Dell PowerFlex Design 2023 Exam Questions and Answers
A customer must restore PowerFlex Manager from a previous backup How can they accomplish this task*?
Options:
Select Restore Irom the Serviceability page in PowerFlex Manager.
Restore trom the standby MDM
Run a script outside of PowerFlex Manager
Answer:
AExplanation:
To restore PowerFlex Manager from a previous backup, the customer should select the Restore option from the Serviceability page in PowerFlex Manager. This process is outlined in the Dell PowerFlex Manager documentation and involves the following steps:
- Login to PowerFlex Manager GUI: Access the PowerFlex Manager user interface through a web browser.
- Navigate to Serviceability: From the dashboard, navigate to the Serviceability page.
- Select Restore: On the Serviceability page, locate and select the Restore option.
- Provide Backup Details: Enter the necessary details of the backup file that you wish to restore from, such as the filename and location.
- Test Connection: Before proceeding with the restore, perform a test connection to ensure that the backup file is accessible.
- Initiate Restore: Once the test connection is successful, initiate the restore process.
The restore operation will then proceed, and upon completion, PowerFlex Manager will be restored to the state captured in the backup file. It is important to follow the instructions carefully and ensure that the backup file is correct and not corrupted to avoid any issues during the restoration process1.
This answer is verified as per the Dell PowerFlex Design documents, ensuring that the information provided is accurate and aligns with the official guidelines for restoring PowerFlex Manager from a backup1.
In a test-dev PowerFlex appliance environment, there are two Compute Only nodes five Storage Only nodes, and one Management node An architect wants to create Fault Sets using all available servers but is unable to do so What is the cause of this issue?
Options:
A Mote than one Management node is required
There are not enough Storage Only nodes.
There are not enough Compute Only nodes.
Answer:
BExplanation:
In a PowerFlex appliance environment, Fault Sets are used to group Storage Data Servers (SDSs) that are managed together as a single fault unit. When Fault Sets are employed, the distributed mesh-mirror copies of data are never placed within the same fault set1. This means that each Fault Set must have enough SDSs to ensure that data can be mirrored across different Fault Sets for redundancy.
Given that there are only five Storage Only nodes available in the described environment, and considering that each node runs an SDS, it may not be possible to create Fault Sets using all available servers if the number of Fault Sets or the distribution of SDSs across those Fault Sets does not allow for proper mirroring of data. The architecture requires a certain number of SDSs to be available to form a Fault Set that can be used for data mirroring and redundancy1.
The other options, such as requiring more than one Management node (Option A) or not having enough Compute Only nodes (Option C), are not directly related to the creation of Fault Sets. The Management node’s primary role is to manage the cluster, not to participate in Fault Sets, and Compute Only nodes do not contribute storage resources to Fault Sets.
Therefore, the correct answer is B. There are not enough Storage Only nodes, as this would prevent the architect from creating Fault Sets that meet the redundancy requirements of the PowerFlex appliance environment.
A customer is setting up PowerFlex Manager and wants to start with the minimal supported configuration Which configuration should be selected''
Options:
36vCPU and 600 GB Disk Space
42vCPU and 400 GB DisK Space
42vCPU and 600 GB DisK Space
36vCPU and 400 GB DisK Space
Answer:
AExplanation:
For setting up PowerFlex Manager with the minimal supported configuration, the customer should select the option with 36vCPU and 600 GB DISK Space. This configuration provides a sufficient amount of resources to support the management operations of PowerFlex Manager while adhering to the minimal requirements.
The selection process for the minimal supported configuration typically involves:
- Evaluating Requirements: Understanding the minimal resource requirements for PowerFlex Manager, which includes CPU and disk space.
- Matching Specifications: Aligning the available options with the known minimal requirements.
- Selecting the Configuration: Choosing the configuration that meets or exceeds the minimal requirements without unnecessary resource allocation.
The reference for this information can be found in the PowerFlex Manager documentation, which outlines the system requirements for different deployment scenarios1. It is important to consult the latest compatibility matrix and administration guides to ensure that the chosen configuration aligns with the current supported standards and recommendations for PowerFlex Manager deployments1.
An administrator wants to migrate a volume from one storage pool to another storage pool What two volume migrations are possible ?(Select 2)
Options:
Prom MG storage pool volume, non-zero padded and Ihick provisioned lo FG storage pool volume zero padded: and thin provisioned
From MG storage pool volume, zero padded, and thick provisioned to FG storage pool volume, zero padded, and thin provisioned
From FG storage pool volume, zero padded, and thin provisioned to MG storage pool volume, non-zero padded and thick provisioned
From MG storage pool volume, non-zero padded, and thin provisioned to MG storage pool volume, zero padded, and thin provisioned
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
Volume migration in PowerFlex allows for the movement of volumes between storage pools, which can be necessary for various operational reasons such as performance tuning, capacity expansion, or infrastructure upgrades. The possible migrations are:
- Option B: Migrating from an MG (Medium Granularity) storage pool volume that is zero padded and thick provisioned to an FG (Fine Granularity) storage pool volume that is also zero padded and thin provisioned. This migration is possible and allows for a change in the provisioning and granularity of the volume, which can be beneficial for optimizing storage efficiency and performance1.
- Option D: Migrating from an MG storage pool volume that is non-zero padded and thin provisioned to another MG storage pool volume that is zero padded and thin provisioned. This migration is within the same granularity type (MG) and involves changing the padding of the volume. It is a viable option when adjusting the volume configuration for specific storage optimization needs1.
These migrations are supported by PowerFlex’s flexible architecture, which allows for non-disruptive volume movements between storage pools. The process involves using PowerFlex’s management tools to initiate and monitor the migration, ensuring data integrity and system stability throughout the operation1.
The references for these migrations come from PowerFlex documentation and best practices, which detail the procedures and capabilities of the system regarding volume management and migration1. It isimportant to follow the recommended guidelines to ensure successful migrations that align with the system’s design and operational principles.
A bank is creating a data center The storage solution must have integrated, fully configured hardware with a single management platform The solution must be supported end-to-end by Dell Which PowerFlex system meets these requirements?
Options:
PowerFlex custom node
PowerFlex rack
PowerFlex appliance
Answer:
BExplanation:
The PowerFlex rack system meets the requirements of a bank creating a data center that needs integrated, fully configured hardware with a single management platform, all supported end-to-end by Dell.
Here’s why the PowerFlex rack is the suitable choice:
- Integrated and Fully Configured Hardware: The PowerFlex rack is a pre-configured solution that includes integrated hardware and software components. It is designed for easy deployment and management1.
- Single Management Platform: PowerFlex rack systems come with a single management platform that simplifies operations and provides a unified view of the entire infrastructure1.
- End-to-End Dell Support: PowerFlex rack solutions are fully supported by Dell, providing customers with a single point of contact for all support needs. This includes hardware, software, and the entire infrastructure stack2.
The PowerFlex rack is specifically designed to meet the needs of organizations like banks that require a robust, scalable, and easy-to-manage storage solution. It offers a turnkey experience with the assurance of comprehensive support from Dell, making it an ideal choice for the bank’s data center requirements1.
Which PowerFlex Manager activity can the System Admin role perform?
Options:
Lifecycle operations
Manage users
Update certificates
Answer:
AExplanation:
The System Admin role in PowerFlex Manager is primarily responsible for performing lifecycle operations. This includes tasks such as deploying, configuring, and updating the PowerFlex system components. The role is designed to manage the operational aspects of the PowerFlex environment, ensuring that the system is running efficiently and is up to date1.
While managing users and updating certificates are important administrative tasks, they are typically associated with different roles within the PowerFlex Manager’s user management system. For instance, managing users would fall under the purview of a User Admin role, which would handle the creation, modification, and deletion of user accounts. Updating certificates, on the other hand, would be more aligned with a Security Admin role, which would be responsible for maintaining the security aspects of the PowerFlex system, including certificate management1.
Therefore, the correct answer is A. Lifecycle operations, as it directly relates to the System Admin role’s responsibilities within PowerFlex Manager.
An administrator wants to track total usage on a PowerFlex File system but does not want to impose any restrictions on their users How can this be accomplished using quotas'?
Options:
Create a usei quota and set an indefinite grace period
Create a user quota and set both the soft and hard limits to zero
Create a tree quota and set an indefinite grace period
Create a tree quota and set both the soft and hard limits lo zero
Answer:
DExplanation:
To track total usage on a PowerFlex File system without imposing any restrictions on users, an administrator can create a tree quota and set both the soft and hard limits to zero. This method allows the administrator to monitor usage without enforcing any quota limits, thus not restricting user behavior.
Here’s how it can be accomplished:
- Access the PowerFlex Management Console: Log in to the PowerFlex Management Console where you can manage quotas.
- Navigate to the File System: Locate the file system for which you want to track usage.
- Create a Tree Quota: Choose to create a new tree quota for the file system.
- Set Limits to Zero: When setting up the quota, input zero for both the soft and hard limits. This effectively means there are no limits enforced on the users.
- Apply the Quota: Save and apply the quota settings to the file system.
By setting both limits to zero, the administrator can use the quota system purely for monitoring purposes, without affecting user operations. The users will not encounter any quota warnings or limits, but the system will still track and report on the total usage, which the administrator can review.
The rationale behind using a tree quota rather than a user quota is that tree quotas are associated with a directory tree, allowing the tracking of usage across a broader scope, which is more suitable for monitoring overall file system usage.
This approach is consistent with best practices for administering PowerFlex systems as described in the Dell PowerFlex Administration Guide1, which provides detailed procedures for managing storage, including the configuration of quotas for monitoring purposes.
An engineer must permanently remove a node from a 10-node PowerFlex system The node is the primary MDM. What must they do before they remove the node to avoid errors and maintain availability'
Options:
Use the renove_standby_imdm SCLI command
Use the switch_ciuster_mcde SCLI command
Use PowerFlex Manager to reconfigure MDM roles
Use PowerFlex Manager to deactivate the Protection Domain.
Answer:
CExplanation:
Before permanently removing a node that is the primary MDM from a PowerFlex system, it is crucial to ensure that the MDM roles are reconfigured to maintain cluster availability and avoid errors. This process involves promoting another node to take over the primary MDM role and ensuring that the cluster continues to function correctly without the node that is being removed.
The steps to reconfigure MDM roles using PowerFlex Manager are as follows:
- Log in to PowerFlex Manager.
- Navigate to the MDM cluster settings.
- Identify a suitable node that can be promoted to the primary MDM role.
- Use the PowerFlex Manager interface to promote the selected node to the primary MDM role.
- Ensure that the cluster is stable and that the new primary MDM is functioning correctly.
- Once the new primary MDM is in place and operational, the original primary MDM node can be safely removed from the cluster.
This process is essential to prevent any disruptions in the management and operation of the PowerFlex system. The other options listed, such as using the remove_standby_mdm SCLI command (Option A) or the switch_cluster_mode SCLI command (Option B), do not directly address the reconfiguration of MDM roles. Deactivating the Protection Domain (Option D) is not related to the removal of an MDM node and would not be a recommended step in this scenario.
Therefore, the correct answer is C. Use PowerFlex Manager to reconfigure MDM roles, as it ensures that the MDM responsibilities are transferred to another node before the primary MDM node is removed, thus maintaining the integrity and availability of the PowerFlex system1.
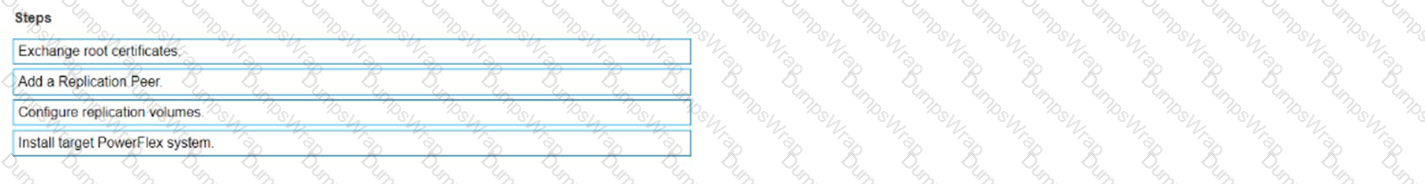
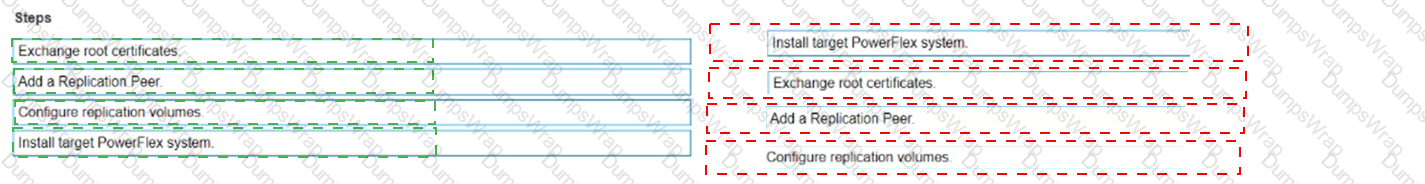
Place the steps to set up remote replication on the Powerflex system in the correct order
Options:
Answer:
Explanation:

The correct sequence of steps to set up remote replication on the PowerFlex system is as follows:
- Install target PowerFlex system: Before replication can be set up, there must be a target system in place to receive the replicated data1.
- Exchange root certificates: This is a security measure to ensure that communication between the source and target systems is secure1.
- Add a Replication Peer: This involves configuring the target system as a replication partner in the source system’s configuration1.
- Configure replication volumes: Finally, specific volumes on the source system are configured to replicate to the target system1.
Setting up remote replication in a PowerFlex system involves a series of steps that establish the necessary components and configurations for the replication process. The sequence begins with the installation of the target PowerFlex system, which will serve as the destination for the replicated data. Next, root certificates are exchanged between the source and target systems to ensure secure communication. The target system is then added as a Replication Peer within the source system’s configuration. Lastly, the volumes intended for replication are configured on the source system to complete the setup process. This sequence ensures that the replication is secure, reliable, and correctly configured to maintain data integrity and availability across both systems1.
Where must a customer go to generate a software troubleshooting bundle?
Options:
PowerFlex Manager Events and Alerts
PowerFlex Manager Serviceability
iDRAC Lrfecycle Controller
CloudLmk Center Console
Answer:
BExplanation:
To generate a software troubleshooting bundle for PowerFlex, a customer must navigate to the PowerFlex Manager Serviceability. The steps to generate the bundle are as follows1:
- Log in to PowerFlex Manager.
- Choose ‘Settings’ from the menu.
- Within the Settings menu, select ‘Virtual Appliance Management’.
- Choose ‘Generate Troubleshooting Bundle’.
- In the popup window, the customer has the option to either send the bundle to Configured Secure Remote Services (Secure Remote Services) or download it locally. If downloading locally, select the path for the downloads and enter the appropriate login information, then click ‘Generate’.
This process is part of the serviceability features of PowerFlex Manager, which provides tools for system maintenance and troubleshooting. It is important to follow these steps carefully to ensure that the troubleshooting bundle is generated correctly and contains all the necessary information for diagnosing issues within the PowerFlex system.
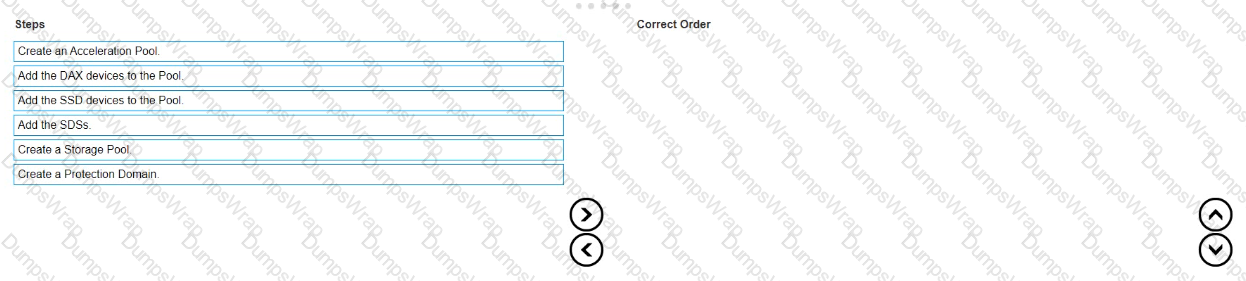
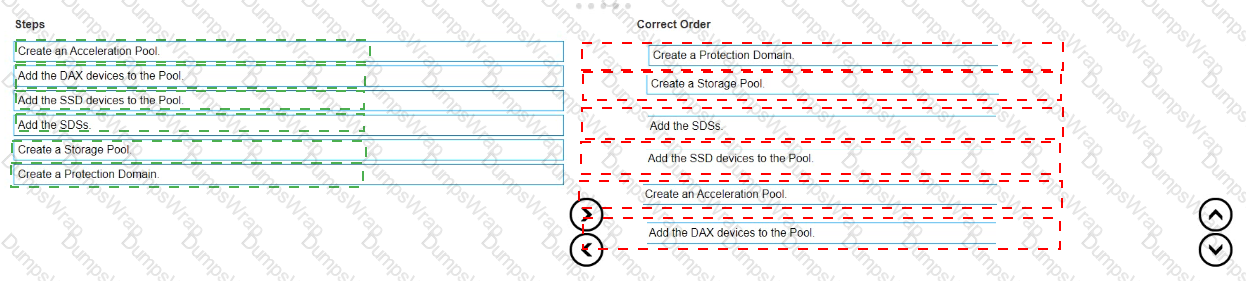
What is the correct sequence of steps to create an FG Storage Pool within a PowerFlex system?
Options:
Answer:
Explanation:
The correct sequence of steps to create an FG (Fine Granularity) Storage Pool within a PowerFlex system is as follows:
- Create a Protection Domain: This is the first step, where you define a logical grouping of storage resources that share the same protection policy and fault tolerance settings1.
- Create a Storage Pool: After establishing a Protection Domain, you create a Storage Pool within it. This pool will contain the physical storage resources1.
- Add the SDSs (Storage Data Servers): The next step is to add SDSs to the Storage Pool. SDSs are the servers that contribute storage capacity to the pool1.
- Add the SSD (Solid-State Drive) devices to the Pool: Once the SDSs are added, you then add the SSD devices to the Storage Pool to provide the actual storage capacity1.
- Create an Acceleration Pool: This step involves creating an Acceleration Pool, which is used for caching to enhance the performance of the storage system1.
- Add the DAX (Direct Access) devices to the Pool: Finally, you add the DAX devices to the Acceleration Pool. DAX devices are typically high-speed storage devices like NVMe drives that serve as cache
The process of creating an FG Storage Pool in a PowerFlex system involves a series of steps that establish the necessary components and configurations for the storage environment. The sequence starts with the creation of a Protection Domain, which sets the stage for defining how storage will be protected and managed. Within this domain, a Storage Pool is created, which is essentially a collection of storage resources. The SDSs are then added to this pool, contributing their storage capacity to the overall system. SSD devices are included next to provide the actual storage space. An Acceleration Pool is created to improve performance through caching, and DAX devices are added to this pool to serve as the cache, completing the setup of an FG Storage Pool1.
This sequence ensures that the storage system is configured for optimal performance and data protection, following the guidelines and best practices outlined in the PowerFlex documentation1. It’s important to follow these steps in order to maintain the integrity and efficiency of the PowerFlex storage system.
A customer has ordered five servers with NVDlMMs Each server has 5 x 3 84 TB SAS and 5 x 3 84 T8 NVMe disks They want to ensure that the highest capacity ot storage is available to the system Which design provides the required storage pool structure''
Options:
One Storage Pool and one Acceleration Pool
One Acceleration Pool only
One Storage Pool only
One Acceleration Pool and two Storage Pools
Answer:
AExplanation:
To maximize the storage capacity available to the system while utilizing NVDIMMs, SAS, and NVMe disks, the design should include both a Storage Pool and an Acceleration Pool. The Storage Pool will be used for the bulk storage provided by the SAS disks, while the Acceleration Pool, leveraging the high-speed NVMe disks, will be used to accelerate the performance of the storage system.
The use of NVDIMMs in PowerFlex is associated with enabling fine-granularity storage pools that provide compression, which is beneficial for space efficiency, especially with heavy snapshot use1. This configuration allows for the creation of a storage pool that can take advantage of the NVDIMMs’ capabilities for compression and the high capacity of the SAS disks, while the NVMe disks in the Acceleration Pool provide high-performance storage for more demanding workloads.
Therefore, the correct answer is A. One Storage Pool and one Acceleration Pool, as this design will provide the highest capacity of storage available to the system while also ensuring optimal performance through the use of NVMe disks in the Acceleration Pool.

