Welding Inspection and Metallurgy Exam Questions and Answers
At any time during the welding inspection, if defects are identified:
Stud arc welding is a specialized process predominantly limited to welding:
When welding using the shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process, which of the following best describes the appearance of excessive penetration on a radiograph?
Which of the following is a hazard associated with in-service welding on a carbon steel pipe containing chlorine?
To avoid burn through during in-service welding on thinner wall equipment, it is generally recommended to:
The WPS gives the welder specific guidelines to:
Refer to the following diagram:
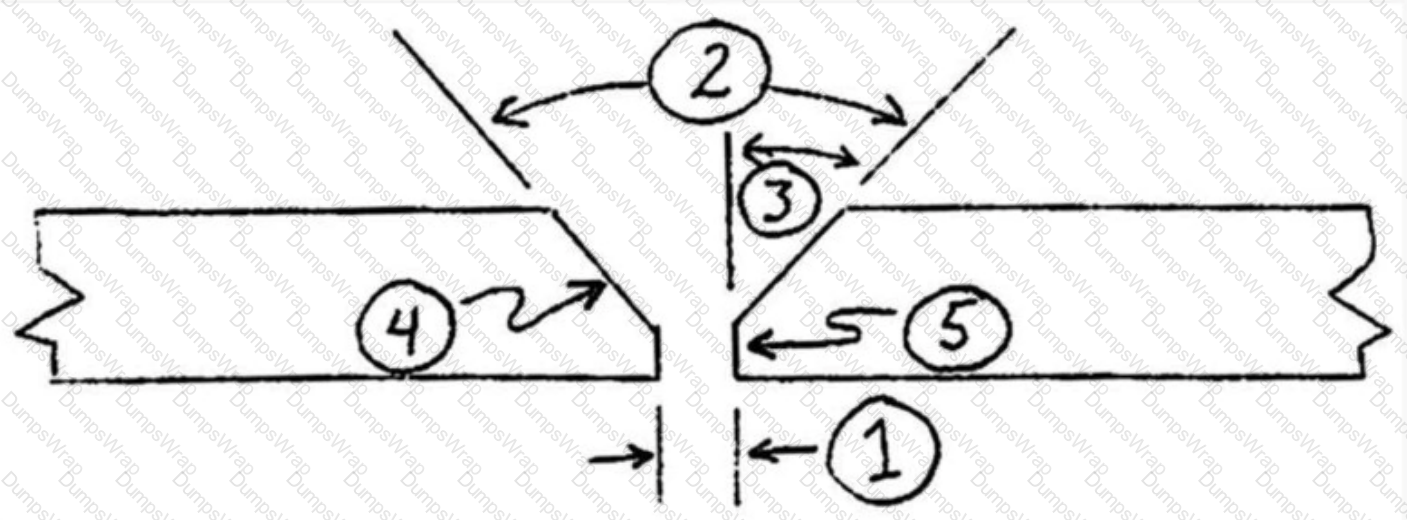
Item#1 represents:
Refer to the following diagram:
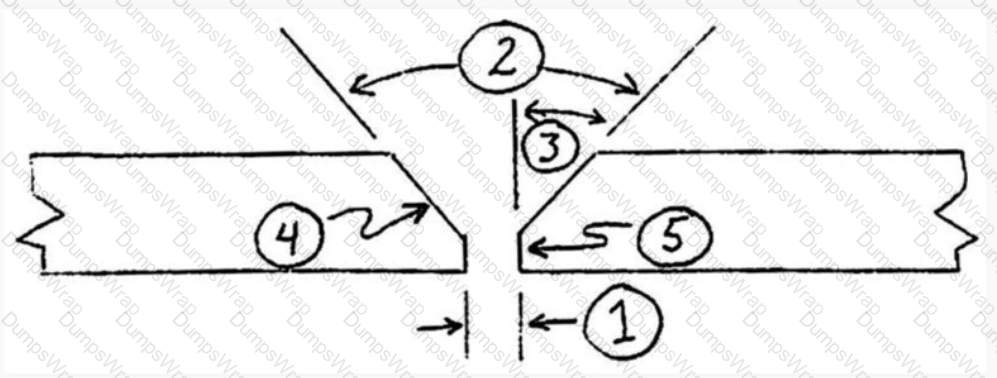
Item#4 represents:
What GMAW welding process uses carbon dioxide as the shielding gas, and is limited to the flat and horizontal position?
What is the major cause of lack of fusion in all welding processes involving carbon steel?
What is(are) the most appropriate action(s) to prepare an in-service carbon steel piping system that has been in caustic service for welding?
In alloy steel, a high hardness measurement could indicate:
Hardness testing of production welds and the HAZ requires test areas to be:
Rules for qualifying welding operators using radiography on a production weld require what minimum weld length to be examined?
The carbon equivalent formula indicates:
What is the minimum liquid level that should be maintained above the area that is to be hot tapped on a storage tank or vessel?
If a test specimen from a welded coupon should fail during PQR mechanical tests:
For SMAW welding, the last number of the electrode identification identifies:
Codes/standards sometimes specify impact testing of weldments at minimum design metal temperatures to:
As a result of welding, metals with a high coefficient of thermal expansion are:
Which of the following can result from residual magnetism left in a partially completed weld?
Remote examination of welds may use aids such as telescopes, borescopes, fiberscopes, cameras, or other suitable instruments provided they have:
API Recommended Practice 2201 primarily covers the:
Which of the following has the lowest range of welding currents and electrode diameters associated with the GMAW process?
A root opening of a groove weld is:
To reduce exposure to moisture of low-hydrogen electrodes after they have been removed from the manufacturer’s packaging, they should be stored:
Base metals are assigned P-numbers by the ASME Code, Section IX to reduce the number of:
API Recommended Practice 577 provides:
Which of the following is a practical solution that could prevent or reduce lack of fusion in carbon steel during the weld process?
In hardness testing of carbon steel weldment specimens, there is an approximate relationship between hardness and:
A-number groupings are based upon the:
For hot tap and in-service welding, above what carbon equivalent limit is it recommended to use extra low hydrogen electrodes to weld carbon steels?
Heating a round bar to an elevated temperature and then quenching one end is a test method to determine:

