Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 Questions and Answers
Exhibit.
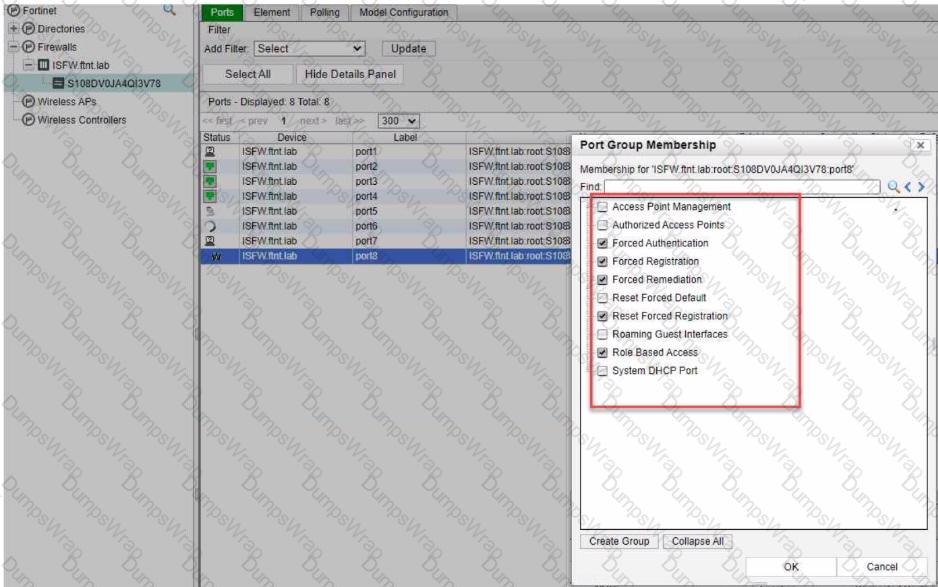
Which port group membership should you enable on FortiNAC to isolate rogue hosts'?
Options:
Forced Authentication
Forced Registration
Forced Remediation
Reset Forced Registration
Answer:
CExplanation:
In FortiNAC, to isolate rogue hosts, you should enable the:
- C. Forced Remediation: This port group membership is used to isolate hosts that have been determined to be non-compliant or potentially harmful. It enforces a remediation process on the devices in this group, often by placing them in a separate VLAN or network segment where they have limited or no access to the rest of the network until they are remediated.
The other options are not specifically designed for isolating rogue hosts:
- A. Forced Authentication: This is used to require devices to authenticate before gaining network access.
- B. Forced Registration: This group is used to ensure that all devices are registered before they are allowed on the network.
- D. Reset Forced Registration: This is used to reset the registration status of devices, not to isolate them.
Which three statements are true about a persistent agent? (Choose three.)
Options:
Agent is downloaded and run from captive portal
Supports advanced custom scans and software inventory.
Can apply supplicant configuration to a host
Deployed by a login/logout script and is not installed on the endpoint
Can be used for automatic registration and authentication
Answer:
B, C, EExplanation:
A persistent agent is an application that works on Windows, macOS, or Linux hosts to identify them to FortiNAC Manager and scan them for compliance with an endpoint compliance policy. A persistent agent can support advanced custom scans and software inventory, apply supplicant configuration to a host, and be used for automatic registration and authentication. References :=
- Persistent Agent
- Persistent Agent on Windows
- Using the Persistent Agent
Which method is used to install passive agent on an endpoint?
Options:
Deployed by using a login/logout script
Agent is downloaded from Playstore
Agent is downloaded and run from captive portal
Installed by user or deployment tools
Answer:
DExplanation:
The method used to install a passive agent on an endpoint is:
- D. Installed by user or deployment tools: Passive agents are typically installed on endpoints either manually by users or automatically through deployment tools used by the organization.
The other options do not accurately describe the installation of passive agents:
- A. Deployed by using a login/logout script: This is not the standard method for deploying passive agents.
- B. Agent is downloaded from Playstore: This is more relevant for mobile devices and does not represent the general method for passive agent installation.
- C. Agent is downloaded and run from captive portal: This method is not typically used for installing passive agents.
References:
- FortiNAC Agent Deployment Guide.
- Installation Methods for Passive Agents in FortiNAC.
Which three methods can you use to trigger layer 2 polling on FortiNAC? (Choose three)
Options:
Polling scripts
Link traps
Manual polling
Scheduled tasks
Polling using API
Answer:
A, C, DExplanation:
To trigger layer 2 polling on FortiNAC, the three methods are:
- A. Polling scripts: These are scripts configured within FortiNAC to actively poll the network at layer 2 to gather information about connected devices.
- C. Manual polling: This involves manually initiating a polling process from the FortiNAC interface to gather current network information.
- D. Scheduled tasks: Polling can be scheduled as regular tasks within FortiNAC, allowing for automated, periodic collection of network data.
The other options are not standard methods for layer 2 polling in FortiNAC:
- B. Link traps: These are more related to SNMP trap messages rather than layer 2 polling.
- E. Polling using API: While APIs are used for various integrations, they are not typically used for initiating layer 2 polling in FortiNAC.
References:
- FortiNAC Layer 2 Polling Documentation.
- Configuring Polling Methods in FortiNAC.
What are two functions of NGFW in a ZTA deployment? (Choose two.)
Options:
Acts as segmentation gateway
Endpoint vulnerability management
Device discovery and profiling
Packet Inspection
Answer:
A, CExplanation:
NGFW stands for Next-Generation Firewall, which is a network security device that provides advanced features beyond the traditional firewall, such as application awareness, identity awareness, threat prevention, and integration with other security tools. ZTA stands for Zero Trust Architecture, which is a security model that requires strict verification of the identity and context of every request before granting access to network resources. ZTA assumes that no device or user can be trusted by default, even if they are connected to a corporate network or have been previously verified.
In a ZTA deployment, NGFW can perform two functions:
- Acts as segmentation gateway: NGFW can act as a segmentation gateway, which is a device that separates different segments of the network based on security policies and rules. Segmentation can help isolate and protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized or malicious access, as well as reduce the attack surface and contain the impact of a breach. NGFW can enforce granular segmentation policies based on the identity and context of the devices and users, as well as the applications and services they are accessing. NGFW can also integrate with other segmentation tools, such as software-defined networking (SDN) and microsegmentation, to provide a consistent and dynamic segmentation across the network.
- Device discovery and profiling: NGFW can also perform device discovery and profiling, which are processes that identify and classify the devices that are connected to the network, as well as their attributes and behaviors. Device discovery and profiling can help NGFW to apply the appropriate security policies and rules based on the device type, role, location, health, and activity. Device discovery and profiling can also help NGFW to detect and respond to anomalous or malicious devices that may pose a threat to the network.
References: =
Some possible references for the answer and explanation are:
What is a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)? | Fortinet : What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)? | Fortinet : Zero Trust Architecture Explained: A Step-by-Step Approach : The Most Common NGFW Deployment Scenarios : Sample Configuration for Post vWAN Deployment
What happens when FortiClient EMS is configured as an MDM connector on FortiNAC?
Options:
FortiNAC sends the hostdata to FortiClient EMS to update its host database
FortiClient EMS verifies with FortiNAC that the device is registered
FortiNAC polls FortiClient EMS periodically to update already registered hosts in FortiNAC
FortiNAC checks for device vulnerabilities and compliance with FortiClient
Answer:
CExplanation:
When FortiClient EMS is configured as an MDM connector on FortiNAC, it allows FortiNAC to obtain host information from FortiClient EMS and use it for network access control. FortiNAC polls FortiClient EMS periodically (every 5 minutes by default) to update already registered hosts in FortiNAC. This ensures that FortiNAC has the latest host data from FortiClient EMS, such as device type, OS, IP address, MAC address, hostname, and FortiClient version. FortiNAC can also use FortiClient EMS as an authentication source for devices that have FortiClient installed. FortiNAC does not send any data to FortiClient EMS or check for device vulnerabilities and compliance with FortiClient123. References := 1: MDM Service Connectors | FortiClient EMS Integration 2: FortiClient EMS Device Integration|FortiNAC 9.4.0 - Fortinet Documentation 3: Technical Tip: Integration with FortiClient EMS
Exhibit.
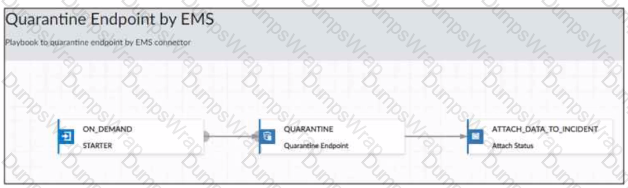
Which statement is true about the FortiAnalyzer playbook configuration shown in the exhibit?
Options:
The playbook is run on a configured schedule
The playbook is run when an incident is created that matches the filters.
The playbook is run when an event is created that matches the filters
The playbook is manually started by an administrator
Answer:
DExplanation:
The FortiAnalyzer playbook configuration shown in the exhibit indicates that:
- D. The playbook is manually started by an administrator: The "ON DEMAND" trigger in the playbook suggests that it is initiated manually, as opposed to being automated or scheduled. This typically means that an administrator decides when to run the playbook based on specific needs or incidents.
Exhibit.
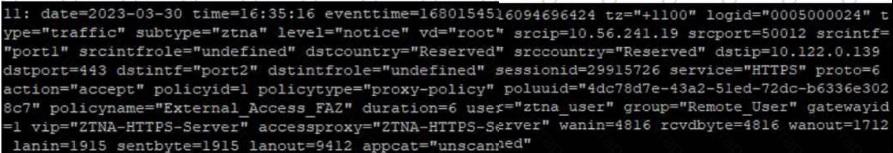
Based on the ZTNA logs provided, which statement is true?
Options:
The Remote_user ZTNA tag has matched the ZTNA rule
An authentication scheme is configured
The external IP for ZTNA server is 10 122 0 139.
Traffic is allowed by firewall policy 1
Answer:
AExplanation:
Based on the ZTNA logs provided, the true statement is:
- A. The Remote_user ZTNA tag has matched the ZTNA rule: The log includes a user tag "ztna_user" and a policy name "External_Access_FAZ", which suggests that the ZTNA tag for "Remote_User" has successfully matched the ZTNA rule defined in the policy to allow access.
The other options are not supported by the information in the log:
- B. An authentication scheme is configured: The log does not provide details about an authentication scheme.
- C. The external IP for ZTNA server is 10.122.0.139: The log entry indicates "dstip=10.122.0.139" which suggests that this is the destination IP address for the traffic, not necessarily the external IP of the ZTNA server.
- D. Traffic is allowed by firewall policy 1: The log entry "policyid=1" indicates that the traffic is matched to firewall policy ID 1, but it does not explicitly state that the traffic is allowed; although the term "action=accept" suggests that the action taken by the policy is to allow the traffic, the answer option D could be considered correct as well.
References:
- Interpretation of FortiGate ZTNA Log Files.
- Analyzing Traffic Logs for Zero Trust Network Access.
With the increase in loT devices, which two challenges do enterprises face? (Choose two.)
Options:
Bandwidth consumption due to added overhead of loT
Maintaining a high performance network
Unpatched vulnerabilities in loT devices
Achieving full network visibility
Answer:
C, DExplanation:
With the increase in IoT devices, enterprises face many challenges in securing and managing their network and data. Two of the most significant challenges are:
- Unpatched vulnerabilities in IoT devices (Option C): IoT devices are often vulnerable to cyber attacks due to their increased exposure to the internet and their limited computing resources. Some of the security challenges in IoT include weak password protection, lack of regular patches and updates, insecure interfaces, insufficient data protection, and poor IoT device management12. Unpatched vulnerabilities in IoT devices can allow hackers to exploit them and compromise the network or data. For example, the Mirai malware infected IoT devices by using default credentials and created a massive botnet that launched DDoS attacks on internet services2.
- Achieving full network visibility (Option D): IoT devices can generate a large amount of data that needs to be collected, processed, and analyzed. However, many enterprises lack the tools and capabilities to monitor and manage the IoT devices and data effectively. This can result in poor performance, inefficiency, and security risks. Achieving full network visibility means having a clear and comprehensive view of all the IoT devices, their status, their connectivity, their data flow, and their potential threats. This can help enterprises optimize their network performance, ensure data quality and integrity, and detect and prevent any anomalies or attacks3.
References := 1: Challenges in Internet of things (IoT) - GeeksforGeeks 2: Top IoT security issues and challenges (2022) – Thales 3: 7 challenges in IoT and how to overcome them - Hologram

