Ericsson Certified Associate - IP Networking Questions and Answers
What is used for Ethernet loop avoidance?
Options:
Time-to-Live (TTL)
Poison-Reverse
Split-Horizon
Spanning-Tree
Answer:
DExplanation:
Spanning-Tree is used for Ethernet loop avoidance. Spanning-Tree is a protocol that prevents loops in Ethernet networks by creating a logical tree topology of the network switches. Spanning-Tree blocks some of the redundant links between switches to ensure that there is only one active path between any two nodes in thenetwork. Spanning-Tree also detects and recovers from link failures by activating alternative paths when needed56.
References: Network loops and loop avoidance - Medium, Spanning Tree Protocol - Wikipedia
Which two statements are true regarding the LSP? (Choose two.)
Options:
The LSP refers to a specific label assigned to a packet by the LSR for a destination.
The LSP refers to a sequence of routers that add. remove, or change label values along the path.
The LSP refers to a sequence of routers that forward the MPLS packet based on labels.
The LSP refers to a sequence of routers that add, remove, or change label values based on the destination MAC address.
Answer:
B, CExplanation:
Two statements that are true regarding the LSP are:
- The LSP refers to a sequence of routers that forward the MPLS packet based on labels. An LSP is a Label Switched Path, which is a path through an MPLS network that is established by signaling protocols such as LDP or RSVP-TE. An LSP consists of a sequence of routers (called Label Switching Routers or LSRs) that forward packets based on labels rather than IP addresses. Labels are short fixed-length identifiers that are attached to packets at the ingress router and removed at the egress router. Labels can be swapped or popped at intermediate routers according to their label forwarding tables78.
- The LSP refers to a sequence of routers that add, remove, or change label values along the path. As mentioned above, an LSP consists of a sequence of routers that forward packets based on labels. Along the path, different routers may perform different operations on the labels depending on their role and configuration. The ingress router adds one or more labels to the packet before sending it into the MPLS network. The egress router removes all labels from the packet before sending it out of the MPLS network. The intermediate routers may swap one label with another label according to their label forwarding tables. This process is called label switching78.
References: MPLS Fundamentals: 3 - MPLS Packet Forwarding, Multiprotocol Label Switching - Wikipedia
What is an important difference between OSPF and IS-IS?
Options:
OSPF runs directly on IP, while IS-IS runs directly on Ethernet.
OSPF is a link state protocol, while IS-IS is a distance vector protocol.
OSPF runs directly on Ethernet, while IS-IS runs directly on IP.
OSPF is a distance vector protocol, while IS-IS is a link state protocol.
Answer:
AExplanation:
OSPF runs directly on IP, while IS-IS runs directly on Ethernet. This means that OSPF uses IP addresses to identify routers and links, while IS-IS uses MAC addresses or other link-layer identifiers. OSPF also requires an IP header for each packet, while IS-IS does not. Both OSPF and IS-IS are link state protocols, which means that they flood information about the network topology to all routers in the same area or domain. References: Ericsson IP Networking - Routing Protocols, Ericsson Router 6000 Series - Ericsson
An operator wants to ensure that they can differentiate their traffic types for the purpose of prioritization in their Ethernet LAN and IP/MPLS backbone.
Which three fields would be used? (Choose three.)
Options:
Traffic Class (TC)
ECN
DSCP
VID
PCP
Answer:
A, C, EExplanation:
To differentiate traffic types for the purpose of prioritization in their Ethernet LAN and IP/MPLS backbone, an operator can use the following three fields:
- Traffic Class (TC): This is a 3-bit field in the MPLS label that can be used to indicate the priority or class of service (CoS) of the packet. The TC field can be mapped to the DSCP field in the IP header or the PCP field in the Ethernet header. The TC field can be used by MPLS routers to apply different per-hop behaviors (PHBs) such as queuing, scheduling, and dropping policies to different traffic classes12.
- DSCP: This is a 6-bit field in the IP header that can be used to mark packets according to the differentiated services (DiffServ) model. The DSCP field can indicate the per-hop behavior (PHB) that the packet should receive at each router along its path. The DSCP field can be mapped to the TC field in the MPLS label or the PCP field in the Ethernet header. The DSCP field can be used by IP routers to provide QoS for different traffic types34.
- PCP: This is a 3-bit field in the Ethernet header that can be used to mark packets according to the IEEE 802.1Q standard. The PCP field can indicate the priority or class of service (CoS) of the packet on an Ethernet LAN. The PCP field can be mapped to the TC field in the MPLS label or the DSCP field in the IP header. The PCP field can be used by Ethernet switches to provide QoS for different traffic types56.
References: MPLS Traffic Engineering - DiffServ-Aware Traffic Engineering, MPLS Traffic Engineering - DiffServ-Aware Traffic Engineering Configuration Guide, Differentiated services - Wikipedia, DSCP and Precedence Values - Cisco, 802.1Q VLAN IDs and Ethernet Interface Types - Juniper Networks, Introduction to Virtual LANs (VLANs) and Tagging - Ubiquiti Support and Help Center
Which conceptual table created by routing protocols is used when processing an IP packet?
Options:
management information base
label information base
traffic engineering data base
forwarding information base
Answer:
DExplanation:
The conceptual table created by routing protocols that is used when processing an IP packet is the forwarding information base (FIB). The FIB is a table that contains the bestroutes to reach each destination network prefix, along with the outgoing interface and the next-hop address for each route. The FIB is derived from the routing information base (RIB), which is a table that contains all the routes learned from different routing protocols and sources. The FIB is used by the router to make fast forwarding decisions for each incoming packet, based on its destination address12.
References: Security Hardening Checklist Guide for Cisco Routers/Switches in 10 Steps, VLAN - Wikipedia
Which two statements are true about router node hardening? (Choose two.)
Options:
LDAP, using the TLS protocol, should be implemented for remote logging.
Any unnecessary services should be disabled within each context.
IPsec should be implemented to secure IGP routing protocols.
Enabling syslog ensures system events are logged to a remote server.
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
Two statements that are true about router node hardening are:
- Any unnecessary services should be disabled within each context. Router node hardening is a process of securing a router from unauthorized access and attacks by applying various configurations and policies. One of these configurations is to disable any services that are not needed for the router’s functionality or purpose, such as telnet, ftp, http, etc. This reduces the attack surface of the router and prevents potential exploits of these services91.
- Enabling syslog ensures system events are logged to a remote server. Syslog is a protocol that allows a router to send system messages and events to a remote server for logging and analysis. By enabling syslog on a router, network administrators can monitor the router’s activity and performance, troubleshoot problems, detect anomalies, and audit security events101.
References: Cisco Router Hardening Step-by-Step | SANS Institute, Security Hardening Checklist Guide for Cisco Routers/Switches in 10 Steps, CCNA SEC: Router Hardening - Cisco Press
Which statement accurately defines an Autonomous System (AS)?
Options:
An AS is a set of routers under a single administration, using an interior gateway protocol and common metrics to route packets within the AS.
An AS is a group of networks directly connected to each other that can distribute eBGP information using directly established links.
An AS is a network that is capable of autonomously forwarding packets, regardless of direct or indirect connectivity to the Internet.
An AS is a collection of IS-IS routes imported into BGP and presented in such a way that networks connected to the AS have a global overview of the network.
Answer:
AExplanation:
The statement that accurately defines an Autonomous System (AS) is that an AS is a set of routers under a single administration, using an interior gateway protocol and common metrics to route packets within the AS. An AS is a logical grouping of networks that share a common routing policy and operate under a single administrative authority. An AS can be a single network or a collection of networks that are interconnected by routers. An AS uses an interior gateway protocol (IGP), such as OSPF or IS-IS, to exchange routing information within the AS. An IGP uses common metrics, such as hop count or bandwidth, to determine the best path to each destination within the AS. An AS also has a unique number assigned by IANA, called an AS number (ASN), which identifies the AS in interdomain routing .
References: [Autonomous system (Internet) - Wikipedia], [What Is an Autonomous System? - Cisco]
A network operator wants to make sure voice data is prioritized.
In this scenario, to which Ethernet traffic class should it be assigned.
Options:
0
2
4
6
Answer:
DExplanation:
A network operator who wants to make sure voice data is prioritized should assign it to Ethernet traffic class 6. Ethernet traffic class is a term used to refer to the priority code point (PCP) field in the VLAN header of an Ethernet frame. The PCP field is a 3-bit field that can encode up to eight different priority levels, ranging from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest). The PCP values can be mapped to different types of traffic according to their QoS requirements. The recommended mapping is as follows :
- PCP 0: Best effort (default)
- PCP 1: Background
- PCP 2: Spare
- PCP 3: Excellent effort
- PCP 4: Controlled load
- PCP 5: Video
- PCP 6: Voice
- PCP 7: Network control
Voice data is a type of real-time traffic that requires the highest priority and lowest delay in the network. Therefore, it should be assigned to PCP 6, which corresponds to Ethernet traffic class 6 .
References: [IEEE 802.1Q - Wikipedia], [What is “link aggregation” and how does it benefit your network? | PC Gamer]
Which statement about IPv6 is correct?
Options:
An interface can only be configured with one IPv6 address.
Broadcast has been replaced with multicast.
There are four billion available addresses.
Addresses are not hierarchical and are assigned at random.
Answer:
BExplanation:
The statement about IPv6 that is correct is that broadcast has been replaced with multicast. IPv6 is the most recent version of Internet Protocol (IP), which provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 has several improvements over IPv4, such as a larger address space, simplified header format, enhanced security, and better support for mobility and QoS.One of the changes in IPv6 is that it does not support broadcast, which is a method of sending a packet to all nodes on a network segment. Instead, IPv6 uses multicast, which is a method of sending a packet to a group of nodes that have joined a multicast address34.
References: IPv6 - Wikipedia, What Is IPv6? - Cisco
What is a reason for using VLANs in an IP network?
Options:
to implement virtual routing
to enable MAC address learning on a router port
to isolate hosts within the same IP subnet
to isolate hosts across multiple IP subnets
Answer:
CExplanation:
A reason for using VLANs in an IP network is to isolate hosts within the same IP subnet. VLANs (Virtual LANs) are logical grouping of devices in the same broadcast domain. VLANs are usually configured on switches by placing some interfaces into one broadcast domain and some interfaces into another. Each VLAN acts as a subgroup of the switch ports in an Ethernet LAN. VLANs allow network administrators to group hosts together even if the hosts are not directly connected to the same network switch. By using VLANs, hosts within the same IP subnet can be separated into different broadcast domains, which enhances security, reduces network congestion, and simplifies network management78.
References: 8 Different Types of VLANs in TCP/IP Networks, What is a VLAN? - Study-CCNA
How many different priorities are available to use in a VLAN header?
Options:
8
16
32
64
Answer:
AExplanation:
There are 8 different priorities available to use in a VLAN header. A VLAN header is a 4-byte field that is inserted into an Ethernet frame to indicate the VLAN membership and priority of the frame. The VLAN header consists of two subfields: the tag protocol identifier (TPID) and the tag control information (TCI). The TCI subfield contains three subfields: the priority code point (PCP), the drop eligible indicator (DEI), and the VLAN identifier (VID). The PCP subfield is a 3-bit field that specifies the priority level of the frame, ranging from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest). The PCP values can be used to implement quality of service (QoS) mechanisms on bridges and switches12.
References: HTML rt Tag - W3Schools, VLAN 0 Priority Tagging Support - Cisco
Which two label actions are performed by a P router? (Choose two.)
Options:
push
php
drop
swap
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
A P router is a provider router that is part of the service provider’s core network in an MPLS environment. A P router does not have any customer routes or VPN information, but only has information about how to reach other P routers and PE routers in the same MPLS domain. A P router performs label switching, which means that it forwards labeled packets based on their top label in the label stack. A P router can perform two possible label actions:
- Swap: The P router replaces the incoming label with a new label that corresponds to the next hop along the label-switched path (LSP). The new label is determined by looking up the label forwarding information base (LFIB) based on the incoming label and interface.
- PHP: The P router removes the top label from the packet at the penultimate hop before reaching the egress PE router. This is done to avoid an extra lookup on the egress PE router, which can forward the packet based on its IP header or another label in the stack.
A P router does not perform push or drop actions on labels. A push action means adding one or more labels to the packet, which is done by an ingress PE router when initiating an LSP. A drop action means discarding a packet, which is done by any router when there is no matching entry in its LFIB or routing table. References: Provider (P) Router in IP MPLS Network - Cisco Community, MPLS Fundamentals: Forwarding Labeled Packets - Cisco Press, MPLS Label Switching | MPLS Operation | Push, Swap,Push ⋆ IPCisco
Review the exhibit.
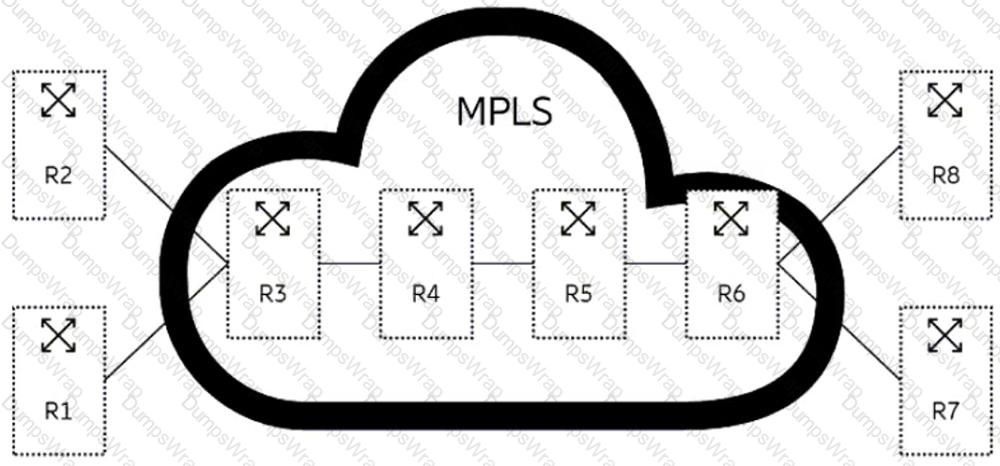
In the exhibit, which action is performed by router R3 for traffic arriving from router R2 towards router R4?
Options:
push
pop
swap
PHP
Answer:
DExplanation:
In the exhibit, the action performed by router R3 for traffic arriving from router R2 towards router R4 is PHP, which stands for penultimate hop popping. PHP is a process in which the penultimate hop router (the router before the egress router) removes the top label from an MPLS packet before forwarding it to the egress router. This reduces the label stack depth of the packet and relieves the egress router from performing a label lookup operation. In the exhibit, router R3 is the penultimate hop for traffic arriving from router R2 towards router R4. Router R3 will perform a PHP operation, removing the top label from the incoming packet before forwarding it to router R478.
References: PHP Tutorial - W3Schools, PHP: Downloads
What are two roles of the DHCP protocol in a network? (Choose two.)
Options:
It is used by hosts to obtain the IP address and other parameters from the DHCP server.
It is used to inform hosts about the default gateway.
It provides information about the number of hops between the source and the destination.
It provides the authorization function to the network.
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
Two roles of the DHCP protocol in a network are:
- It is used by hosts to obtain the IP address and other parameters from the DHCP server. DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, which is a protocol that provides automatic and centralized management of IP addresses and other network configuration parameters for devices connected to a network. A host that needs an IP address can send a request to a DHCP server, which will assign an available IP address from a pool and lease it to the host for a certain period of time34.
- It is used to inform hosts about the default gateway. The default gateway is the IP address of the router that connects the host to other networks. The default gateway is one of the parameters that can be delivered by the DHCP server to the host, along with other parameters such as subnet mask, DNS server, domain name, etc. The host can use the default gateway to send packets to destinations outside of its local network34.
References: What Is DHCP? (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - Lifewire, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - Wikipedia
Which route type is restricted in an OSPF stub area?
Options:
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
Type 5
Answer:
DExplanation:
The route type that is restricted in an OSPF stub area is type 5. Type 5 LSAs are external LSAs that are generated by ASBRs to advertise routes from other routing domains or protocols into OSPF. Type 5 LSAs are flooded throughout the OSPF domain by default, except in stub areas. Stub areas are special OSPF areas that block type 5 LSAs from entering the area in order to reduce the size of the LSDB and the routing table. Stub areas only receive information about intra-area routes (type 1 and 2 LSAs), inter-area routes (type 3 LSAs), and a default route (type 3 LSA with destination 0.0.0.0/0) from the ABRs910.
References: Introduction to OSPF Stub Areas - NetworkLessons.com, What Are OSPF Areas and Virtual Links? - Cisco
In an Ericsson Router 6000, which command is used to begin making changes to the router settings?
Options:
capabilities
commit
configure
set metric
Answer:
CExplanation:
The command that is used to begin making changes to the router settings in an Ericsson Router 6000 is configure. This command enters the configuration mode, where various commands can be used to modify the router parameters, such as interfaces, protocols, services, security, etc. To exit the configuration mode, the command end can be used. To save the changes made in the configuration mode, the command commit can be used56.
References: Router 6000 Series - Ericsson, Ericsson Router 6000 series (6471/6672/6675) Commands for 2G/3G/4G/5G technologies… - YouTube
What is the purpose of the RT attribute?
Options:
to identify the destination VPN on the efress PE
to prevent OSPF routing loops in an L3VPN environment
to indicate an MPLS LSP as the next hop routing target
to request BGP neighbors to avoid routing through a private AS
Answer:
AExplanation:
The purpose of the RT attribute is to identify the destination VPN on the egress PE. RT stands for route target, which is a BGP extended community attribute that is used in MPLS VPNs. RT is attached to VPN routes by the ingress PE router and is used to control the import and export of routes between different VPNs. The egress PE router uses the RT value to determine which VPN routes belong to which VPN customers and installs them in the appropriate VRF table56.
References: IP Routing: BGP Configuration Guide - BGP-RT and VPN … - Cisco,
Which two statements are true about priority queuing (PQ)? (Choose two.)
Options:
Traffic in the highest priority queue will experience the least amount of jitter and delay compared to traffic in the other queues.
Traffic in the highest priority queue is only reserved for voice traffic.
Traffic in lower priority queues can be starved of bandwidth.
Traffic in all queues are always guaranteed a minimum bandwidth.
Answer:
A, CExplanation:
Priority queuing (PQ) is a queuing method that establishes four interface output queues that serve different priority levels: high, medium, normal, and low. Traffic in the highest priority queue will experience the least amount of jitter and delay compared to traffic in the other queues, because PQ always services the higher-priority queues first. However, this can also cause traffic in lower priority queues to be starved of bandwidth, especially if the highest priority queue is oversubscribed. Traffic in the highest priority queue is not only reserved for voice traffic, but can also include network control and routing traffic. Traffic in all queues are not always guaranteed a minimum bandwidth, because PQ does not provide any bandwidth reservation mechanism. References: Quality of Service (QoS) Queues and Queuing Explained, Chapter: Configuring Priority Queueing - Cisco

