FCP - FortiManager 7.4 Administrator Questions and Answers
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part o an ADOM-level database on FortiManager?
Push updates are failing on a FortiGate device that is located behind a NAT device. Which two settings should the administrator check? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
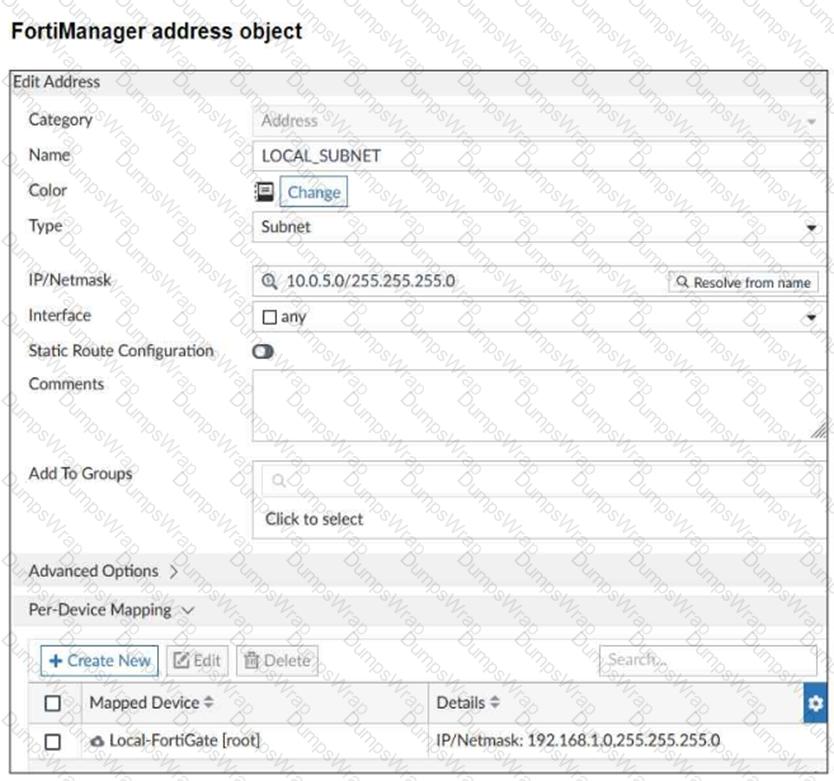
An administrator has created a firewall address object that is used in multiple policy packages for multiple FortiGate devices in an ADOM.
After the installation operation is performed, which IP/netmask will be installed on Local-FortiGate for theLOCAL_SUBNETfirewall address object?
Exhibit.

Given the configuration shown in the exhibit, what are two results from this configuration? {Choose two.)
An administrator created a new ADOM named Training for FortiGate devices only, and added the root FortiGate device of a Security Fabric group to the Training ADOM.
Given the administrator's actions, which statement correctly describes the expected result for the downstream devices in the Security Fabric?
What does a policy package status of Never Installed indicate?
Exhibit.
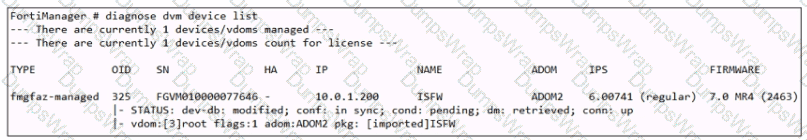
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
An administrator created a new global policy package that includes header and footer policies and then assigned it to an ADOM. What are two outcomes of this action? (Choose two.)
An administrator has assigned a global policy package to custom ADOM1. Then the administrator creates a new policy package. Fortinet. in the custom ADOM1. What happens to the Fortinet policy package when it is created?
Refer to the exhibit.
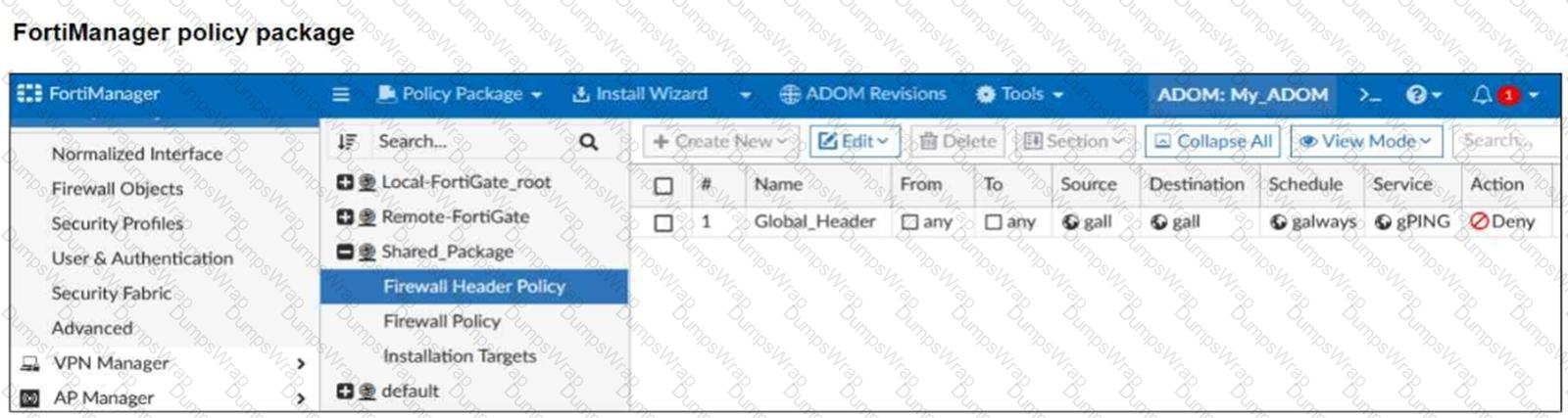
A service provider administrator has assigned a global policy package to a managed customer ADOM namedMy_ADOM, which has four policy packages. The customer administrator has access only toMy_ADOM.
How can the customer or service provider administrators remove the global header policy from the policy package namedShared_Package?
Refer to the exhibit.
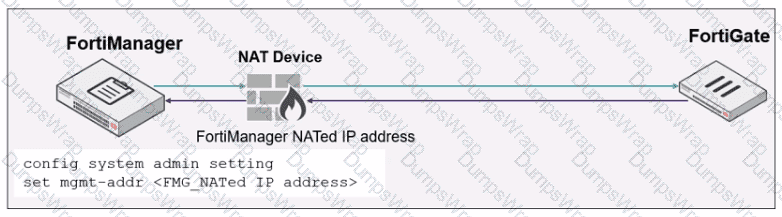
An administrator is about to add the FortiGate device to FortiManager using the discovery process.
FortiManager is operating behind a NAT device, and the administrator configured the FortiManager NATed IP address under the FortiManager system administration settings.
What is the expected result?
Which API method is used to create objects or overwrite existing ones?
Which statement about the policy lock feature on FortiManager is true?
An administrator has enabled Service Access on FortiManager. What is the purpose of Service Access on the FortiManager interface?
What are two outcomes of ADOM revisions? (Choose two.)
An administrator is in the process of copying a system template profile between ADOMs by running the following command: execute fmprofile import-profile ADOM2 3547 /tmp/myfile Where does this command import the system template profile from?
An administrator, Trainer, who is assigned the Super_User profile, is trying to approve a workflow session that was submitted by another administrator, Student. However, Trainer is unable to approve the workflow session.
What can prevent an admin account that has Super_User rights over the device from approving a workflow session?
If both FortiManager and FortiGate are behind NAT devices, what are the two expected results? (Choose two.)

