Financial Strategy Questions and Answers
JAG and ZEB are two listed companies. JAG is approximately 20 times the size of ZEB.
10 days ago JAG made a hostile bid for ZEB. offering a share exchange.
The bid price represents a 10% profit to the shareholders of ZEB at today's market prices to reflect the high levels of synergistic benefits that JAG expects to realise from the transaction.
Which of the following is the greatest future threat to the post-transaction value for JAG?
WX, an advertising agency, has just completed the all-cash acquisition of a competitor, YZ. This was seen by the market as a positive strategic move byWX.
Which THREE of the following will WX's shareholders expect the company's directors to prioritise following the acquisition?
At the last financial year end, 31 December 20X1, a company reported:

The corporate income tax rate is 30% and the bank borrowings are subject to an interest cover covenant of 4 times.
The results are presently comfortably within the interest cover covenant as they show interest cover of 8.3 times. The company plans to invest in a new product line which is not expected to affect profit in the first year but will require additional borrowings of $20 million at an annual interest rate of 10%.
What is the likely impact on the existing interest cover covenant?
An entity prepares financial statements to 30 June.
During the year ended 30 June 20X2 the following events occurred:
1 July 20X1
• The entitiy borrowed $100 million at a variable rate of interest.
• In order to protect itself against the variability of its interest cashflows, the entity entered into a pay-fixed-receive-variable interest swap with annual settlements. The fair value of the swap on this date was zero.
30 June 20X2
• The entity received a net settlement of $2 million under the swap. After this net settlement, the fair value of the swap was $5 million - a financial asset.
The entity decides to use hedge accounting for this arrangement and has designated it as a cash flow hedge. The swap is a perfect hedge of the variability of the cash interest payments.
Which of the following describes the treatment of the settlement and the change in the fair value of the swap in the statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the year ended 30 June 20X2?
The Senior Management Team of ABC, an owner-managed, capital intensive start-up engineering business, is considering the options for its dividend policy. It has so far been a successful business and is expanding quickly Once in place, the Senior Management Team anticipates that its current investment plans will yield returns for many years to come The first agenda item at every meeting currently concerns arranging and funding new equipment and premises.
Which of the following dividend policies is likely to be the most suitable?
The Treasurer of Z intends to use interest rate options to set an interest rate cap on Z’s borrowings.
Which of the following statement is correct?
Company C has received an unwelcome takeover bid from Company P.
Company P is approximately twice the size of Company C based on market capitalisation.
Although the two companies have some common business interests, the main aim of the bid is diversification for Company P.
The offer from Company P is a share exchange of 2 shares in Company P for 3 shares in Company C.
There is a cash alternative of $5.50 for each Company C share.
Company C has substantial cash balances which the directors were planning to use to fund an acquisition.
These plans have not been announced to the market.
The following share price information is relevant. All prices are in $.

Which of the following would be the most appropriate action by Company C's directors following receipt of this hostile bid?
An unlisted software development company has recently reported disappointing results. This was partly due to weak economic conditions but also because of its poor competitive position. The company has a number of exciting development opportunities which would enable it to achieve significant future growth. The company's growth potential has been hindered by its inability to secure sufficient new finance.
To enable the company raise new finance the Directors are considering working forwards an IPO in 10 years and accepting finance from a venture capitalist in order support in the intervening period.
The directors are keen to retain a controlling stake in the company and full representation on the board. They therefore require venture capitalists to provide funds as a mix of debt and equity and not soley equity finance.
Which THREE of the following are most likely to disrupt the directors' plans to use venture capital finance?
A company enters into a floating rate borrowing with interest due every 12 months over the five year life of the borrowing.
At the same time, the company arranges an interest rate swap to swap the interest profile on the borrowing from floating to fixed rate.
These transactions are designated as a hedge for hedge accounting purposes under IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement.
Assuming the hedge is considered to be effective, how would the swap be accounted for 12 months later?
A company is financed as follows:
• 400 million $1 shares quoted at $3.00 each.
• $800 million 5% bonds quoted at par.
The company plans to raise $200 million long term debt to finance a project with a net present value of $100 million.
The bank that is providing the debt is insisting on a maximum gearing level covenant.
Gearing will be based on market values and calculated as debt/(debt + equity).
What is the lowest figure for the gearing covenant that the bank could impose without the company breaching the agreement?
Which TWO of the following statements about debt instruments are correct?
A company is financed as follows:
• 400 million $1 shares quoted at $3.00 each.
• $800 million 5% bonds quoted at par.
The company plans to raise $200 million long term debt to finance a project with a net present value of $100 million.
The bank that is providing the debt is insisting on a maximum gearing level covenant.
Gearing will be based on market values and calculated as debt/(debt + equity).
What is the lowest figure for the gearing covenant that the bank could impose without the company breaching the agreement?
A company has just received a hostile bid. Which of the following response strategies could be considered?
Company BBB has prepared a valuation of a competitor company, Company BBD. Company BBB is intending to acquire a controlling interest in the equity of Company BBD and therefore wants to value only the equity of Company BBD.

The directors of Company BBB have prepared the following valuation of Company BBD:
Value of Equity = 4.63 + 5.14 + 5.56 = S15.33 million
Additional information on Company BBD:

Which THREE of the following are weaknesses of the above valuation?
Company A is subject to a takeover bid from Company B, both companies operate in the same industry and each of them demand a significant market share Company B h3S made an of an of $5 per share to the shareholders of Company A.
The directors of Company A do not believe the takeover would be in the best interests of the stakeholders and other stakeholders of Company A due to the following reruns
1. Company B has recently taken ever several ether companies resulting in them breaking up the company and se ling on the assets.
2 The directors of Company A believe the offer of $5 per snare undervalues tie company
The directors of Company A are therefore keen to prevent the bid from going ahead
Which THREE of the following defence strategies could be used by the directors of Company Air this situation?
An all equity financed company plans an issue of new ordinary shares to the general public to raise finance for a new project
The following data applies:
• 10 million ordinary shares are currently in issue with a market value of S3 each share
• The new project will cost S2.88 million and is expected to give a positive NPV of S1 million
• The issue will be priced at a AaA discount to the current share price.
What gam or loss per share will accrue to the existing shareholders?
A manufacturing company is based in Country L whose currency is the L$.
One of the company's products is exported to Country M, a rapidly growing economy, whose currency is the M$.
In the most recent financial year:
• 100,000 units of the product were sold to customers in country M
• The unit selling price was M$12
The spot rate today is L$1 = M$5
The company has an objective of growth in total sales value in L$ of 10% a year.
If the L$ strengthens by 5% next year against the M$, what volume of sales of this product is needed next year to achieve the objective?
A company is currently all-equity financed.
The directors are planning to raise long term debt to finance a new project.
The debt:equity ratio after the bond issue would be 40:60 based on estimated market values.
According to Modigliani and Miller's Theory of Capital Structure without tax, the company's cost of equity would:
AA is considering changing its capital structure. The following information is currently relevant to AA:
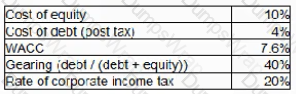
The gearing rating raising the new debt finance will be 50%.
Which THREE of the following statement about the impact of AA’s change in capital structure are true under Modigliani and Miler’s capital structure theory with tax.
A company's Board of Directors wishes to determine a range of values for its equity.
The following information is available:
Estimated net asset values (total asset less total liabilities including borrowings):
• Net book value = $20 million
• Net realisable value = $25 million
• Free cash flows to equity = $3.5 million each year indefinitely, post-tax.
• Cost of equity = 10%
• Weighted Average Cost of Capital = 7%
Advise the Board on reasonable minimum and maximum values for the equity.
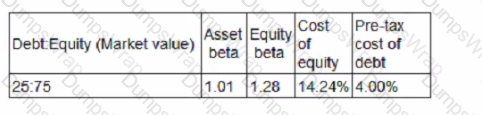
The following information relates to Company A's current capital structure:

Company A is considering a change in the capital structure that will increase gearing to 30:70 (Debt:Equity).
The risk -free rate is 3% and the return on the market portfolio is expected to be 10%.
The rate of corporate tax is 25%
Using the Capital Asset Pricing Model, calculate the cost of equity resulting from the proposed change to the capital structure.
Company X is an established, unquoted company which provides IT advisory services.
The company's results and cashflows are growing steadily and it has few direct competitors due to the very specialised nature of it's business. Dividends are predictable and paid annually.
Company P is looking to buy 30% of company X's equity shares.
Which TWO of the following methods are likely to be considered most suitable valuation methods for valuing company P's investment in Company X?
A company's directors plan to increase gearing to come in line with the industry average of 40%. They need to know what the effect will be on the company's WACC.
According to traditional theory of gearing the WACC is most likely to:
On 1 January:
• Company ABB has a value of $55 million
• Company BBA has a value of $25 million
• Both companies are wholly equity financed
Company ABB plans to take over Company BBA by means of a share exchange Following the acquisition the post-tax cashflow of Company ABB for the foreseeable future is estimated to be $10 million each year The post-acquisition cost of equity is expected to be 10%
What is the best estimate of the value of the synergy that would arise from the acquisition?
A consultancy company is dependent for profits and growth on the high value individuals it employs.
The company has relatively few tangible assets.
Select the most appropriate reason for the net asset valuation method being considered unsuitable for such a company.
The directors of a multinational group have decided to sell off a loss-making subsidiary and are considering the following methods of divestment:
1. Trade sale to an external buyer
2. A management buyout (MBO)
The MBO team and the external buyer have both offered the same price to the parent company for the subsidiary.
Which of the following is an advantage to the parent company of opting for a MBO compared to a trade sale as the preferred method of divestment?
A company is valuing its equity prior to an initial public offering (IPO).
Relevant data:
• Earnings per share $1.00
• WACC is 8% and the cost of equity is 12%
• Dividend payout ratio 40%
• Dividend growth rate 2% in perpetuity
The current share price using the Dividend Valuation Model is closest to:
Listed company R is in the process of making a cash offer for the equity of unlisted company S.
Company R has a market capitalisation of $200 million and a price/earnings ratio of 10.
Company S has a market capitalisation of $50 million and earnings of $7 million.
Company R intends to offer $60 million and expects to be able to realise synergistic benefits of $20 million by combining the two businesses. This estimate excludes the estimated $8 million cost of integrating the two businesses.
Which of the following figures need to be used when calculating the value of the combined entity in $ millions?
The following information relates to Company ZZA's current capital structure:
Company ZZA is considering a change in the capital structure that will increase gearing to 35:65 (Debt Equity).
The risk-free rate is 4% and the return on the market portfolio is expected to be 12%.
The rate of corporate tax is 25%
Using the Capital Asset Pricing Model, calculate the cost of equity resulting from the proposed change to the capital structure.
Company AB was established 6 years ago by two individuals who each own 50% of the shares.
Each individual heads a separate division within the company, which now has annual turnover of GBP10 million and employs 40 people.
Some of the employees are very highly paid as they are important contributors to the company's profitability.
The owners of the company wish to realise the full value of their investment within the next 12 months.
Which TWO of the following options are most likely to be acceptable exit strategies to the two owners of the company?
The long-term prospects for inflation in the UK and the USA are 1% and 4% per annum respectively.
The GBP/USD spot rate is currently GBP/USD1.40
Using purchasing power parity theory, what GBP/USD spot rate would you expect to see in six months’ time?
Company MB is in negotiations to acquire the entire share capital of Company BBA. Information about each company is as follows:
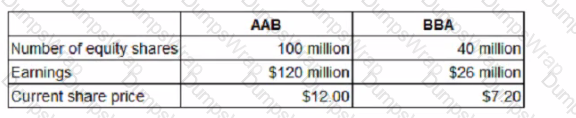
It is expected that Company BBA's profit before interest and tax will be $30 million in each of the two years after acquisition. Company AAB is considering how best to structure the offer Company AAB's discount factor and appropriate cost of equity for use in valuing Company BBA is 10%
Shareholders taxation implications should be ignored
Which of the following provides the shareholders of Company BBA with the highest offer price?
Company A needs to raise AS500 mi lion to invest in a new project and is considering using a pub ic issue of bonds to finance the investment.
Which THREE of the following statements-relating to this bond issue are true?
DFG is a successful company and its shares are listed on a recognised stock exchange. The company's gearing ratio is currently in line with the industry average and the directors of DFG do not want to increase the company's financial risk. The company does not carry a large cash balance and its shareholders are not expected to be willing to support a rights issue at this time
LMB is a small services company owned and managed by a small board of directors who are going to retire within the next year
DFG wishes to purchase LMB and has approached LMB's owners, who are broadly open to the proposal, to discuss the bid and the consideration to be offered by DFG. LMB's owners explain to DFG that they are also keen to defer any tax liabilities they would be subject to on receipt of the consideration.
Based on the information provided, which of the following types of consideration would be most suitable to finance the acquisition?
The financial assistant of a geared company has prepared the following calculation of the company's equity value:


Useful information;
• Tax rate - 20%
• Cost of equity = 12%
• Weighted average cost of capital (WACC)« 10%
" Debt finance of the company comprises a $6 million 7% undated bond trading at par Valuation workings.
Which of the following errors has been made by the financial assistant?
Which of the following statements is true of a spin-off (or demerger)?
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of a share repurchase?
ART manufactures traditional scooters. It has an equity beta of 1.4 and is financed entirely by equity. It plans to continue to be all-equity financed in future.
It is considering producing a range of electric scooters
GGG is a comparable quoted electric scooter manufacturer GGG has an equity beta of 2 4 reflecting its high level of gearing (the ratio of debt to equity is VI using market values).
The risk-free rate is 5%, and the market premium is 6%. The rate of corporation tax is 20%
What is the recommended discount rate that ART should use to assess the project to manufacture electric scooters?

A company is in the process of issuing a 10 year $100 million bond and is considering using an interest rate swap to change the interest profile on some or all of the $100 million new finance.
The company has a target fixed versus floating rate debt profile of 1:1. Before issuing the bond its debt profile was as follows:
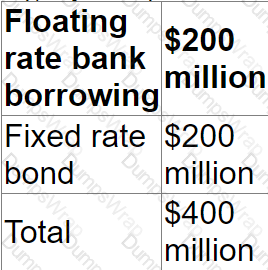
Which of the following is the most appropriate interest rate swap structure for the company?
A listed company has recently announced a profit warning.
The company's share price fell 20% on the day of the announcement but had been fairly static in the weeks leading up to the announcement.
Which form of efficient market is most likely to be indicated by this share price movement?
Listed company R is in the process of making a cash offer for the equity of unlisted company S.
Company R has a market capitalisation of $200 million and a price/earnings ratio of 10.
Company S has a market capitalisation of $50 million and earnings of $7 million.
Company R intends to offer $60 million and expects to be able to realise synergistic benefits of $20 million by combining the two businesses. This estimate excludes the estimated $8 million cost of integrating the two businesses.
Which of the following figures need to be used when calculating the value of the combined entity in $ millions?
A listed company has recently announced a profit warning.
The company's share price fell 20% on the day of the announcement but had been fairly static in the weeks leading up to the announcement.
Which form of efficient market is most likely to be indicated by this share price movement?
Company Z has identified four potential acquisition targets: companies A, B, C and D.
Company Z has a current equity market value of $580 million.
The price it would have to pay for the equity of each company is as follows:

Only one of the target companies can be acquired and the consideration will be paid in cash.
The following estimations of the new combined value of Company Z have been prepared for each acquisition before deduction of the cash consideration:
Ignoring any premium paid on acquisition, which acquisition should the directors pursue?
Company HJK is planning to bid for listed company BNM
Financial data for BNM for the financial year ended 31 December 20X1:

HJK is not forecasting any growth in these figures for the foreseeable future
Profit and cost data above should be assumed to be equivalent to cash flow data when answenng this question
Which THREE of the following approaches would be most appropriate for HJK to use to value the equity of BNM?
Company X plans to acquire Company Y.
Pre-acquisition information:
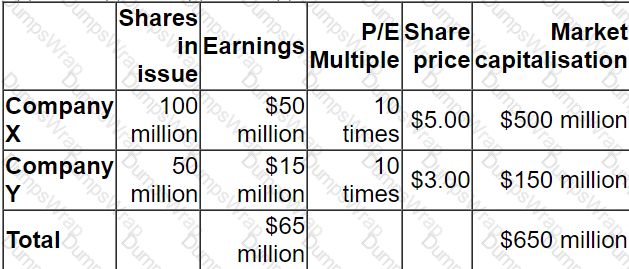
Post-acquisition information:
Total combined earnings are expected to increase by 10%
Total combined P/E multiple will remain at 10 times
Which of the following share-for-share exchanges will result in an increase of 10% in Company X's share price post-acquisition?
Which of the following statements are true with regard to interest rate swaps?
Select ALL that apply.
A listed company in a high technology industry has decided to value its intellectual capital using the Calculated Intangible Value method (CIV).
Relevant data for the company:
• Pays corporate income tax at 30%
• Cost of equity is 9%, pre-tax cost of debt is 7% and the WACC is 8%
• The value spread has been calculated as $26 million
Calculate the CIV for the company.
A company is planning a share repurchase programme with the following details:
• Repurchased shares will be immediately cancelled.
• The shares will be purchased at a premium to the market share price.
The current market share price is greater than the nominal value of the shares.
Which of the following statements about the impact of the share repurchase programme on the company's financial statements is correct?
A new company was set up two years ago using the personal financial resources of the founders.
These funds were used to acquire suitable premises.
The company has entered into a long-term lease on the premises which are not yet fully fitted out.
The founders are considering requesting loan finance from the company's bank to fund the purchase of custom-made advanced technology equipment.
No other companies are using this type of equipment.
The company expects to continue to be profitable for the forseeable future.
It re-invests some of its surplus cash in on-going essential research and development.
Which THREE of the following features are likely to be considered negatives by the bank when assessing the company's credit-worthiness?
A UK based company is considering investing GBP1 ,000,000 in a project it the USA. It is anticipated that the project will yield net cash inflows of USD580.000 each year for the next three years. These surplus cash flows will be remitted to the UK at the end of each year.
Currently GBP1.00 is worth USD1.30.
The expected inflation rates in the two countries over the next four years are 2% in the UK and 4% in the USA.
Applying the purchasing power parity theory, which of the following represents the expected remittance at the end of year three, in GBP whole the nearest whole GBP)?
Company A is a listed company that produces pottery goods which it sells throughout Europe. The pottery is then delivered to a network of self employed artists who are contracted to paint the pottery in their own homes. Finished goods are distributed by network of sales agents.The directors of Company A are now considering acquiring one or more smaller companies by means of vertical integration to improve profit margins.
Advise the Board of Company A which of the following acquisitions is most likely to achieve the stated aim of vertical integration?
Companies A, B, C and D:
• are based in a country that uses the K$ as its currency.
• have an objective to grow operating profit year on year.
• have the same total levels of revenue and cost.
• trade with companies or individuals in the eurozone. All import and export trade with companies or individuals in the eurozone is priced in EUR.
Typical import/export trade for each company in a year are as follows:

Which company's growth objective is most sensitive to a movement in the EUR/K$ exchange rate?
Company A has a cash surplus.
The discount rate used for a typical project is the company's weighted average cost of capital of 10%.
No investment projects will be available for at least 2 years.
Which of the following is currently most likely to increase shareholder wealth in respect of the surplus cash?
Which THREE of the following statements are disadvantages of the net asset basis of valuation?
Company A is a large listed company, with a wide range of both institutional and private shareholders.
It is planning a takeover offer for Company B.
Company A has relatively low cash reserves and its gearing ratio of 40% is higher than most similar companies in its industry.
Which TWO of the following would be the most feasible ways of Company A structuring an offer for Company B?
A company is planning to repurchase some of its shares. Relevant details are as follows:
• 100 million shares in issue
• Current share price $5
• 5 million shares to be repurchased
• 10% repurchase premium
• Repurchased shares to be cancelled
What would you expect the share price after the repurchase to be?
Give your answer to two decimal places.
$ ?
A listed company plans to raise $350 million to finance a major expansion programme.
The cash flow projections for the programme are subject to considerable variability.
Brief details of the programme have been public knowledge for a few weeks.
The directors are considering two financing options, either a rights issue at a 20% discount to current share price or a long term bond.
The following data is relevant:

The company's share price has fallen by 5% over the past 3 months compared with a fall in the market of 3% over the same period.
The directors favour the bond option.
However, the Chief Accountant has provided arguments for a rights issue.
Which TWO of the following arguments in favour of a right issue are correct?
The table below shows the forecast for a company's next financial year:
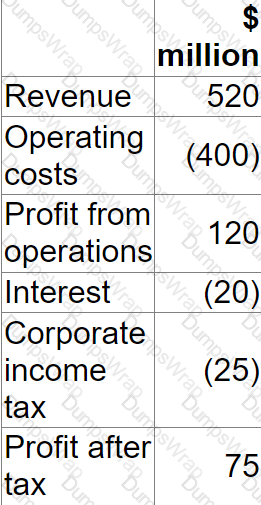
The forecast incorporates the following assumptions:
• 25% of operating costs are variable
• Debt finance comprises a $400 million fixed rate loan at 5%
• Corporate income tax is paid at 25%
The company plans to do the following next year from the forecast earnings on the assumption that earnings will be equivalent to free cash flow:
• Pay a total dividend of $20 million
• Invest $40 million in new projects
What is the maximum % reduction in operating activity that could occur next year before the company's dividend and investment plans are affected?
Give your answer to the nearest 0.1%.
Company A has made an offer to take over all the shares in Company B on the following terms:
• For every 20 shares currently held, Company B's shareholders will receive $100 bond with a coupon rate of 3%
• The bond will be repaid in 10 years' time at its par value of $100.
• The current yield on 10 year bonds of similar risk is 6%.
What is the effective offer price per share being made to Company B's shareholders?
A company is planning to issue a 5 year $100 million bond at a fixed rate of 6%.
It is also considering whether or not to enter into a 10 year $100 million swap to receive 5% fixed and pay Libor + 1% once a year.
The company predicts that Libor will be 4% over the life of the 5 years.
What is the impact of the swap on the company's annual interest cost assuming that the Libor prediction is correct?
A company is undertaking a lease-or-buy evaluation, using the post-tax cost of bank borrowing as the discount rate.
Details of the two alternatives are as follows:
Buy option:
• To be financed by a bank loan
• Tax depreciation allowances are available on a reducing-balance basis
• Assets depreciated on a straight-line basis
Lease option:
• Finance lease
• Maintenance to be paid by the lessee
• Tax relief available on interest payments and book depreciation
Which THREE of the following are relevant cashflows in the lease-or-buy appraisal?
A listed entertainment and media company produces and distributes films globally. The company invests heavily in intellectual property in order to create the scope for future film projects. The company has five separate distribution companies, each managed as a separate business unit The company is seeking to sell one of its business units in a management buy-out (MBO) to enable it to raise finance for proposed new investments
The business unit managers have been in discussions with a bank and venture capitalists regarding the financing for the MBO The venture capitalists are only prepared to invest a mixture of debt and equity and have suggested the following:
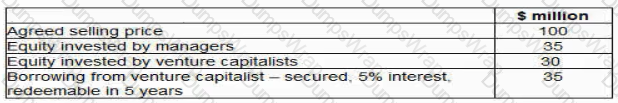
The venture capitalists have stated that they expect a minimum return on their equity investment of 3Q°/o a year on a compound basis over the first 5 years of the MBO No dividends will be paid during this period.
Advise the MBO team of the total amount due to the venture capitalist over the 5-year period to satisfy their total minimum return?
Company WWW is considering making a takeover bid for Company KKA Company KKA's current share price is $5.00
Company WWW is considering either
" A cash payment of $5.75 for each share in Company KKA
" A 5 year corporate bond with a market value of $90 in exchange for 15 shares in Company KKA
Calculate the highest percentage premium which Company KKA shareholders will receive.
A company needs to raise $20 million to finance a project.
It has decided on a rights issue at a discount of 20% to its current market share price.
There are currently 20 million shares in issue with a nominal value of $1 and a market price of $5 per share.
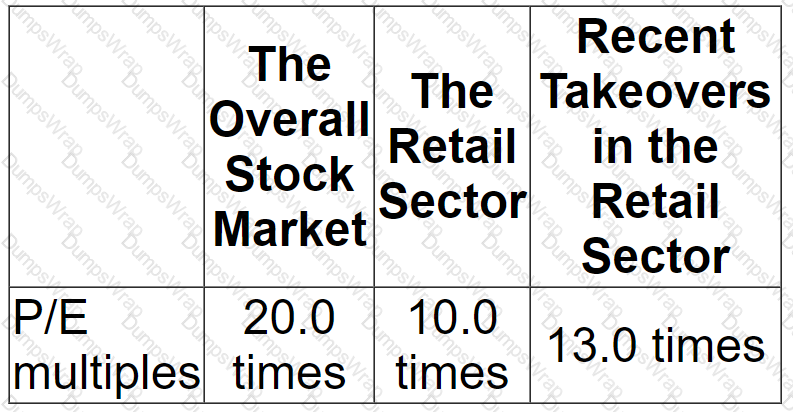
Calculate the terms of the rights issue.
A company is considering hedging the interest rate risk on a 3-year floating rate borrowing linked to the 12-month risk-free rate.
If the 12-month risk-free rate for the next three years is 2%, 3% and 4%, which of the following alternatives would result in the lowest average finance cost for the company over the three years?
A listed company is planning a share repurchase.
The following data applies:
• There are 10 million shares in issue
• The share repurchase will involve buying back 20% of the shares at a price of $0.75
• The company is holding $2 million cash
• Earnings for the current year ended are $2 million
The Directors are concerned about the impact that this repurchase programme will have on the company's cash balance and current year earnings per share (EPS) ratio.
Advise the directors which of the following statements is correct?
A company is considering the issue of a convertible bond compared to a straight bond issue (non-convertible bond).
Director A is concerned that issuing a convertible bond will upset the shareholders for the following reasons:
• it will dilute their control
• the interest payments will be higher therefore reducing liquidity
• it will increase the gearing ratio therefore increasing financial risk
Director B disagrees, and is preparing a board paper to promote the issue of the convertible bond rather than a non-convertible.
Advise the Director B which THREE of the following statements should be included in his board paper to promote the issue of the convertible bond?
The Board of Directors of a listed company have decided that it needs to increase its equity capital to ensure it is in a more stable financial position.
The shareholder profile is a mix of institutional and individual small shareholders.
The board is considering either:
• A scrip dividend
• A zero dividend
Which THREE of the following would be considered disadvantages of a scrip dividend compared to a zero dividend?
A company plans to acquire new machinery.
It has two financing options; buy outright using a bank loan, or a finance lease.
Which of the following is an advantage of a finance lease compared with a bank loan?
Company W is a manufacturing company with three divisions, all of which are making profits:
• Division A which manufactures cars
• Division B which manufactures trucks
• Division C which manufactures agricultural machinery
Company W is facing severe competitive pressure in all of its markets, and is currently operating with a high level of gearing Company W's latest forecasts suggest that it needs to raise cash to avoid breaching loan covenants on its existing debt finance in 6 months' time
In a recent strategy review. Divisions A and B were identified as being the core divisions of Company W
The management of Division C is known to be interested in the possibility of a management buy-out. Company Z is known to be interested in making a takeover bid for Company W's truck manufacturing division
A rival to Company W has recently successfully demerged its business, this was well received by the Financial markets
Which of the following exit strategies will be most suitable for company W?
A listed company follows a policy of paying a constant dividend. The following information is available:
• Issued share capital (nominal value $0.50) $60 million
• Current market capitalisation $480 million
The shareholders are requesting an increased dividend this year as earnings have been growing. However, the directors wish to retain as much cash as possible to fund new investments. They therefore plan to announce a 1-for-10 scrip dividend to replace the usual cash dividend.
Assuming no other influence on share price, what is the expected share price following the scrip dividend?
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
$ ?
ZZZ is a listed company based in Brinland. a European country. It is the largest owner and operator of residential care homes for elderly people in Brinland
Most of the residential care homes in Brinland are run by small private operators, and the standards of cafe are extremely variable However. 22Z has developed a good reputation because its client service is considered to be extremely good even though its prices are higher than those of most of its competitors.
ZZZ has expanded rapidly in the last few years, partly by acquisition and partly by organic growth consequently, the company's share price now stands at a record high, and the dividend declared at the end of the most recent accounting period was 10% higher than the previous year's dividend.
The Brinland government has recently set up a regulatory body to monitor the residential care homes industry. The regulatory body is considering introducing a variety of regulations to improve the customer experience in the industry. Following a period of consultation and investigation, the regulatory body is expected to announce a range of new regulations in the near future.
The directors of ZZZ are concerned that the new regulations may adversely affect their company
Which THREE of the following new regulations are likely to have the greatest negative impact on ZZTs performance?
Company H is considering the valuation of an unlisted company which it hopes to acquire.
It has obtained the target company's financial statements.
Company H has been advised that the book value of net assets as shown in the financial statements of the target company does not provide a reliable indicator of their true value.
Advise the Board of Directors which of the following THREE statements are disadvantages of the net asset basis of valuation?
B, a European based modern art dealer, frequently imports and sells single high value items created in the United States. The price is fixed at the date of sale but the items are commissioned and made to order with a lead time of three to nine months depending on the individual specification
B holds payment for his customers from the point of purchase and passes funds when the items are shipped However, despite putting the money on short term deposit, there have been times when B's profits have been almost entirely eroded by adverse movements m interest rates Advise B by matching the appropriate instrument to B's requirements.

Using the CAPM, the expected return for a company is 11%. The market return is 8% and the risk free rate is 2%.
What does the beta factor used in this calculation indicate about the risk of the company?
PPP's home currency is the PS. An overseas customer is due to make a payment of A$5,000,000 to PPP in 3 months. The present spot rate is 1PS = 5A$. P can obtain an interest rate of 4% per year on P$ deposits and 6% per year on AS deposits.
Forecast the value of the customer's payment to PPP, in PS, when the payment is made in 3 months' time.
Give your answer to the nearest thousand PS.

An unlisted company:
- Is owned by the original founder and member of their families.
- Is growing more rapidly than other companies in the same industry.
- Pays a fixed annual divided
Which of the following methods would be the most appropriate to value this company’s equity?
A company has in a 5% corporate bond in issue on which there are two loan covenants.
• Interest cover must not fall below 3 times
• Retained earnings for the year must not fall below $3.5 million
The Company has 200 million shares in issue.
The most recent dividend per share was $0.04.
The Company intends increasing dividends by 10% next year.
Financial projections for next year are as follows:
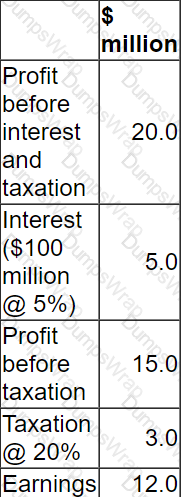
Advise the Board of Directors which of the following will be the status of compliance with the loan covenants next year?
A company has a cash surplus which it wishes to distribute to shareholders by a share repurchase rather than paying a special dividend.
Which THREE of the following statements are correct?
Which THREE of the following statements are correct?
A company wishes to raise additional debt finance and is assessing the impact this will have on key ratios.
The following data currently applies:
• Profit before interest and tax for the current year is $500,000
• Long term debt of $300,000 at a fixed interest rate of 5%
• 250,000 shares in issue with a share price of $8
The company plans to borrow an additional $200,000 on the first day of the year to invest in new project which will improve annual profit before interest and tax by $24,000.
The additional debt would carry an interest rate of 3%.
Assume the number of shares in issue remain constant but the share price will increase to $8.50 after the investment.
The rate of corporate income tax is 30%.
After the investment, which of the following statements is correct?
A UK company enters into a 5 year borrowing with bank P at a floating rate of GBP Libor plus 3%
It simultaneously enters into an interest rate swap with bank Q at 4.5% fixed against GBP Libor plus 1.5%
What is the hedged borrowing rate, taking the borrowing and swap into account?
Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
A company has a covenant on its 5% long-term bond, stipulating that its retained earnings must not fall below $2 million.
The company has 100 million shares in issue.
Its most recent dividend was $0.045 per share. It has committed to grow the dividend per share by 4% each year.
The nominal value of the bond is $60 million. It is currently trading at 80% of its nominal value.
Next year's earnings before interest and taxation are projected to be $11.25 million.
The rate of corporate tax is 20%.
If the company increases the dividend by 4%, advise the Board of Directors if the level of retained earnings will comply with the covenant?
Company A is planning to acquire Company B. Both companies are listed and are of similar size based on market capitalisation No approach has yet been made to Company B's shareholders as the directors of Company A are undecided about the most suitable method of financing the offer Two methods are under consideration a share exchange or a cash offer financed by debt.
Company A currently has a gearing ratio (debt to debt plus equity) of 30% based on market values. The average gearing ratio (debt to debt plus equity) for the industry is 50% Although no formal offer has been made there have been market rumours of the proposed bid. which is seen as favorable to Company A. As a consequence. Company As share price has risen over the past few weeks while Company B's share price has fallen.
Which THREE of the following statements are most likely to be correct?
A company is based in Country Y whose functional currency is YS. It has an investment in Country Z whose functional currency is ZS This year the company expects to generate ZS20 million profit after tax.
Tax Regime
• Corporate income tax rate in Country Y is 60%
• Corporate income tax rate in Country Z Is 30%
• Full double tax relief is available
Assume an exchange rate of YS1 = ZS5
What is the expected profit after tax in YS if the ZS profit is remitted to Country Y?
Which TIIRCC of the following are most likely to reduce the long term credit rating co a company?
A company is currently all-equity financed with a cost of equity of 8%.
It plans to raise debt with a pre-tax cost of 4% in order to buy back equity shares.
After the buy-back, the debt-to-equity ratio at market values will be 1 to 2.
The corporate income tax rate is 30%.
Which of the following represents the company's cost of equity after the buy-back according to Modigliani and Miller's Theory of Capital Structure with taxes?
The International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) was formed in August 2010 and brings together a cross-section of representatives from a wide variety of business sectors.
The primary purpose of the IIRC's framework is to help enable an organsation to communicate how it:
A listed company has suffered a period of falling revenues and profit margins. It has been obliged to issue a profit warning to the market and its share price has fallen sharply. The company relies heavily on debt finance and is discussing with its banks possible refinancing options to assist with a restructuring programme.
Which THREE of the following are likely to be of MOST interest to the company's banks when they review the refinancing requests?
A company's gearing (measured as debt/(debt + equity)) is currently 60% and it is investigating whether an optimal gearing structure exists within the industry.
It has analysed the capital structure of similar companies in the industry and it would appear that there is evidence supporting the traditional theory of capital structure.
Companies with the lowest WACC in the industry have gearing of around 45% to 50%.
Which of the following actions would result in the company achieving a more optimal capital structure?
RST wishes to raise at least $40 million of new equity by issuing up to 10 million new equity shares at a minimum price of $3.00 under an offer for sale by tender. It receives the following tender offers:

What is the maximum amount that RST can raise by this share issue?
(Give your answer to the nearest $ million).

PYP is a listed courier company. It is looking to raise new finance to fit each of its delivery vans with new equipment to allow improved parcel tracking for customers The senior management team of PYP have decided on a 10-year secured bond to finance this investment-
Which TWO of the following variables are most likely to decrease the yield to maturity of the bond?
A company plans a four-year project which will be financed by either an operating lease or a bank loan.
Lease details:
• Four year lease contract.
• Annual lease rentals of $45,000, paid in advance on the 1st day of the year.
Other information:
• The interest rate payable on the bank borrowing is 10%.
• The capital cost of the project is $200,000 which would have to be paid at the beginning of the first year.
• A salvage or residual value of $100,000 is estimated at the end of the project's life.
• Purchased assets attract straight line tax depreciation allowances.
• Corporate income tax is 20% and is payable at the end of the year following the year to which it relates.
A lease-or-buy appraisal is shown below:
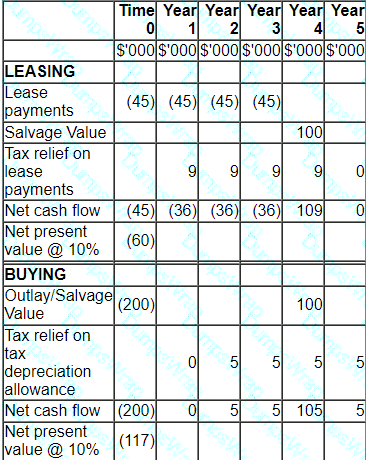
Which THREE of the following items are errors within the appraisal?
A listed company in a high growth industry, where innovation is a key driver of success has always operated a residual dividend policy, resulting in volatility in dividends due to periodic significant investments in research and development.
The company has recently come under pressure from some investors to change its dividend policy so that shareholders receive a consistent growing dividend. In addition, they suggested that the company should use more debt finance.
If the suggested change is made to the financial policies, which THREE of the following statements are true?
A company is considering a divestment via either a management buyout (MBO) or sale to a private equity purchaser. Which of the following is an argument in favour of the MBO from the viewpoint of the original company?
Company Z wishes to borrow $50 million for 10 years at a fixed rate of interest.
Two alternative approaches are being considered:
A. Issue a 10 year bond at a fixed rate of 6%, or
B. Borrow from the bank at Libor +2.5% for a 10 year period and simultaneously enter into a 10 year interest rate swap.
Current 10 year swap rates against Libor are 4.0% - 4.2%.
What is the difference in the net interest cost between the two alternative approaches?
Company AAB is located in Country A with the A$ as its functional currency It plans to grow by acquisition and has identified Company BBA as a potential takeover candidate Company BBA is located in Country B with the BS as its functional currency.
The directors of Company AAB are concerned about foreign currency risk if the acquisition goes ahead
Which of the following will be most effective in reducing Company AAB's exposure to translation risk if the acquisition is successful1?
Which of the following statements about companies seeking a stock market listing is correct?
Company M's current profit before interest and taxation is $5.0 million.
It has a long-term 10% corporate bond in issue with a nominal value of $10 million.
The rate of corporate tax is 25%.
It plans to continue to pay out 50% of its earnings in dividends and earnings are expected to grow by 3% each year in perpetuity.
Its cost of equity is 10%.
Using the dividend growth model, advise the Board of Directors of Company M which of the following provide a reasonable valuation of Company M's equity?
A company's Board of Directors is assessing the likely impact of financing future new projects using either equity or debt.
The directors are uncertain of the effects on key variables.
Which THREE of the following statements are true?
A company wishes to raise new finance using a rights issue to invest in a new project offering an IRR of 10%
The following data applies:
• There are currently 1 million shares in issue at a current market value of $4 each.
• The terms of the rights issue will be $3.50 for 1 new share for 5 existing shares.
• The company's WACC is currently 8%.
What is the yield-adjusted theoretical ex-rights price (TERP)?
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
$ ?
A venture capitalist invests in a company by means of buying:
• 9 million shares for $2 a share and
• 8% bonds with a nominal value of $2 million, repayable at par in 3 years' time.
The venture capitalist expects a return on the equity portion of the investment of at least 20% a year on a compound basis over the first 3 years of the investment.
The company has 10 million shares in issue.
What is the minimum total equity value for the company in 3 years' time required to satisify the venture capitalist's expected return?
Give your answer to the nearest $ million.
$ million.
A listed company in a high growth industry, where innovation is a key driver of success has always operated a residual dividend policy, resulting in volatility in dividends due to periodic significant investments in research and development.
The company has recently come under pressure from some investors to change its dividend policy so that shareholders receive a consistent growing dividend. In addition, they suggested that the company should use more debt finance.
If the suggested change is made to the financial policies, which THREE of the following statements are true?
Which of the following statements about the tax impact on debt finance is correct?
Company A plans to acquire Company B.
Both firms operate as wholesalers in the fashion industry, supplying a wide range of ladies' clothing shops.
Company A sources mainly from the UK, Company B imports most of its supplies from low-income overseas countries.
Significant synergies are expected in management costs and warehousing, and in economies of bulk purchasing.
Which of the following is likely to be the single most important issue facing Company A in post-merger integration?
A company has a loss-making division that it has decided to divest in order to raise cash for other parts of the business.
The losses stem from a combination of a lack of capital investment and poor divisional management.
The loss-making division would require new capital investment of at least $20 million in order to replace worn out and obsolete assets.
If this investment was carried out, the present value of the future cashflows, excluding the investment expenditure, is expected to be $15 million.
Which TWO of the following divestment methods are most likely to be suitable for the company?
Company Y plans to diversify into an activity where Company X has an equity beta of 1.6, a debt beta of zero and gearing of 50% (debt/debt plus equity).
The risk-free rate of return is 5% and the market portfolio is expected to return 10%.
The rate of corporate income tax is 30%.
What would be the risk-adjusted cost of equity if Company Y has 60% equity and 40% debt?
Company J is in negotiations to acquire Company K and believes it can turn around Company K's performance to match its own.
The following information is available for the two companies:

Select the maximum price for each share that Company J should place on Company K during negotiations.
A listed company is financed by debt and equity.
If it increases the proportion of debt in its capital structure it would be in danger of breaching a debt covenant imposed by one of its lenders.
The following data is relevant:

The company now requires $800 million additional funding for a major expansion programme.
Which of the following is the most appropriate as a source of finance for this expansion programme?
Company AAB is located in country A whose currency is the AS It has a subsidiary, BBA, located m country B that has the BS as its currency AAB has asked BBA to pay BS40 million surplus funds to AAB to assist with a planned new capital investment in country A The exchange rate today is AS1 = BS3
Tax regimes
• Company BBA pays withholding tax of 25% on all cash remitted to the parent company
• Company AAB pays tax of 10% on at cash received from its subsidiary
How much will company AAB have available for investment after receiving the surplus funds from BBA?
A company has 6 million shares in issue. Each share has a market value of $4.00.
$9 million is to be raised using a rights issue.
Two directors disagree on the discount to be offered when the new shares are issued.
• Director A proposes a discount of 25%
• Director B proposes a discount of 30%
Which THREE of the following statements are most likely to be correct?
A company is concerned about the interest rate that it will be required to pay on a planned bond issue.
It is considering issuing bonds with warrants attached.
Advise the directors which of the following statements about warrants is NOT correct?
ADC is planning to acquire DEF in order to benefit from the expertise of DEF's owner ‘managers Both are Listed companies. ADC is trying to decide whether to offer cash or shares in consideration for DEF's shares.
Which THREE of the following are advantages to ABC of offering shares to acquire CEF?
A large, listed company is planning a major project that should greatly improve its share price in the long term.
These plans require a significant capital cost that the company plans to finance by debt.
All of the debt options being considered are for the same duration of time.
Which of the following sources of debt finance is likely to be the most expensive for the company over the full term of the debt?
Listed company R is in the process of making a cash offer for the equity of unlisted company S.
Company R has a market capitalisation of $200 million and a price/earnings ratio of 10.
Company S has a market capitalisation of $50 million and earnings of $7 million.
Company R intends to offer $60 million and expects to be able to realise synergistic benefits of $20 million by combining the two businesses. This estimate excludes the estimated $8 million cost of integrating the two businesses.
Which of the following figures need to be used when calculating the value of the combined entity in $ millions?
Company A plans to acquire a minority stake in Company B.
The last available share price for Company B was $0.60.
Relevant data about Company B is as follows:
• A dividend per share of $0.08 has just been paid
• Dividend growth is expected to be 2%
• Earnings growth is expected to be 4%
• The cost of equity is 15%
• The weighted average cost of capital is 13%
Using the dividend growth model, what would be the expected change in share price?
HHH Company has a fixed rate loan at 10.0%, but wishes to swap to variable. It can borrow at the risk-free rate +8%. The bank is currently quoting swap rates of 3.1% (bid) and 3.5% (ask). What net rate will HHH Company pay if it enters into the swap?
An unlisted software development business is to be sold by its founders to a private equity house following the initial development of the software. The business has not yet made a profit but significantprofits are expected for the next three years with only negligible profits thereafter. The business owns the freehold of the property from which it operates. However, it is the industry norm to lease property.
Which THREE of the following are limitations to the validity of using the Calculated Intangible Value (CIV) method for this business?
A company has borrowings of S5 million on which it pays interest at 8%. It has an operating profit margin of 20%.
The company plans to increase borrowings by S2 million Interest on additional borrowings would be 10% and the operating profit margin would remain unchanged
A debt covenant attached to the new borrowings requires interest cover to be at least 4 times throughout the period of the borrowing
Interest cover is defined in the loan documentation as being based on operating profit
What is the minimum sales value required each year to avoid a breach of the interest cover covenant'
WW is a quoted manufacturing company. The Finance Director has addressed the shareholders during WW's annual general meeting-She has told the shareholders that WW raised equity during the year and used the funds to repay a large loan that was maturing, thereby reducing WW's gearing ratio
At the conclusion of the Finance Director's speech one of the shareholders complained that it had been foolish for WW to have used equity to repay debt The shareholder argued that the Modigliani and Miller model (with tax) offers proof that debt is cheaper than equity when companies pay tax on their profits.
Which THREE arguments could the Finance Director have used in response to the shareholder?
A company financed by equity and debt can be valued by discounting:
A major energy company, GDE, generates and distributes electricity in country A. The government of country A is concerned about rising inflation and has imposed price controls on GDE, limiting the price it can charge per unit of electricity sold to both domestic and commercial customers. It is likely that price controls will continue for the foreseeable future.
The introduction of price controls is likely to reduce the profit for the current year from $3 billion to $1 billion.
The company has:
• Distributable reserves of $2 billion.
• Surplus cash at the start of the year of $1 billion.
• Plans to pay a total dividend of $1.5 billion in respect of the current year, representing a small annual increase as in previous years. However, no dividends have yet been announced.
Which THREE of the following responses would be MOST appropriate for GDE following the imposition of price controls?
Company GDD plans to acquire Company HGG, an unlisted company which has been in business for 3 years.
Company HGG has incurred losses in its first 3 years but is expected to become highly profitable in the near future
There are no listed companies in the country operating in the same business field as Company HGG The future success of Company HGG's business and hence the future growth rate in earnings and dividends is difficult to determine
Company GDD is assessing the validity of using the dividend growth method to value Company HGG
Which THREE of the following are weaknesses of using the dividend growth model to value an unlisted company such as Company HGG?
The shares of a company in a high technology industry have been listed on a stock exchange for 10 years. During this period, it has paid no dividends but invested all retained earnings in growth. The company is now entering a period of relatively stable growth and the directors are considering beginning to pay dividends They are reviewing the following suggestions made by members of the board:
• Pay cash dividends linked to growth in earnings
• Use a residual theory approach to establish cash dividends
• Issue scrip dividends (shares instead of cash)
• Continue to pay no dividends as dividends are irrelevant to the value of the company
Which THREE of the following are correct statements for the directors to take into consideration when making a decision about future dividend policy?
On 1 January 20X1 a company entered into a S200 million interest rate swap with a bank at a fixed rate of 4% against the 6-month risk-free rate to hedge the interest rale risk on a floating rate borrowing.
6-month risk-free rate was as follows:

What is the net settlement due under the swap contract on 1 July 20X1?
A venture capitalist is most likely to take which THREE of the following exit routes?
An unlisted company.
• Is owned by the original founders and members of their families
• Pays annual dividends each year depending on the cash requirements of the dominant shareholders.
• Has earnings that are highly sensitive to underlying economic conditions.
• Is a small business in a large Industry where there are listed companies with comparable capital structures
Which of the following methods is likely to give the most accurate equity value for this unlisted company?
A company's current earnings before interest and taxation are $5 million.
These are expected to remain constant for the forseeable future.
The company has 10 million shares in issue which currently trade at $3.60.
It also has a $10 million long term floating rate loan.
The current interest rate on this loan is 5%.
The company pays tax at 20%.
The company expects interest rates to increase next year to 6% and it's Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio to move to 9.5 times by the end of next year.
What percentage reduction in the share price will occur by the end of next year if the interest rate increase and the P/E movement both occur?
On 31 October 20X3:
• A company expected to agree a foreign currency transaction in January 20X4 for settlement on 31 March 20X4.
• The company hedged the currency risk using a forward contract at nil cost for settlement on 31 March 20X4.
• The transaction was correctly treated as a cash flow hedge in accordance with IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement.
On 31 December 20X3, the financial year end, the fair value of the forward contract was $10,000 (asset).
How should the increase in the fair value of the forward contract be treated within the financial statements for the year ended 31 December 20X3?
A consultancy company is dependent for profits and growth on the high value individuals it employs.
The company has relatively few tangible assets.
Select the most appropriate reason for the net asset valuation method being considered unsuitable for such a company.