Dell VPLEX Operate Achievement Questions and Answers
Which VPLEX model is recommended for VPLEX for All Flash (VAF)?
Options:
VS1
VS6 only
VS2 only
VS2 and VS6
Answer:
DExplanation:
For VPLEX for All Flash (VAF), both the VS2 and VS6 models are recommended. Here’s why:
VS2 Model: The VS2 model is a previous generation of VPLEX hardware that supports all-flash configurations.It is designed to handle the high throughput and low latency requirements of all-flash storage1.
VS6 Model: The VS6 is the latest generation of VPLEX hardware, offering enhanced performance and scalability compared to the VS2.It is also suitable for all-flash environments and is designed to leverage the full capabilities of flash storage1.
Upgrade Path: Organizations with existing VS2 hardware can continue to use it for VAF, but they may consider upgrading to VS6 for improved performance and newer features.The VPLEX architecture allows for non-disruptive upgrades from VS2 to VS6, making it a future-proof solution1.
VPLEX Technology: Both VS2 and VS6 utilize VPLEX technology that virtualizes storage across multiple arrays, allowing for seamless data mobility and continuous availability.This technology is particularly beneficial in all-flash environments where performance and uptime are critical1.
Documentation: The Dell VPLEX Operate Achievement documents provide detailed information on the capabilities of both VS2 and VS6 models, including their suitability for VAF environments1.
By choosing either VS2 or VS6 models for VPLEX for All Flash, organizations can ensure they have a robust and high-performing storage virtualization platform that meets the demands of modern all-flash arrays.
What is required before a host can detect the virtual volumes presented by the VPLEX?
Options:
RAID configuration must be enabled for Virtual volumes
Virtual volumes can only be detected after a reboot
EZ Provisioning wizard must be run on the host
Host must initiate a bus-scan of the HBAs
Answer:
DExplanation:
Before a host can detect the virtual volumes presented by VPLEX, it is necessary for the host to initiate a bus-scan of the Host Bus Adapters (HBAs). This process allows the host to recognize new storage devices that have been presented to it, such as the virtual volumes from VPLEX.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
Host Bus Adapters (HBAs): HBAs are the hardware interfaces that connect a host system to a network or storage device. In the context of VPLEX, they connect the host to the VPLEX storage system.
Bus-Scan: A bus-scan is a command that can be issued from the host to scan the storage network for any changes, such as newly added storage volumes. This is typically done using operating system-specific commands or utilities.
Virtual Volumes Detection: Once the bus-scan is complete, the host’s operating system can detect the virtual volumes presented by VPLEX and make them available for use by applications and services running on the host.
No RAID Requirement: The detection of virtual volumes does not require RAID configuration to be enabled for the volumes themselves, as this is managed within the VPLEX system.
No Reboot Necessary: It is not necessary to reboot the host to detect virtual volumes. A bus-scan can be performed while the system is running without requiring a restart.
No Wizard Required: The EZ Provisioning wizard is a tool used within the VPLEX system for provisioning storage, but it is not required to be run on the host for virtual volume detection.
By initiating a bus-scan of the HBAs, the host can detect and utilize the virtual volumes presented by VPLEX, allowing for flexible and dynamic storage management.
What condition would prevent volume expansion?
Options:
Migration occurring on the volume
Volume not belonging to a consistency group
Metadata volume being backed up
Logging volume in re-synchronization state
Answer:
AExplanation:
Volume expansion in Dell VPLEX is a process that allows for increasing the size of a virtual volume. However, certain conditions can prevent this operation from taking place:
Migration Occurring on the Volume: If there is an ongoing migration process involving the volume, it cannot be expanded until the migration is complete.This is because the volume’s data layout is being altered during migration, and any attempt to change its size could lead to data corruption or other issues1.
Consistency Group Membership: Whether or not a volume belongs to a consistency group does not directly prevent volume expansion. Consistency groups in VPLEX areused to ensure write-order fidelity across multiple volumes but do not restrict the expansion of individual volumes within the group.
Metadata Volume Backup: Backing up a metadata volume is a separate operation that does not interfere with the ability to expand a storage volume. Metadata backups are typically performed to preserve the configuration and state information of the VPLEX system.
Logging Volume Re-synchronization: While a logging volume in a re-synchronization state indicates that there is an ongoing process to align data across clusters or devices, it does not inherently prevent the expansion of a storage volume.
Therefore, the condition that would prevent volume expansion is when there is a migration occurring on the volume (OA).
A service provider has implemented a VPLEX Metro cluster without VPLEX Witness and has implemented a static rule set. The static rule set has been set to "cluster-2
detaches". A Microsoft Windows host in the Cluster-1 data center uses a distributed volume. However, the WAN COM fails.
What is the result of this failure?
Options:
1. VPLEX suspends I/O to all distributed devices on both clusters
2. VPLEX starts a delay timer
3. If connectivity is not restored within the timer expiration period, VPLEX resumes I/O on Cluster-1 and keeps I/O suspended on Cluster-2
1. VPLEX starts a delay timer
2. VPLEX suspends I/O to all distributed devices on both clusters
3. If connectivity is not restored within the timer expiration period, VPLEX resumes I/O on Cluster-2 and keeps I/O suspended on Cluster-1
1. VPLEX suspends I/O to all distributed devices on both clusters
2. VPLEX starts a delay timer
3. If connectivity is not restored within the timer expiration period, VPLEX resumes I/O on Cluster-2 and keep I/O suspended on Cluster-1
1. VPLEX starts a delay timer
2. VPLEX suspends I/O to all distributed devices on both clusters
3. If connectivity is not restored within the timer expiration period, VPLEX resumes I/O on Cluster-1 and keeps I/O suspended on Cluster-2
Answer:
BExplanation:
In a VPLEX Metro cluster without a VPLEX Witness and with a static rule set to “cluster-2 detaches”, the result of a WAN COM failure would be as follows:
Delay Timer: Initially, VPLEX starts a delay timer upon detecting the WAN COM failure.This timer allows for a temporary network issue to be resolved without immediate impact on I/O operations1.
Suspension of I/O: While the delay timer is active, VPLEX suspends I/O to all distributed devices on both clusters to prevent data corruption and ensure data integrity1.
Resumption of I/O: If the WAN COM connectivity is not restored within the expiration period of the delay timer, VPLEX will resume I/O operations on Cluster-2, as per the static rule set.I/O will remain suspended on Cluster-1 to maintain a consistent data state and prevent a split-brain scenario1.
This process ensures that data remains consistent and available on at least one cluster in the event of a WAN COM failure, aligning with the predefined static rule set and maintaining the integrity of the VPLEX Metro cluster operations.
What steps are performed during extent and device migration?
Options:
Start, commit, clean, and remove
Create, commit, clean, and terminate
Create, clean, commit, and remove
Start, commit, clean, and terminate
Answer:
BExplanation:
The process of extent and device migration in a Dell VPLEX environment typically involves the following steps:
Create: The initial step is to create a migration job for the extent or device. This involves specifying the source and target extents or devices and setting up the migration parameters.
Commit: Once the migration job is created, the next step is to commit the jB.This action will start the migration process, where data begins to move from the source to the target.
Clean: After the data has been successfully migrated, the system performs a cleanup operation to remove any temporary data structures or logs that were used during the migration process.
Terminate: The final step is to terminate the migration jB.This step concludes the migration process and releases any resources that were allocated for the migration.
References:
The Dell VPLEX documentation provides detailed procedures on how to perform data migration, including the steps involved in migrating extents and devices1.
Best practices and technical guides from Dell also cover the topic of data migration, offering insights into the process and how to ensure a smooth migration experience1.
By following these steps, a storage administrator can successfully migrate extents and devices within the VPLEX environment, ensuring data availability and minimal disruption to services.
Which mobility operation must be used to perform storage volume defragmentation?
Options:
Device mobility
Virtual volume mobility
Data mobility
Extent mobility
Answer:
CExplanation:
Data mobility in VPLEX is used for various operations, including storage volume defragmentation. Here’s the explanation:
Data Mobility: This operation is designed to move data within the VPLEX system, which can include moving data from fragmented storage volumes to contiguous storage, effectively defragmenting the storage1.
Device Mobility: Device mobility is typically used for moving devices within the VPLEX cluster or across clusters but is not specifically for defragmentation purposes.
Virtual Volume Mobility: While virtual volume mobility can move virtual volumes within the VPLEX environment, it does not directly address storage volume defragmentation.
Extent Mobility: Extent mobility involves moving extents, which are segments of storage within a volume, but this is not the operation used specifically for defragmentation.
Defragmentation Process: During defragmentation, data mobility would be used to relocate data from fragmented extents to a set of contiguous extents, thereby optimizing the layout of the data on the physical storage and improving performance1.
VPLEX Administration Guides: For detailed procedures on how to perform data mobility operations, including defragmentation, administrators should refer to the VPLEX Administration Guides2.
By using data mobility operations, administrators can manage and optimize the storage within the VPLEX system, ensuring efficient use of resources and maintaining performance.
Which command can be used to create a distributed virtual volume from specified storage volumes?
Options:
storage-tool compose
storage-volume compose
virtual-volume create
ds dd create
Answer:
DExplanation:
Questions no:Q34
Verified Answer:D.ds dd create
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed Explanation with References:
To create a distributed virtual volume from specified storage volumes in Dell VPLEX, the command used is ds dd create. This command stands for “distributed storage distributed device create” and is part of the VPLEX CLI (Command Line Interface) commands that manage distributed devices across clusters in a VPLEX Metro environment.
Command Usage: The ds dd create command is used to create a distributed device, which is a virtual volume that spans across two VPLEX clusters, providing high availability and data mobility1.
Distributed Virtual Volume: A distributed virtual volume in VPLEX is a volume that is accessible from both clusters in a VPLEX Metro configuration.It allows for simultaneous read and write operations from both locations1.
Creating the Volume: The process involves specifying the storage volumes from each cluster that will be part of the distributed device.The command then creates a virtual volume that combines these storage volumes into a single distributed device1.
High Availability: The resulting distributed virtual volume can be used in scenarios that require high availability, such as active-active data center configurations.It ensures that data is accessible even if one of the clusters becomes unavailable1.
CLI Command Structure: The VPLEX CLI commands follow a structured format where the initial letters indicate the scope and type of operation.In this case, ds indicates distributed storage, and dd indicates a distributed device, which together specify the creation of a distributed virtual volume1.
By using the ds dd create command, administrators can effectively set up distributed virtual volumes in a VPLEX Metro environment, leveraging the system’s capabilities for data availability and mobility.
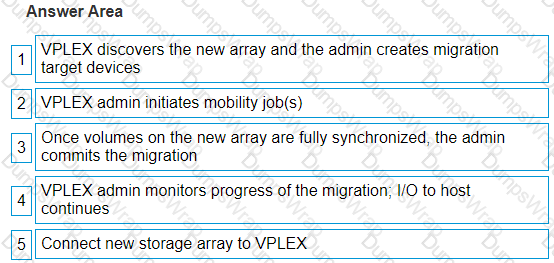
What is the correct order of steps to migrate from an old array to a new one without disruption using VPLEX?

Options:
Answer:
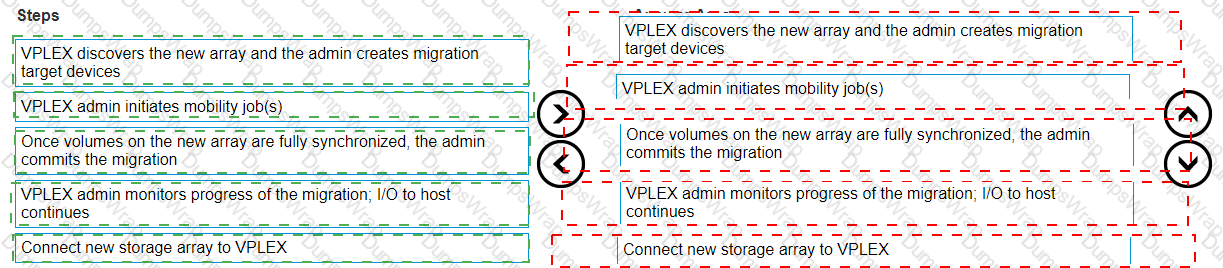
Explanation:
The correct order of steps to migrate from an old array to a new one without disruption using VPLEX is:
VPLEX discovers the new array and the admin creates migration target devices.
VPLEX admin initiates mobility job(s).
Once volumes on the new array are fully synchronized, the admin commits the migration.
VPLEX admin monitors progress of the migration; I/O to host continues.
Connect new storage array to VPLEX.
Discovery and Creation: The initial step involves VPLEX identifying the presence of a new storage array within its environment. Following this discovery, a system administrator is responsible for setting up migration target devices on this newly recognized array.
Initiation of Mobility Jobs: Subsequently, a system administrator must initiate mobility jobs through the VPLEX management interface, which facilitates data movement from the existing source storage to the target devices on the new array.
Synchronization and Commitment: After initiating mobility jobs, data synchronization between source and target arrays begins automatically. Once synchronization reaches completion, indicating that both arrays have identical data sets, an administrator must commit to finalizing this stage of migration.
Monitoring Migration Progress: Throughout this process, it’s crucial for an administrator to monitor ongoing operations ensuring that input/output operations continue uninterrupted for hosts accessing data during transition phases.
Connecting New Array: The final step involves integrating the newly populated storage array into production by connecting it with VPLEX systems thus completing migration.
To which VPLEX component does the SNMP management station connect to gather statistics?
Options:
VPLEX Witness
Management server
Director-A
Director-B
Answer:
BExplanation:
The SNMP management station connects to the VPLEX Management Server to gather statistics. The Management Server acts as the central point for managing and monitoring the VPLEX environment, including the collection of SNMP statistics.
Management Server Role: The VPLEX Management Server provides a centralized interface for system administration and monitoring.It is responsible for managing the VPLEX clusters and all associated components1.
SNMP Statistics Collection: SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used for collecting performance and health data from networked devices.The VPLEX Management Server supports SNMP and can be configured to send SNMP traps to a management station1.
Configuration: To enable SNMP monitoring, the VPLEX administrator must configure the Management Server with the appropriate SNMP settings, including the community string and the remote host (management station) details1.
Monitoring with SNMP: Once configured, the SNMP management station can connect to the VPLEX Management Server to collect statistics, which can include a wide range of metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and I/O rates1.
Troubleshooting: If there are issues with SNMP data collection, such as the inability to ping the remote host from the VPLEX Management Server, the administrator may need to check network configurations, such as firewall settings, to ensure proper connectivity1.
By connecting to the VPLEX Management Server, the SNMP management station can effectively gather statistics for monitoring the health and performance of the VPLEX system.
Which method of virtual volume expansion requires the volume to be expanded on the array first?
Options:
Storage volume
Concatenation
Extent expansion
RAID-C expansion
Answer:
AExplanation:
The method of virtual volume expansion that requires the volume to be expanded on the array first is the storage volume expansion methD.This method involves increasing the size of the physical storage volume on the array before expanding the virtual volume in VPLEX.
Array Expansion: The first step is to expand the physical storage volume on the array.This is typically done through the array’s management interface and involves adding more storage or extending the existing volume1.
VPLEX Recognition: Once the storage volume is expanded on the array, VPLEX must recognize the new size of the volume.This may require a rescan or refresh within the VPLEX management interface1.
Virtual Volume Expansion: After VPLEX recognizes the new size of the storage volume, the virtual volume can then be expanded to utilize the additional space.This is done within the VPLEX management interface, where the virtual volume is configured to include the additional capacity1.
Storage Volume Method: The storage volume expansion method is distinct from other methods like concatenation, extent expansion, or RAID-C expansion, which involve different approaches to increasing virtual volume size within VPLEX itself1.
By expanding the storage volume on the array first, administrators can ensure that the additional capacity is available for use by VPLEX, allowing for the seamless expansion of virtual volumes to accommodate growing data needs.
What happens to global cache size if a director fails and is removed from the cluster?
Options:
Increases
Decreases
Suspends
Remains as-is
Answer:
BExplanation:
When a director fails and is removed from a VPLEX cluster, the global cache size decreases. This is because each director contributes to the total global cache available in the VPLEX cluster. Here’s the explanation:
Global Cache: The global cache in a VPLEX system is a shared resource that is used by all directors in the cluster to cache data for improved performance1.
Director Contribution: Each director within the VPLEX cluster has its own local cache, which collectively forms the global cache.When a director is operational, its cache is part of the global cache pool1.
Director Failure: If a director fails, its cache is no longer available to the cluster.As a result, the total size of the global cache is reduced by the amount that was contributed by the failed director1.
Removal from Cluster: When the failed director is physically removed from the cluster, its cache is permanently removed from the global cache pool, resulting in a decrease in the total global cache size1.
Impact on Performance: The reduction in global cache size may impact the performance of the VPLEX system, as there is less cache available for data storage and retrieval operations1.
System Architecture: VPLEX architecture allows for multiple director failures without loss of access to data down to a single director, but the global cache size will decrease with each director failure1.
By understanding the role of each director’s cache in contributing to the global cache, administrators can anticipate the effects of director failures on the overall performance of the VPLEX system.
When using VPLEX Metro, what is the supported round trip time between clusters?
Options:
30 ms
20 ms
15 ms
5 ms
Answer:
DExplanation:
When using VPLEX Metro, the supported round trip time (RTT) between clusters is 5 milliseconds (ms). This is the maximum latency that is supported to ensure proper synchronization and performance of the VPLEX Metro system.
VPLEX Metro: VPLEX Metro is a storage virtualization solution that allows for the creation of distributed virtual volumes across two geographically separated clusters1.
Round Trip Time (RTT): RTT is the time it takes for a signal to travel from one cluster to another and back again.It is a critical factor in the performance of distributed systems like VPLEX Metro1.
5 ms Limitation: The 5 ms RTT limitation is set to ensure that the clusters can maintain synchronization without significant performance degradation.Latencies higher than this can lead to issues with data consistency and application performance1.
Network Considerations: When planning a VPLEX Metro deployment, it is important to consider the network infrastructure and ensure that the RTT between clusters does not exceed the 5 ms threshold1.
Performance Impact: Adhering to the 5 ms RTT is crucial for maintaining the high availability and data mobility features of VPLEX Metro, as it affects the ability to perform real-time data mirroring and failover between clusters1.
By ensuring that the RTT between VPLEX Metro clusters does not exceed 5 ms, organizations can achieve the desired level of performance and reliability from their VPLEX Metro deployment.
What is the purpose of issuing the batch-migrate check-plan command?
Options:
Verifies that the source devices are not in a storage view
Verifies that the target devices have no virtual volumes configured
Determines if there is currently enough back-end bandwidth
Determines if the front-end IO rate is below the predetermined threshold
Answer:
CExplanation:
The batch-migrate check-plan command in Dell VPLEX is used to determine if there is currently enough back-end bandwidth to carry out a migration plan. This is crucial to ensure that the migration does not negatively impact the performance of other operations within the VPLEX environment.
Back-End Bandwidth: The back-end bandwidth refers to the data transfer capacity between the VPLEX and its connected storage arrays.Adequate back-end bandwidth is essential for migration operations to prevent bottlenecks1.
Migration Plan: Before executing a migration plan created by the batch-migrate create-plan command, it is important to check that the system has the necessary resources, such as sufficient back-end bandwidth, to support the migration without disruption1.
Command Function: The batch-migrate check-plan command analyzes the current system load and the expected load from the migration to determine if the migration can proceed without exceeding the system’s bandwidth capabilities1.
Ensuring Performance: By verifying the availability of back-end bandwidth, the command helps to ensure that the migration will not interfere with the normal operations of the VPLEX system, maintaining overall system performance1.
Pre-Migration Assessment: This command is part of the pre-migration assessment process, which is critical for planning and executing migrations effectively and efficiently within the VPLEX environment1.
The batch-migrate check-plan command is an important tool for administrators to validate the feasibility of migration plans and to ensure that migrations do not adversely affect the performance of the VPLEX system.
What is the maximum number of virtual volumes that can be placed into a single consistency group?
Options:
800
1000
900
1100
Answer:
AExplanation:
The maximum number of virtual volumes that can be placed into a single consistency group in a Dell VPLEX environment is800. This limit is set to ensure the manageability and performance of the consistency group within the VPLEX system.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
Consistency Group Capacity:A consistency group in VPLEX is a collection of virtual volumes that are managed together to maintain write-order fidelity, which is crucial for applications requiring strong consistency guarantees.
Limit Rationale:The limit of 800 virtual volumes is determined based on the VPLEX system’s ability to handle the overhead associated with managing a large number of volumes in a consistency group, including the coordination of writes and snapshots.
Operational Management:By capping the number of virtual volumes in a consistency group, VPLEX ensures that the group can be managed effectively without compromising the performance of the storage system.
Documentation Reference:The Dell VPLEX Operate Achievement documents outline the specifications and limitations of VPLEX systems, including the details of consistency group capacities1.
Best Practices:Administrators are advised to follow best practices and guidelines provided by Dell when configuring and managing consistency groups to avoid exceeding the recommended limits and to ensure optimal system performance.
It’s important for storage administrators to be aware of these limitations when planning and implementing VPLEX storage solutions to ensure they are operating within the supported configurations.
A new VPLEX system has been installed that uses ESRS. The firewall administrator has opened ports 25, 9010, and 5901 between VPLEX and ESRS. A support ticket is
logged. While trying to troubleshoot, the technical support engineer cannot access the GUI of VPLEX.
Which port needs to be opened on the firewall?
Options:
8080
443
3268
21
Answer:
BExplanation:
When setting up a VPLEX system that uses ESRS (EMC Secure Remote Services), it is essential to ensure that the correct ports are open to allow for various types of communication, including access to the VPLEX GUI. The port that needs to be opened on the firewall to allow access to the VPLEX GUI is port 443.
Port 443: This port is commonly used for HTTPS traffic, which is the protocol used for secure web communications.The VPLEX GUI is accessed over a web browser using HTTPS, hence the need for port 443 to be open1.
Firewall Configuration: The firewall administrator must configure the firewall to allow inbound and outbound traffic on port 443 to the VPLEX system’s IP address.This ensures that the technical support engineer and other users can access the VPLEX GUI through a secure connection1.
Troubleshooting Access Issues: If the technical support engineer cannot access the VPLEX GUI, one of the first steps in troubleshooting is to check the firewall settings to confirm that the necessary ports, including port 443, are open1.
ESRS Communication: While ports 25, 9010, and 5901 are important for ESRS communication and other services, they do not facilitate access to the VPLEX GUI.Port 25 is typically used for SMTP email services, port 9010 may be used for internal services, and port 5901 could be used for VNC or other remote access protocols1.
Secure Access: Opening port 443 not only allows access to the VPLEX GUI but also ensures that the communication is encrypted and secure, protecting sensitive data and system configurations1.
By opening port 443 on the firewall, the company ensures secure and reliable access to the VPLEX GUI for administration, monitoring, and troubleshooting purposes.
Which type of statistics is used to track latencies, determine median, mode, percentiles, minimums, and maximums?
Options:
Buckets
Counters
Monitors
Readings
Answer:
AExplanation:
In the context of Dell VPLEX Operate, the type of statistics used to track latencies and determine statistical measures such as median, mode, percentiles, minimums, and maximums is referred to as “buckets.” Buckets are a statistical method used to group data points into ranges or “buckets” to analyze the distribution and performance characteristics over time1.
Buckets: Buckets are used in performance monitoring to categorize data points into defined ranges.This allows for a detailed analysis of how often data points fall within certain latency ranges, which is essential for understanding system performance1.
Latency Tracking: By using buckets, VPLEX can track the latency of operations over time.This helps in identifying trends, such as increased latencies that may indicate potential performance issues1.
Statistical Measures: Buckets enable the calculation of statistical measures like median, mode, percentiles, minimums, and maximums.These measures provide insights into the typical and extreme values of latencies experienced by the system1.
Performance Analysis: The use of buckets is crucial for performance analysis, as it helps administrators understand the behavior of the system under different load conditions and during various operational scenarios1.
Monitoring Tools: VPLEX provides monitoring tools that utilize buckets to present latency and other performance-related statistics in a way that is meaningful and actionable for system administrators1.
By leveraging buckets to track and analyze latencies and other performance metrics, VPLEX administrators can gain a comprehensive understanding of system behavior and make informed decisions to optimize performance and address any issues that arise.
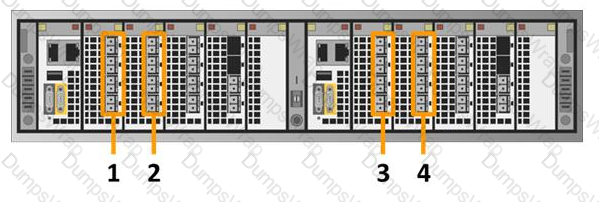
Which number in the exhibit highlights the Director-A back-end ports?
Options:
1
2
4
3
Answer:
DExplanation:
The image provided appears to be a diagram or photograph of the back panel of a Dell VPLEX system. The back panel is divided into two sections, each presumably representing a director module. Each section has a set of ports highlighted and labeled with numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4. According to the question provided, which asks to identify the Director-A back-end ports from the options given (OA 1, OB 2, OC 4, OD 3), the verified answer is number 3. This can be inferred because typically in such systems, ‘A’ might refer to the first director or left side when looking at the back panel.
Which type of VPLEX statistic provides an instantaneous value that displays CPU utilization and memory utilization?
Options:
Buckets
Journal Lag
Readings
Counters
Answer:
DExplanation:
Questions no:Q29
In VPLEX, the type of statistic that provides an instantaneous value displaying CPU utilization and memory utilization is referred to as “counters.” These counters offer real-time metrics that reflect the current state of the system’s resources.
Counters: Counters are a type of statistic in VPLEX that provide immediate, real-time values for various system metrics, including CPU and memory utilization.They are used to monitor the current performance and resource usage of the VPLEX system1.
CPU Utilization: CPU utilization counters show the percentage of CPU resources currently being used by the VPLEX directors.This information is crucial for understanding the load on the system and for capacity planning1.
Memory Utilization: Memory utilization counters display the amount of RAM currently in use by the VPLEX system.This helps administrators monitor memory consumption and ensure that the system has enough memory to operate efficiently1.
Monitoring and Management: Counters are an essential tool for the ongoing monitoring and management of a VPLEX environment.They help administrators identify potential performance bottlenecks and take proactive measures to optimize system performance1.
Instantaneous Values: Unlike other statistics that may provide averages or aggregated data over a period, counters offer instantaneous snapshots of resource usage, making them ideal for real-time monitoring1.
By utilizing counters, VPLEX administrators can gain immediate insights into the system’s CPU and memory utilization, enabling them to maintain optimal performance and address issues as they arise.

