understand user comfort and spatial behavior. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual outlines these zones and their typical distances.
Hall’s proxemics zones (based on North American cultural norms) are:
Intimate space: 0 to 18 inches (0 to 457 mm) – Used for close relationships (e.g., hugging, whispering).
Personal space: 18 inches to 4 feet (457 mm to 1219 mm) – Used for conversations with friends or acquaintances, allowing for comfortable interaction while maintaining some distance.
Social informal space: 4 feet to 12 feet (1219 mm to 3658 mm) – Used for casual interactions, such as business meetings or social gatherings.
Public space: 12 feet and beyond (3658 mm and beyond) – Used for public speaking or interactions with strangers, where greater distance is preferred.
The question asks for the proxemics zone between 18 inches (457 mm) and 4 feet (1219 mm):
This range falls directly within thepersonal spacezone, as defined by Hall. Personal space is used for interactions where individuals feel comfortable but still maintain a degree of separation, such as conversations with colleagues or friends.
Let’s evaluate the options:
A. Public space: Public space starts at 12 feet (3658 mm), far beyond the given range, so this is incorrect.
B. Intimate space: Intimate space ends at 18 inches (457 mm), so the range of 18 inches to 4 feet exceeds this zone.
C. Personal space: This matches the range of 18 inches to 4 feet (457 mm to 1219 mm), making it the correct answer.
D. Social informal space: Social informal space starts at 4 feet (1219 mm), so the range of 18 inches to 4 feet only partially overlaps with this zone, but the majority of the range fallswithin personal space.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual confirms that the proxemics zone between 18 inches and 4 feet is personal space, as defined by Hall’s framework, which is widely used in interior design to plan spatial relationships.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 6: Human Factors and Ergonomics): "The proxemics zone between 18 inches (457 mm) and 4 feet (1219 mm) is personal space, used for comfortable interactions with acquaintances or colleagues."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that personal space, as defined by Edward T. Hall, spans from 18 inches to 4 feet, making it the appropriate zone for the given range. This zone is used for interactions where individuals maintain a comfortable distance, such as casual conversations, and is a key consideration in designing spaces like lobbies or meeting rooms.
Objectives:
Understand the proxemics zones and their spatial ranges.
Apply proxemics principles to determine appropriate spatial zones for interactions.
What is the best way for a designer to convey the locations of flooring transitions between materials?
Options:
Provide a detailed finish schedule
Reference the floor covering schedule
Refer to the finish legend and specifications
Include a finish plan in the construction documents
Answer:
DExplanation:
Flooring transitions occur where different flooring materials meet (e.g., tile to carpet, hardwood to vinyl), and their locations must be clearly communicated in construction documents to ensure accurate installation. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and standard architectural drafting practices (e.g., as outlined by the American Institute of Architects [AIA]) specify the best methodsfor conveying such information.
A. Provide a detailed finish schedule: A finish schedule is a table that lists the finishes for each room or area (e.g., flooring, walls, ceilings) with details like material type and manufacturer. While it specifies what materials are used, it does not show the specific locations of transitions between materials, as it is not a spatial representation.
B. Reference the floor covering schedule: Similar to a finish schedule, a floor covering schedule lists flooring materials but does not provide a visual representation of where transitions occur. It is not the best way to convey spatial information like transition locations.
C. Refer to the finish legend and specifications: A finish legend defines symbols or codes for different finishes, and specifications provide detailed information about the materials. While these tools are useful for understanding what materials are used, they do not show the precise locations of transitions in a spatial context.
D. Include a finish plan in the construction documents: A finish plan is a drawing that overlays the floor plan with annotations or symbols indicating the locations of different finishes, including transitions between materials. It visually shows where one flooring material ends and another begins (e.g., with a line or symbol at the transition), ensuring clarity for contractors during installation. This is the best way to convey the locations of flooring transitions, as it provides a spatial, visual representation that is easy to interpret.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual emphasizes that a finish plan is the most effective method for communicating the locations of flooring transitions, as it provides a clear, visual guide within the construction documents.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 5: Construction Drawings and Specifications): "The best way to convey the locations of flooring transitions between materials is to include a finish plan in the construction documents, which visually indicates where different finishes meet."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that a finish plan is a drawing that shows the spatial distribution of finishes, including the precise locations of transitions between flooring materials. This visual representation ensures that contractors can accurately install the flooring as intended, making it the most effective method compared to schedules, legends, or specifications, which lack spatial context.
Objectives:
Understand the role of different construction documents in conveying design intent.
Identify the best method for communicating flooring transitions in a project.
A criteria matrix helps designers achieve what PRIMARY goal?
Options:
Defining the orientation of user spaces and responses to environmental conditions
Determining zoned spaces by their user occupants and establishing activity groupings
Interpreting and translating the programming process into usable diagrams and charts
Condensing and formatting programming requirements, including square footage needs and adjacencies
Answer:
DExplanation:
A criteria matrix is a tool used during the programming phase to organize and summarize the project’s requirements in a clear, tabular format. Its primary goal is to condense and format programming requirements, such as square footage needs, adjacencies, and other functional criteria, making it easier to analyze and use in the design process. Option A (defining orientation and environmental responses) is more related to site analysis, not the primary use of a criteria matrix. Option B (determining zoned spaces and activity groupings) is a secondary outcome, not the primary goal. Option C (interpreting the programming process into diagrams) is too broad, as the matrix is a specific tool for data organization, not diagram creation.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on programming tools.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “The primary goal of a criteria matrix is to condense and format programming requirements, including square footage needs and adjacencies, into a usable format for design.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum highlights the criteria matrix as a key programming tool for organizing complex data, ensuring all requirements are clearly documented for the design phase.
Objectives:
Use programming tools to organize project requirements (IDFX Objective: Programming and Site Analysis).
Fabric for seating in a busy waiting room should have a MINIMUM of double rubs.
Options:
Martindale 15,000
Martindale 25,000
Wyzenbeek 10,000
Wyzenbeek 30,000
Answer:
DExplanation:
A busy waiting room requires durable upholstery fabric due to high traffic and frequent use. The Wyzenbeek test measures abrasion resistance in double rubs, while the Martindale test uses cycles. For commercial spaces like waiting rooms, industry standards recommend a minimum of 30,000 Wyzenbeek double rubs for heavy-duty use. Option D (Wyzenbeek 30,000) meets this requirement. Option C (Wyzenbeek 10,000) is too low, suitable for light residential use. Options A and B use the Martindale test, but even 25,000 Martindale cycles (equivalent to about 18,000 Wyzenbeek double rubs) is insufficient for a busy waiting room, where higher durability is needed.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on material specifications and durability.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “For high-traffic commercial spaces like waiting rooms, upholstery fabric should have a minimum of 30,000 Wyzenbeek double rubs to ensure durability.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum requires designers to specify materials based on performance criteria, with Wyzenbeek double rubs being a standard measure for upholstery durability in commercial settings.
Objectives:
Specify durable materials for commercial interiors (IDFX Objective: Material Selection and Specification).
Which thick-set method would produce the BEST bond for installing tile on an uneven subfloor?
Options:
Additional grout
An extra thick layer of adhesive
A mesh substrate with membrane backing
Wire mesh reinforcement of the mortar bed
Answer:
DExplanation:
Installing tile on an uneven subfloor requires a method that ensures a strong bond and a level surface. The thick-set method involves using a mortar bed to create a stable base for the tile. Wire mesh reinforcement of the mortar bed (Option D) is the best method because the wire mesh strengthens the mortar, helping it adhere to the uneven subfloor and providing a durable, levelsurface for the tile. This method is commonly used in commercial and high-traffic areas for its reliability. Option A (additional grout) is incorrect, as grout fills joints between tiles, not the subfloor bond. Option B (extra thick layer of adhesive) can lead to uneven drying and cracking. Option C (mesh substrate with membrane backing) is more for waterproofing or crack isolation, not for leveling an uneven subfloor.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on material installation methods.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “For uneven subfloors, the thick-set method with wire mesh reinforcement of the mortar bed provides the best bond and stability for tile installation.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum covers installation methods for flooring, emphasizing the thick-set method with wire mesh for uneven surfaces to ensure a strong, lasting bond.
Objectives:
Specify appropriate installation methods for flooring (IDFX Objective: Material Selection and Specification).
How is building code satisfied in a mixed-use property that includes a cafe, retail, and office tenant?
Options:
Installing an automatic sprinkler system for each tenant
Building a demising wall that extends to the underside of the structure
Requesting that the landlord apply for change of occupancy
Constructing fire resistance-rated assemblies between the tenants
Answer:
DExplanation:
A mixed-use property with a cafe (likely Group A-2, Assembly), retail (Group M, Mercantile), and office (Group B, Business) tenants involves multiple occupancy classifications, as defined by the International Building Code (IBC). The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Chapter 5 (General Building Heights and Areas) provide requirements for handling mixed occupancies to ensure fire safety and compliance.
The IBC offers three approaches for mixed occupancies:
Non-separated occupancies(IBC Section 508.3): Occupancies are treated as a single occupancy based on the most restrictive requirements, with no fire-rated separations required.
Separated occupancies(IBC Section 508.4): Occupancies are separated by fire resistance-rated assemblies (e.g., walls, floors), with ratings determined by IBC Table 508.4 based on the occupancy types.
Accessory occupancies(IBC Section 508.2): A smaller occupancy is considered accessory to the main occupancy and does not require separation if it meets certain size limits.
Given the distinct nature of a cafe, retail, and office, the separated occupancies approach is most appropriate to ensure safety. Let’s evaluate the options:
A. Installing an automatic sprinkler system for each tenant: While sprinklers can reduce fire ratings or increase allowable area (per IBC Section 903), they are not the primary method to satisfy building code for mixed occupancies. Sprinklers may be required depending on the occupancy and size, but the code still requires separation unless the non-separated approach is used.
B. Building a demising wall that extends to the underside of the structure: A demising wall separates tenant spaces, but "extending to the underside of the structure" (e.g., the floor slab above) does not necessarily mean it is fire-rated. Without a fire resistance rating, this wall does not meet the requirements for separated occupancies under IBC Section 508.4.
C. Requesting that the landlord apply for change of occupancy: A change of occupancy applies when converting a building from one use to another (e.g., office to residential, per IBC Chapter 10). In a mixed-use property, the occupancies are already defined (cafe, retail, office), so a change of occupancy is not relevant.
D. Constructing fire resistance-rated assemblies between the tenants: This is the correct approach for separated occupancies. IBC Table 508.4 specifies the required fire resistance ratings between occupancies. For example, between Group A-2 (cafe) and Group B (office), a 2-hour fire resistance-rated assembly is typically required in a non-sprinklered building (1 hour if sprinklered). Between Group M (retail) and Group B (office), a 1-hour rating is often required. These fire-rated assemblies (walls and floors) ensure fire safety by preventing the spread of fire between occupancies, satisfying the building code for a mixed-use property.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual confirms that constructing fire resistance-rated assemblies between tenants is the standard method to satisfy building code requirements for mixed occupancies, ensuring safety and compliance.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and IBC Section 508.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 2: Building Codes and Standards): "In a mixed-use property, building code is satisfied by constructing fire resistance-rated assemblies between tenants to separate occupancies, as required by the IBC."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that the separated occupancies approach, using fire resistance-rated assemblies (e.g., walls, floors) between tenants, is the standard method to comply with building code in a mixed-use property. This ensures fire safety by preventing fire spread between different occupancy types, as specified in IBC Table 508.4, making it the most appropriate solution.
Objectives:
Understand building code requirements for mixed-use properties.
Apply the separated occupancies approach to ensure fire safety in design.
A completed programming package MUST contain which feature?
Options:
Selection of colors and finishes
A list of project needs and concerns
A budget with detailed cost estimates
Preliminary drawings and design concepts
Answer:
BExplanation:
The programming phase in interior design involves gathering and analyzing information to define the project’s requirements. A completed programming package must include a list of project needs and concerns, such as spatial requirements, functional needs, and client goals, as this forms the foundation for the design process. Option A (selection of colors and finishes) occurs later, during the design development phase. Option C (budget with detailed cost estimates) may be part of programming but is not a required component of the package. Option D (preliminary drawings and design concepts) is part of the schematic design phase, not programming.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on the programming phase.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “The programming package must include a comprehensive list of project needs and concerns, including spatial, functional, and client-specific requirements.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum defines programming as the process of identifying the client’s needs and project requirements, which are documented in a programming package to guide the design process.
Objectives:
Understand the components of the programming phase (IDFX Objective: Programming andSite Analysis).
Which paint finish is best for areas where regular cleaning may be required?
Options:
Satin
Matte
Eggshell
High gloss
Answer:
DExplanation:
Paint finishes (sheens) vary in their durability, washability, and reflectivity, which affects their suitability for different applications. Areas where regular cleaning is required, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or high-traffic public spaces, need a paint finish that can withstand frequent washing without damage. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and industry standards (e.g., from the Master Painters Institute [MPI]) provide guidance on selecting paint finishes based on performance requirements.
A. Satin: Satin paint has a slight sheen and is more durable and washable than matte or eggshell finishes. It is suitable for moderate-traffic areas like living rooms or bedrooms, but in areas requiring regular cleaning, satin may wear down over time with frequent washing, as it is not as durable as higher-sheen finishes.
B. Matte: Matte (or flat) paint has no gloss and provides a non-reflective finish, ideal for hiding surface imperfections. However, it is the least durable and washable, as cleaning can damage the finish or leave marks. It is not suitable for areas requiring regular cleaning.
C. Eggshell: Eggshell paint has a subtle sheen, slightly more than matte, and offers better washability than matte but less than satin. It is still not durable enough for areas that needfrequent cleaning, as it can wear or show marks with repeated washing.
D. High gloss: High gloss paint has a shiny, highly reflective finish and is the most durable and washable of all paint finishes. It can withstand frequent cleaning with water, soap, or even mild chemicals without damage, making it ideal for areas like kitchens, bathrooms, or public spaces where regular cleaning is required. While its high reflectivity can highlight surface imperfections, this is a trade-off for its superior cleanability.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual recommends high gloss paint for areas requiring regular cleaning due to its durability and washability, despite its reflective nature. This aligns with industry practices for specifying finishes in high-maintenance environments.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "High gloss paint is best for areas where regular cleaning is required, as it offers the highest durability and washability, withstanding frequent cleaning without damage."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that high gloss paint is the most suitable for areas needing regular cleaning because its hard, glossy surface resists wear and can be cleaned repeatedly without degrading. This makes it ideal for high-maintenance spaces, even though its reflectivity may require careful surface preparation to avoid highlighting imperfections.
Objectives:
Understand the properties of different paint finishes in interior design.
Select appropriate paint finishes for areas requiring frequent cleaning.
What color has the best perceptual properties for creating a calming environment?
Options:
Red
Blue
Gray
Yellow
Answer:
BExplanation:
Color psychology in interior design examines how colors influence human emotions, perceptions, and behaviors. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and color theory principles outline the perceptual properties of colors and their effects on creating specific environments, such as a calming atmosphere.
A. Red: Red is a warm, stimulating color that increases heart rate and energy levels, often associated with excitement, passion, or urgency. It is not calming and can even create feelings of agitation or alertness, making it unsuitable for a calming environment.
B. Blue: Blue is a cool color widely recognized for its calming and soothing effects. It is associated with tranquility, peace, and relaxation, as it can lower heart rate and blood pressure. Blue’s perceptual properties make it the best choice for creating a calming environment, often used in spaces like bedrooms, spas, or meditation rooms.
C. Gray: Gray is a neutral color that can create a calm, understated atmosphere, especially in softer shades. However, it lacks the emotional warmth or vibrancy of blue and can sometimes feel cold or sterile, making it less effective for creating a truly calming environment.
D. Yellow: Yellow is a warm, cheerful color that can evoke happiness and energy. However, in brighter shades, it can be overstimulating and may cause anxiety or irritation, making it less suitable for a calming environment compared to blue.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual highlights blue as the color with the best perceptual properties for creating a calming environment, as it aligns with psychological research on color effects, such as reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "Blue has the best perceptual properties for creating a calming environment, as it is associated with tranquility and can reduce stress and promote relaxation."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that blue’s calming effects are well-documented in color psychology, making it the most effective color for creating a serene environment. Its ability to lower physiological responses like heart rate and blood pressure supports its use in spaces intended for relaxation, distinguishing it from red (stimulating), gray (neutral), and yellow (energizing).
Objectives:
Understand the psychological effects of color in interior design.
Select appropriate colors to create a calming environment.
What is the most important reason to pursue licensing and/or title registration?
Options:
Improve insurability
Justify fee increases
Expand job opportunities
Meet jurisdiction requirements
Answer:
DExplanation:
Licensing and title registration for interior designers are critical for legal practice in many jurisdictions, particularly for projects involving public safety, such as those requiring code compliance for egress, fire safety, and accessibility. The NCIDQ certification, which is often a prerequisite for licensing, ensures that designers meet professional standards and can legally practice in regulated areas.
A. Improve insurability: While licensing may make it easier to obtain professional liability insurance, this is a secondary benefit rather than the primary reason for pursuing licensing.
B. Justify fee increases: Licensing might allow a designer to charge higher fees due to their credentials, but this is a business decision, not the most important reason for licensing.
C. Expand job opportunities: Licensing can open doors to more projects, especially in regulated jurisdictions, but this is a byproduct of meeting legal requirements, not the primary reason.
D. Meet jurisdiction requirements: Many states and provinces require interior designers to be licensed or registered to practice legally, especially for projects that involve public spaces where health, safety, and welfare (HSW) are concerns. For example, in the U.S., states like Florida and Louisiana have strict licensing laws for interior designers, and failing to meet these requirements can result in legal penalties or the inability to practice. The NCIDQ certification is often required to obtain this licensure, making this the most important reason.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and CIDQ guidelines emphasize that licensing ensures compliance with jurisdictional laws, protecting both the public and the designer by ensuring a minimum standard of competency.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is D, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and CIDQ professional practice guidelines.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 1: Professional Practice): "Licensing and title registration are primarily pursued to meet jurisdictional requirements, ensuring that interior designers can legally practice in regulated areas while protecting public health, safety, and welfare."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that the primary purpose of licensing is to comply with legal requirements set by jurisdictions. This is especially critical in states or provinces where interior design is a regulated profession, and designers must be licensed to submit drawings for permitting or to work on projects involving public safety.
Objectives:
Understand the role of licensing in interior design practice.
Identify the legal and professional reasons for pursuing NCIDQ certification and licensure.
What is required on a window schedule?
Options:
Finish and glazing dimensions
Model number and style of trim
Unit size and location on elevations
Type of glass and rough opening dimensions
Answer:
CExplanation:
A window schedule is a table in construction documents that provides detailed information about the windows in a project, ensuring accurate specification and installation. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and standard architectural drafting practices (e.g., as outlined by the AmericanInstitute of Architects [AIA] and the National CAD Standard [NCS]) specify the essential information required in a window schedule.
A. Finish and glazing dimensions: While the finish of a window (e.g., painted, anodized) and glazing dimensions (e.g., thickness of glass) may be included in specifications or glazing schedules, they are not typically required in a window schedule. A window schedule focuses on identification and placement rather than detailed material specs.
B. Model number and style of trim: Model numbers may be included in a window schedule to specify the exact window product, but they are not always required, depending on the project. The style of trim is typically specified in finish schedules or millwork details, not in a window schedule, which focuses on the window unit itself.
C. Unit size and location on elevations: A window schedule must include the unit size (e.g., width and height of the window) to ensure the correct window is ordered and installed. It also includes the location on elevations (e.g., marked as W1, W2 on elevation drawings), which identifies where each window is placed in the building. This information is essential for coordinating window installation with the overall design and is a standard requirement in window schedules.
D. Type of glass and rough opening dimensions: The type of glass (e.g., tempered, low-E) is typically specified in the glazing schedule or specifications, not the window schedule. Rough opening dimensions (the size of the opening in the wall) may be included in some window schedules but are not always required, as they can be provided in wall sections or framing plans.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual confirms that a window schedule must include the unit size and location on elevations to ensure accurate identification and placement of windows in the project. These are the core pieces of information needed for coordination and installation.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 5: Construction Drawings and Specifications): "A window schedule must include the unit size and location on elevations to identify each window’s dimensions and placement in the building design."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that a window schedule is a critical part of construction documents, providing essential information for window installation. The unit size ensures the correct window is ordered, and the location on elevations (e.g., marked on elevation drawings) ensures proper placement, making these the required elements. Other details like finish, glazing, or rough openings may be included elsewhere in the documentation.
Objectives:
Understand the purpose and content of a window schedule in construction documents.
Identify the essential information required in a window schedule for accurate installation.
A client is looking at toilet compartment options that provide ease of cleanability when it comes to mopping the floor. Which option would be the most suitable?
Options:
Ceiling-hung compartments
Floor-anchored compartments
Floor-and-ceiling compartments
Overhead-braced compartments
Answer:
AExplanation:
Toilet compartments (partitions) in public restrooms are available in various mounting styles, each with implications for maintenance, including ease of cleaning the floor. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and industry standards (e.g., from the American Society for Testing and Materials [ASTM] and restroom design guidelines) provide guidance on selecting partition types based on factors like cleanability, durability, and accessibility.
A. Ceiling-hung compartments: Ceiling-hung compartments are suspended from the ceiling, leaving the floor completely open underneath. This design allows for unobstructed access to the floor, making it the easiest option for mopping and cleaning, as there are no floor supports or braces to work around. It is a preferred choice in high-traffic restrooms where hygiene is a priority, such as in commercial or institutional settings.
B. Floor-anchored compartments: Floor-anchored compartments are mounted directly to the floor, typically with posts or panels that extend to the floor surface. This creates obstacles that make mopping more difficult, as cleaners must work around the supports, potentially leaving dirt in hard-to-reach areas.
C. Floor-and-ceiling compartments: These compartments are anchored to both the floor and the ceiling, providing maximum stability but creating the same cleaning challenges as floor-anchored compartments due to the floor supports.
D. Overhead-braced compartments: Overhead-braced compartments are floor-mounted with an additional brace at the top that connects to the wall or another partition for stability. Like floor-anchored compartments, they have supports that touch the floor, making mopping more difficult compared to a ceiling-hung design.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual highlights that ceiling-hung compartments are the best option for ease of cleanability, as they provide a clear floor surface for mopping, which is critical for maintaining hygiene in restrooms.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "Ceiling-hung toilet compartments are the most suitable for ease of cleanability, as they leave the floor unobstructed, allowing for efficient mopping and maintenance."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that ceiling-hung compartments facilitate cleaning by eliminating floor supports, providing a clear path for mopping and ensuring better hygiene in restrooms. This design is particularly advantageous in high-traffic areas where frequent cleaning is necessary.
Objectives:
Understand the impact of toilet compartment design on maintenance and cleanability.
Select appropriate partition types for restroom design based on functional requirements.
A designer is specifying an acoustical ceiling cloud centered over a conference room table. The ceiling cloud will be 12" [305 mm] lower than the rest of the ceiling. Where is the BEST location to note the height differences?
Options:
Finish plan
Architectural plan
Interior elevations
Reflected ceiling plan
Answer:
DExplanation:
An acoustical ceiling cloud is a suspended ceiling element designed to improve acoustics, and its height difference from the main ceiling (12" lower) is a critical detail for construction. The reflected ceiling plan (RCP) is the best location to note this height difference because it is a drawing specifically designed to show ceiling elements, such as lighting, HVAC, and ceiling clouds, from a top-down view as if reflected onto the floor plan. The RCP can include notes or symbols indicating the ceiling cloud’s location and its height relative to the main ceiling, ensuring clear communication to contractors. Option A (finish plan) shows material finishes, not height details. Option B (architectural plan) typically refers to floor plans, which don’t focus on ceiling details. Option C (interior elevations) can show the cloud’s height in a side view but is not the primary location for ceiling layout and height notations.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on construction documentation.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “Height differences for ceiling elements, such as acoustical clouds, should be noted on the reflected ceiling plan, which is the primary drawing for ceiling design and layout.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the use of reflected ceiling plans to document ceiling features, including height differences, to ensure accurate construction.
Objectives:
Develop reflected ceiling plans for ceiling design (IDFX Objective: Design Communication).
In the northern hemisphere, which window orientation would maximize passive solar energy without the use of fans, pumps, or complex controllers?
Options:
East
West
North
South
Answer:
DExplanation:
Passive solar energy relies on the design of a building to capture, store, and distribute solar heat without mechanical systems. In the northern hemisphere, the sun rises in the east, sets in the west, and is at its highest and most direct angle in the south during the day, especially in winter when heating is most needed. South-facing windows maximize passive solar energy because they receive the most direct sunlight throughout the day, allowing for optimal heat gain. East-facing windows (Option A) get morning sun but miss afternoon heat. West-facing windows (Option B) get afternoon sun but can overheat in summer. North-facing windows (Option C) receive the least direct sunlight and are not effective for passive solar gain.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on sustainable design and passive solar strategies.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “In the northern hemisphere, south-facing windows maximize passive solar energy by capturing the most direct sunlight for heating without mechanical systems.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum includes passive solar design as a sustainable strategy, highlighting south-facing orientations for optimal solar gain in the northern hemisphere.
Objectives:
Apply passive solar design principles (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
What is the minimum gypsum board finish level when applying a heavily textured wallcovering?
Options:
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
Answer:
BExplanation:
Gypsum board (drywall) finish levels are defined by the Gypsum Association (GA) in GA-214, "Recommended Levels of Finish for Gypsum Board," which is referenced in the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual. These levels range from 0 to 5, with each level specifying the degree of surface preparation required for different types of finishes, such as paint or wallcoverings. The question asks for the minimum finish level for a heavily textured wallcovering, which requires a smooth surface to ensure proper adhesion and appearance.
Level 0: No finishing; used for temporary construction. Not suitable for any wallcovering.
Level 1: Basic taping of joints and fastener heads; used in concealed areas (e.g., plenums). Not suitable for wallcoverings.
Level 2: Taping and one coat of joint compound over joints and fastener heads, with a skim coat over the surface. This level is typically used for water-resistant gypsum board in wet areas or as a substrate for tile. It is not smooth enough for wallcoverings, especially heavily textured ones, as the texture may not adhere properly.
Level 3: Taping, one coat of joint compound, and a second coat over joints and fastener heads, with a skim coat over the entire surface. This level provides a smoother surface than Level 2, making it suitable for heavily textured wallcoverings. The smoother surface ensures better adhesion and prevents the wallcovering from showing underlying imperfections,which is critical for textured finishes that may highlight surface irregularities.
Level 4: Taping, two coats of joint compound, and a skim coat over the entire surface, providing a very smooth finish. This level is typically used for flat or low-sheen paints or light wallcoverings. While it can be used for heavily textured wallcoverings, it exceeds the minimum requirement.
Level 5: The highest level, with taping, two coats of joint compound, and a full skim coat over the entire surface, plus additional smoothing. This level is used for high-gloss finishes or critical lighting conditions where imperfections must be eliminated. It is more than necessary for a heavily textured wallcovering.
For a heavily textured wallcovering, a Level 3 finish is the minimum required to ensure a smooth enough surface for proper adhesion and appearance, as the texture can mask minor imperfections. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual aligns with GA-214, recommending Level 3 for textured wallcoverings.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is B, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "A minimum Level 3 gypsum board finish is required for heavily textured wallcoverings to ensure a smooth surface for proper adhesion and appearance."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that a Level 3 finish provides a smooth surface with taping, two coats of joint compound, and a skim coat, which is sufficient for heavily textured wallcoverings. This level ensures the wallcovering adheres properly and does not show underlying imperfections, while higher levels (4 and 5) are unnecessary unless specified for other finishes like high-gloss paint.
Objectives:
Understand the gypsum board finish levels and their applications.
Select the appropriate finish level for textured wallcoverings.
A design firm submits a bid for a healthcare project noting that they specialize in healthcare design, when they have only completed education projects that contain one small nurse room per project. This is an example of violating the
Options:
Code of ethics
RFP guidelines
Permitting requirements
Health and safety guidelines
Answer:
AExplanation:
Ethical behavior in interior design is governed by professional codes of conduct, such as the NCIDQ Code of Ethics and codes from organizations like the American Society of Interior Designers (ASID) and the International Interior Design Association (IIDA). These codes emphasize honesty, integrity, and transparency in professional practice.
A. Code of ethics: The NCIDQ Code of Ethics requires designers to be truthful in their professional representations. Claiming to specialize in healthcare design when the firm hasonly completed education projects with minimal healthcare components (e.g., a small nurse room) is a misrepresentation of their expertise. This violates the code of ethics, specifically the principle of honesty, as it could mislead the client about the firm’s qualifications and experience, potentially compromising the project’s outcome.
B. RFP guidelines: A Request for Proposal (RFP) outlines the requirements for submitting a bid, such as project scope and submission format. While misrepresenting expertise might not align with the spirit of an RFP, it is not a direct violation of RFP guidelines unless the RFP explicitly requires proof of healthcare experience, which is not indicated in the question.
C. Permitting requirements: Permitting requirements involve complying with local building codes and regulations to obtain permits for construction. Misrepresenting expertise does not directly violate permitting requirements, as this issue pertains to professional conduct, not regulatory compliance.
D. Health and safety guidelines: Health and safety guidelines relate to designing spaces that protect occupants (e.g., following codes for egress, fire safety). While a lack of healthcare expertise could potentially impact health and safety in a project, the act of misrepresenting expertise is not a direct violation of these guidelines.
The NCIDQ Code of Ethics explicitly prohibits misrepresentation of qualifications, making this a clear violation of ethical standards.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is A, as verified by the NCIDQ Code of Ethics.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ Code of Ethics (Section 1: Responsibility to the Profession): "Interior designers shall not misrepresent their qualifications, experience, or expertise, ensuring honesty in all professional representations to clients and stakeholders."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ Code of Ethics states that designers must be truthful about their qualifications and experience. Claiming to specialize in healthcare design without substantial experience in that area is a misrepresentation, violating the ethical principle of honesty. This could mislead the client and affect the project’s success, making it a clear ethical violation.
Objectives:
Understand ethical standards in interior design practice.
Identify behaviors that violate the NCIDQ Code of Ethics.
A client requires design services for their new office, which will occupy an entire floor in an existing building. During the programming phase, what group of tasks would the designer perform?
Options:
Review lease agreement; select color schemes; review building codes and zoning.
Develop as-built drawings; review lease agreements; develop workstation standards.
Conduct user interviews; review building codes and zoning; analyze spatial requirements.
Review building codes and zoning; develop as-built drawings; develop preliminary cost estimates.
Answer:
CExplanation:
During the programming phase for a new office occupying an entire floor, the designer focuses on gathering and analyzing information to define the project’s requirements. The key tasks include conducting user interviews to understand the client’s needs (e.g., number of employees, workflow), reviewing building codes and zoning to ensure compliance (e.g., occupancy limits, egress requirements), and analyzing spatial requirements to determine the necessary square footage and adjacencies. Option A includes selecting color schemes, which occurs later in the design development phase. Option B includes developing as-built drawings and workstation standards, which are part of the schematic design phase. Option D includes developing preliminary cost estimates, which may occur but is not a primary programming task.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on the programming phase.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “During the programming phase, the designer should conduct user interviews, review building codes and zoning, and analyze spatial requirements to define the project’s needs.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum defines programming as the process of gathering data through user interviews, ensuring compliance with codes, and analyzing spatial needs to create a program document.
Objectives:
Conduct programming tasks to define project requirements (IDFX Objective: Programming and Site Analysis).
What millwork standard would provide the highest quality?
Options:
Modular casework in a C select grade
Finish carpentry in a Prime VG finish quality
Finish carpentry in Superior VG finish quality
Architectural woodwork in a B or better grade
Answer:
CExplanation:
Millwork standards define the quality of woodwork in interior design, including casework, finish carpentry, and architectural woodwork. The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual references standards from the Architectural Woodwork Institute (AWI) and the Woodwork Institute (WI), such as the Architectural Woodwork Standards (AWS), which categorize quality levels for different types of woodwork. The question asks for the highest quality standard among the options.
A. Modular casework in a C select grade: Modular casework refers to pre-manufactured cabinets or shelving. The "C select grade" indicates a lower quality level, typically allowing for more natural defects (e.g., knots, color variations) in the wood. In the AWS, Grade C is an economy grade, suitable for utilitarian applications but not high quality.
B. Finish carpentry in a Prime VG finish quality: Finish carpentry includes trim, moldings, and other visible woodwork installed on-site. "Prime VG" (Vertical Grain) indicates a high-quality finish with a uniform grain, often used for painted or stainedapplications. In the AWS, "Prime" is a mid-level quality grade, better than economy but not the highest, allowing for some minor defects.
C. Finish carpentry in Superior VG finish quality: "Superior VG" (Vertical Grain) indicates the highest quality level for finish carpentry. In the AWS, "Superior" grade requires the finest materials and craftsmanship, with minimal defects, tight grain, and a flawless finish. This is the highest quality standard for finish carpentry, often used in high-end applications where aesthetics are critical.
D. Architectural woodwork in a B or better grade: Architectural woodwork includes custom woodwork like paneling or cabinetry. "B or better grade" refers to a veneer or lumber grade (per the Hardwood Plywood and Veneer Association [HPVA] standards), where Grade B allows for some natural defects but is still high quality. However, this is a material grade, not a finished quality standard like "Superior," and architectural woodwork at this grade is not necessarily the highest quality compared to finish carpentry at a Superior level.
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual and AWS confirm that "Superior VG finish quality" for finish carpentry represents the highest quality standard, as it demands the best materials, craftsmanship, and finish, surpassing the other options.
Verified Answer from Official Source:The correct answer is C, as verified by the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual.
Exact Extract:
From the NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual (Chapter 7: Design Elements and Principles): "Finish carpentry in Superior VG finish quality provides the highest quality, requiring the finest materials and craftsmanship with minimal defects, ideal for high-end applications."
Explanation from Official Source:
The NCIDQ IDFX Reference Manual explains that Superior VG finish quality for finish carpentry is the highest standard, as defined by the AWS, requiring exceptional materials and craftsmanship. This surpasses modular casework at a C select grade, Prime VG finish carpentry, and architectural woodwork at a B or better grade, which are lower quality levels in their respective categories.
Objectives:
Understand millwork quality standards in interior design.
Identify the highest quality standard for finish carpentry.
If a client requires a full-scale representation of a proposed workstation, what would be requested?
Options:
Mock-up
Shop drawing
Finish sample
Specifications
Answer:
AExplanation:
A full-scale representation of a proposed workstation allows the client to experience the design in real life, including its size, functionality, and appearance. A mock-up is a full-scale, physical model of the workstation, often built to test the design before final production. This is the best option for a client to evaluate the workstation in a tangible way. Option B (shop drawing) is a detailed technical drawing for fabrication, not a physical model. Option C (finish sample) is a small material sample, not a full-scale representation. Option D (specifications) is a written document, not a physical model.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on design communication and prototyping.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “A mock-up is a full-scale physical model requested when a client needs to evaluate a proposed design, such as a workstation, in real space.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum highlights mock-ups as a tool for client review and design validation, especially for custom or complex elements like workstations.
Objectives:
Use mock-ups to communicate and validate design solutions (IDFX Objective: Design Communication).
The client has expressed a desire for a new space that supports a highly collaborative environment. Which aspect of the design is MOST important?
Options:
Ergonomic seating
Furniture placement
Integrated daylighting
Acoustical wall finishes
Answer:
BExplanation:
A highly collaborative environment requires a design that facilitates interaction, communication, and teamwork among occupants. Furniture placement is the most important aspect because it directly impacts how people interact—arranging furniture to create open, flexible spaces encourages collaboration by allowing for group discussions, easy movement, and shared work areas. For example, placing tables in a circular or U-shaped arrangement fosters face-to-face interaction. Option A (ergonomic seating) is important for comfort but does not directly address collaboration. Option C (integrated daylighting) enhances the overall environment but is secondary to spatial arrangement for collaboration. Option D (acoustical wall finishes) helps with sound control, which is important but not the primary factor for fostering collaboration.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on human behavior and space planning.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “In collaborative environments, furniture placement is the most critical design aspect to facilitate interaction and teamwork, such as arranging seating to encourage face-to-face communication.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the role of spatial arrangement in supporting specific user activities, with furniture placement being key to creating collaborative spaces.
Objectives:
Design spaces to support user activities and interactions (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
When finalizing carpet selections for an extended-care facility, what carpet pattern is MOST appropriately specified?
Options:
Patterned and sculpted carpet to allow objects to be identifiable
Carpet contrasting with the walls to highlight the edges of the room
High contrast, wide-striped pattern carpet that gives the room dimension
Carpet that does not contrast with the furniture in order to reduce distortion
Answer:
AExplanation:
In an extended-care facility, carpet selections must consider the needs of residents, many of whom may have visual impairments or mobility issues. A patterned and sculpted carpet allows objects (e.g., dropped items) to be identifiable because the texture and pattern create visual and tactile cues, aiding residents in navigation and safety. Option B (contrasting with walls) may help define room edges but does not address object identification. Option C (high contrast, wide-striped pattern) can create visual confusion or a tripping hazard for residents with impaired vision. Option D (no contrast with furniture) reduces visibility of furniture, increasing the risk of tripping or disorientation.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on designing for special populations.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “In extended-care facilities, patterned and sculpted carpets are most appropriate to allow objects to be identifiable, aiding residents with visual impairments.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes designing for aging populations, with patterned and sculpted carpets providing visual and tactile cues to enhance safety and navigation.
Objectives:
Design for special populations in healthcare settings (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
A designer is selecting furnishings for a weight loss clinic lobby. Which type of chair would the designer MOST likely include in their selections?
Options:
An exam chair
A reclining chair
A bariatric chair
An ergonomic chair
Answer:
CExplanation:
A weight loss clinic lobby serves clients who may have higher body weights, requiring furniture that can safely and comfortably accommodate them. A bariatric chair is specifically designed for individuals with higher weight capacities (typically 300–500 lbs or more) and wider seat dimensions, ensuring safety, comfort, and inclusivity. Option A (exam chair) is for medical examination rooms, not a lobby. Option B (reclining chair) may be comfortable but is not designedfor higher weight capacities. Option D (ergonomic chair) focuses on posture and comfort for office settings, not specifically for bariatric needs.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on furniture selection for specific user groups.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “In healthcare settings like a weight loss clinic, bariatric chairs should be included in lobby furnishings to accommodate clients with higher weight capacities safely and comfortably.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes designing for diverse user groups, with bariatric furniture being a key consideration in healthcare settings to ensure inclusivity and safety.
Objectives:
Select furniture for specific user needs (IDFX Objective: Human Behavior and the Designed Environment).
What factors determine the MAXIMUM allowable travel distance to an exit?
Options:
Corridor width and occupant load
Occupant load and construction type
Sprinkler protection and occupancy classification
Construction type and total square feet [square meters]
Answer:
CExplanation:
The maximum allowable travel distance to an exit is a life safety requirement defined by the International Building Code (IBC) to ensure occupants can evacuate safely during an emergency. This distance is determined by two primary factors: sprinkler protection (whether the building has a sprinkler system) and occupancy classification (e.g., assembly, business, residential). Sprinkler protection can increase the allowable travel distance because it enhances fire suppression, giving occupants more time to evacuate. Occupancy classification affects the distance based on the risk level and typical occupant behavior (e.g., assembly spaces have shorter distances due to higher occupant loads). Option A (corridor width and occupant load) affects egress width, not travel distance. Option B (occupant load and construction type) is partially correct, but construction type is secondary to sprinkler protection. Option D (construction type and total square feet) is unrelated to travel distance.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on life safety codes.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualreferences IBC standards, stating, “The maximum allowable travel distance to an exit is determined by sprinkler protection and occupancy classification, as these factors directly impact evacuation safety.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum requires knowledge of IBC life safety requirements, with sprinkler protection and occupancy classification being the key determinants of travel distance to exits.
Objectives:
Understand life safety requirements for egress (IDFX Objective: Codes and Standards).
A client has approved concept sketches for a three-dimensional wall treatment. The treatment will be constructed using multiple finishes in an intricate design. Which document or drawing is MOST important to include in the construction documents and drawings to explain how interlocking finishes should be constructed?
Options:
Details in section
Finish specifications
Construction elevations
As-built (record) drawings
Answer:
AExplanation:
A three-dimensional wall treatment with interlocking finishes requires precise instructions for construction, especially to show how the finishes are layered, joined, or integrated in a complex design. Details in section (a cross-sectional drawing) are the most important because they provide a detailed view of the wall’s construction, showing the relationship between different finishes, their thicknesses, and how they interlock in three dimensions. This level of detail is critical forcontractors to execute the design accurately. Option B (finish specifications) provides material information but lacks the spatial detail needed for construction. Option C (construction elevations) shows the wall’s appearance but not the internal construction details. Option D (as-built drawings) is created after construction, not during the design phase.
Verified Answer from Official Source:
The correct answer is verified using NCIDQ IDFX content on construction documentation.
Exact Extract:TheNCIDQ IDFX Reference Manualstates, “For complex wall treatments with multiple finishes, details in section are essential to show the construction and integration of materials in the construction documents.”
The NCIDQ IDFX curriculum emphasizes the importance of detailed drawings, such as sections, to communicate intricate construction requirements to contractors.
Objectives:
Develop detailed construction drawings for complex designs (IDFX Objective: Design Communication).

