Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Questions and Answers
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
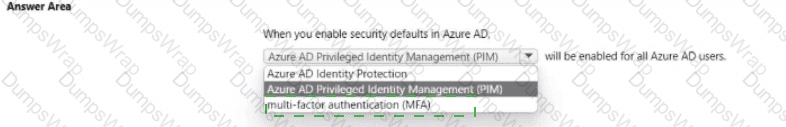
Explanation:
multi-factor authentication (MFA)
In Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Security defaults are a baseline of recommended identity protections that, when turned on, automatically apply tenant-wide. Microsoft’s guidance explains that security defaults “help protect your organization with preconfigured security settings” and specifically require that “all users register for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.” When enabled, the defaults enforce MFA challenges for users and admins during risky or sensitive operations, and they block legacy authentication protocols that can’t satisfy modern MFA requirements. Microsoft further notes that security defaults “provide basic identity security mechanisms… such as requiring multi-factor authentication for all users and administrators.” These controls are designed to raise the overall security posture without custom policy design, which is ideal for small and medium organizations or any tenant that hasn’t yet implemented Conditional Access. Therefore, when you enable security defaults, MFA is enabled for all Azure AD users, driving strong authentication as the default and reducing account-takeover risk stemming from password-only sign-ins.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft Entra Conditional Access (CA) evaluates signals from the user, device, location, and risk to make access decisions. The platform explicitly notes that CA decisions occur after primary sign-in: “Conditional Access policies are enforced after the first-factor authentication has been completed.” This means a user must successfully present their initial credentials (e.g., password, Windows Hello, FIDO2) before the CA engine evaluates policy logic. Therefore, the statement that CA is evaluated before a user is authenticated is not correct.
Regarding scoping, CA can target ordinary and privileged identities. The assignment options allow administrators to aim policies at users, groups, and directory roles: “You can include or exclude users and groups… [and] include or exclude specific Azure AD directory roles from a Conditional Access policy.” Because Global Administrator is a directory role, policies can be applied to those accounts (with Microsoft’s best-practice guidance to maintain at least one excluded break-glass account to prevent lockout).
For signals/conditions, CA supports device platform filtering. The documented device platform condition states: “This condition is based on the operating system platform of the device… iOS, Android, Windows, macOS (and others).” Administrators commonly use this to require different controls (like MFA or compliant device) based on Android or iOS.
Putting these together:
CA can apply to Global Administrators (Yes).
CA is evaluated after first-factor authentication (No to “before”).
Device platform (e.g., Android/iOS) is a valid CA signal (Yes).
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft Defender for Identity (formerly Azure ATP) is designed to protect on-premises identity infrastructures by analyzing signals from Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). In Microsoft’s SCI guidance, Defender for Identity is described as a “cloud service that uses sensors installed on your domain controllers to monitor and analyze user activities and information across your on-premises Active Directory.” The sensors “collect authentication, replication, and other security-relevant events and network traffic,” enabling analytics to detect techniques such as Pass-the-Hash, Pass-the-Ticket, Golden Ticket, reconnaissance, lateral movement, and domain dominance. The product’s purpose is to surface advanced threats, compromised identities, and malicious insider actions by continuously profiling and learning from AD DS behavior and security events.
While Defender for Identity integrates with other Microsoft security solutions (for example, Microsoft 365 Defender and Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps) to enrich investigations, it does not rely on Azure Active Directory (Microsoft Entra ID) signals for its core detections, nor does it collect telemetry from Azure AD Connect itself. Instead, its foundational telemetry source is on-premises AD DS domain controllers via lightweight sensors, which provide the deep authentication and directory-service context required to identify sophisticated identity-based attacks in hybrid environments.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
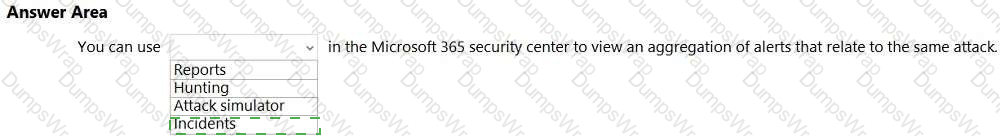
Explanation:

In Microsoft 365 Defender (Microsoft 365 security center), Incidents are designed to consolidate and correlate security signals so analysts can see the full scope of an attack. Microsoft’s documentation explains that an incident is “a collection of related alerts that, when viewed together, provide a richer context for the attack and its impact.” The service “automatically groups alerts that are likely to be associated with the same threat activity,” which allows security teams to investigate a single incident rather than many fragmented alerts. Microsoft further notes that incidents “aggregate alerts, affected assets (users, devices, mailboxes), evidences, and entities into one view,” helping analysts triage, investigate, and remediate more efficiently.
This is distinct from other areas in the portal: Reports provide trend and posture reporting; Hunting offers proactive, query-based threat hunting across raw data; and Attack simulator (in Defender for Office 365) is used to run training and awareness simulations (e.g., phishing), not to aggregate real alerts. Therefore, when you need to “view an aggregation of alerts that relate to the same attack” in the Microsoft 365 security center, the correct place is Incidents, which presents the correlated attack story and enables end-to-end response and remediation from a single, consolidated record.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
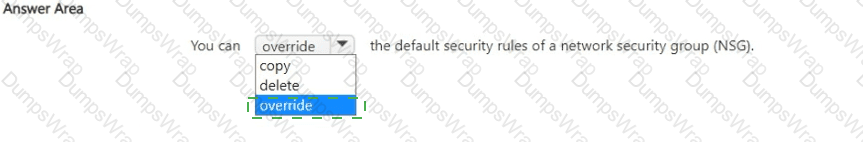
Explanation:

In Azure networking, each Network Security Group (NSG) is created with a built-in set of default security rules. Microsoft’s documentation for NSGs explains: “Azure creates several default security rules within each network security group. You can’t remove the default security rules, but you can override them by creating rules with a higher priority.” The rule processing model is priority-based: “Security rules are processed in priority order, with lower numbers processed before higher numbers. Once a rule matches traffic, processing stops.” Because the defaults have relatively low precedence (high priority numbers), an administrator can create an explicit allow or deny rule with a lower priority number to supersede the default behavior.
This is why the correct completion is override rather than copy or delete. You cannot delete the default rules; they remain present to provide baseline behavior (such as denying inbound traffic from the internet by default and allowing virtual network traffic). Instead, you override the defaults by adding your own NSG rules—using lower priority numbers—to achieve the desired access control outcome while preserving Azure’s baseline protections and evaluation logic.
Which pillar of identity relates to tracking the resources accessed by a user?
Options:
auditing
authorization
authentication
administration
Answer:
AExplanation:
Microsoft’s identity model highlights four pillars: administration, authentication, authorization, and auditing. In this model, auditing is the capability that records and reports identity-related activities, providing visibility into “who accessed what, when, from where, and how.” SCI-aligned guidance explains that authentication verifies identity and authorization grants permissions, while auditing tracks and logs the resulting access to resources so organizations can investigate activity, satisfy compliance obligations, and detect anomalies. Microsoft services such as Microsoft Entra ID (sign-in logs and audit logs), Access Reviews, Privileged Identity Management (PIM) reports, and Microsoft Purview Audit are explicitly positioned to capture user access events and administrative changes across cloud apps and services. This evidence enables security operations and compliance teams to monitor access patterns, prove regulatory adherence, and respond to incidents. Therefore, when the question focuses on tracking the resources accessed by a user, the pillar that directly addresses this requirement is auditing, not authentication (identity proof), authorization (permission assignment), or administration (lifecycle and configuration).
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft identity and access scenarios, federation is explicitly defined as a mechanism to create trust between autonomous organizations so that identities authenticated in one can be accepted by another. Microsoft describes this as: “Federation is a collection of domains that have established trust.” In a federation, “this trust relationship lets each organization accept the other’s user authentication” and enables access to resources without the need to duplicate user accounts or require separate credentials. Within Azure AD/Microsoft Entra and AD FS guidance, Microsoft further explains that federation enables “claims-based access across security boundaries” and “allows users to access applications in a partner organization using their existing credentials.” These statements underline that the purpose of federation is to establish a trust relationship across identity providers or directories, not to provide multi-factor authentication, synchronize accounts, or build network tunnels. MFA is an authentication strength that can be applied on top of federated sign-in, user account synchronization is handled by services like Microsoft Entra Connect (Azure AD Connect), and VPNs provide network connectivity, not identity trust. Therefore, the completion that aligns with Microsoft SCI documentation is that federation establishes a trust relationship between organizations.
What is the purpose of Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Password Protection?
Options:
to control how often users must change their passwords
to identify devices to which users can sign in without using multi-factor authentication (MFA)
to encrypt a password by using globally recognized encryption standards
to prevent users from using specific words in their passwords
Answer:
DExplanation:
Explanation
Azure AD Password Protection detects and blocks known weak passwords and their variants, and can also block additional weak terms that are specific to your organization.
With Azure AD Password Protection, default global banned password lists are automatically applied to all users in an Azure AD tenant. To support your own business and security needs, you can define entries in a custom banned password list.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft describes Windows Hello for Business (WHfB) as replacing passwords with a device-bound credential: “Windows Hello for Business replaces passwords with strong two-factor authentication on devices. This authentication consists of a new type of user credential that is tied to a device and uses a biometric or a PIN.” WHfB authenticators are biometric gesture or PIN unlocking an asymmetric key stored on the device (typically in the TPM). Microsoft clarifies that the PIN is not a password and is “local to the device” and used to unlock the user’s private key. Consequently, Yes—a PIN is a supported WHfB sign-in gesture.
Conversely, the Microsoft Authenticator app is a separate Azure AD (Microsoft Entra ID) authentication method (push notifications, TOTP, passwordless phone sign-in). It is not the WHfB credential; WHfB relies on keys/certificates on the device, not on the Authenticator app.
Finally, WHfB credentials are per-device: Microsoft states the credential is “tied to a device” and the private key never leaves the device, which means it does not roam/sync across a user’s different devices. Each device enrolls and provisions its own WHfB key and gesture. These statements from Microsoft SCI documentation lead to the outcomes: No / Yes / No.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft Azure Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native, security information event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution.
Which score measures an organization's progress in completing actions that help reduce risks associated to data protection and regulatory standards?
Options:
Microsoft Secure Score
Productivity Score
Secure score in Azure Security Center
Compliance score
Answer:
DExplanation:
The Compliance score in Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager is a measurement tool that evaluates an organization’s progress toward meeting data protection and regulatory compliance requirements. It is specifically designed to help organizations reduce risks related to data governance, privacy, and compliance with various standards such as GDPR, ISO 27001, NIST 800-53, and Microsoft Data Protection Baselines.
According to Microsoft’s official documentation on Compliance Manager, the Compliance score “helps organizations track, improve, and demonstrate their compliance posture by providing a quantifiable measure of compliance with regulations and standards.” Each action within Compliance Manager contributes a certain number of points to the overall score. These points are weighted based on risk, meaning that actions with a greater impact on reducing compliance risk contribute more significantly to the total score.
The score is not an absolute measure of legal compliance but rather an indicator of progress toward implementing recommended controls and risk-reducing actions. Microsoft emphasizes that Compliance score “assists organizations in identifying areas of improvement, prioritizing compliance tasks, and maintaining an auditable record of their compliance activities.”
By contrast, Microsoft Secure Score measures security posture related to identity, device, and application protection, while Productivity Score evaluates collaboration and technology experience. Thus, the metric that specifically assesses data protection and regulatory compliance progress is the Compliance score in Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:
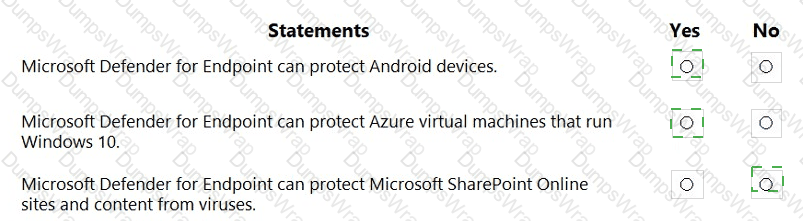
Explanation:

Microsoft documents for Defender for Endpoint (MDE) describe it as an enterprise endpoint security platform that supports Windows 10/11, Windows Server, Linux, macOS, and mobile platforms (Android and iOS/iPadOS). The platform provides threat and vulnerability management, attack surface reduction, next-generation protection, endpoint detection and response, and automated investigation and remediation across those supported operating systems. Because MDE supports Windows client operating systems and servers, it can also be used on Azure virtual machines that run supported Windows versions; onboarding methods include local scripts, Microsoft Endpoint Manager, or cloud integrations, allowing VM endpoints to receive the same protection and EDR capabilities as physical devices.
By contrast, malware scanning in SharePoint Online, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams is provided by Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (Safe Attachments for SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams)—a different service within the Microsoft 365 Defender family. This service analyzes files as they are uploaded or shared to detect and block malicious content in collaboration workloads, which is outside the scope of MDE’s endpoint-focused protections. Therefore: Android protection (Yes), Azure VMs running Windows 10 (Yes), and SharePoint Online anti-virus protection by MDE (No, handled by Defender for Office 365).
What can you specify in Microsoft 365 sensitivity labels?
Options:
how long files must be preserved
when to archive an email message
which watermark to add to files
where to store files
Answer:
CExplanation:
Sensitivity labels can apply content markings (headers, footers, and watermarks) to documents and emails, and can also enforce encryption and access controls. When configuring a label, you can specify the watermark text, size, and placement so that protected content is visibly marked according to your organization’s policy.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft states that Microsoft Sentinel includes connectors for both Microsoft and non-Microsoft sources. The product overview explains that Sentinel “comes with built-in connectors” for services such as Microsoft 365, Defender, and Azure sources, and also built-in connectors for non-Microsoft solutions like firewalls and other security products. Therefore, the claim that data connectors support only Microsoft services is false.
For visualization and monitoring, the documentation clarifies that “Microsoft Sentinel uses Azure Monitor workbooks to provide rich visualizations of your data.” Workbooks are the native dashboarding framework in Sentinel and can be customized to monitor logs, incidents, and telemetry that Sentinel ingests. Hence, using Azure Monitor Workbooks to monitor data collected by Sentinel is true.
Regarding threat hunting, Microsoft describes the Hunting capability as a proactive feature: “Hunting lets you proactively hunt for security threats,” using Kusto Query Language queries and analytic patterns to find indicators of compromise before alerts are generated. Analysts can run, save, and schedule hunts to uncover suspicious activity that hasn’t yet raised an alert, making the statement about identifying threats before an alert is triggered true.
You have an Azure subscription.
You need to implement approval-based time-bound role activation.
What should you use?
Options:
Microsoft Entra ID Protection
Microsoft Entra Conditional access
Microsoft Entra Privileged Management
Microsoft Entra Access Reviews
Answer:
CExplanation:
Microsoft documents describe Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (PIM) as the service that delivers approval-based, time-limited elevation to privileged roles. Official guidance states: “Privileged Identity Management (PIM) enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in Microsoft Entra ID, Azure, and Microsoft 365.” PIM specifically supports just-in-time and time-bound activations: “PIM provides just-in-time privileged access to Microsoft Entra roles and Azure resources” and “allows you to make access time-bound by setting start and end dates.” It also supports approval workflows: “You can require approval to activate privileged roles, and designate approvers to receive and approve requests.” Additional controls include “require multi-factor authentication to activate, provide a justification, and ticket number,” and auditing: “PIM records all activations and changes for review and alerting.”
By contrast, Microsoft Entra ID Protection focuses on risk detections and automated remediation, not role elevation workflows. Conditional Access enforces access policies at sign-in and session but does not provide approval-based role activation. Access Reviews help you “review and attest to continued access” but do not supply just-in-time elevation. Therefore, the Microsoft Purview/Entra feature that implements approval-based, time-bound role activation is Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (PIM).
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft’s security guidance for hybrid and cloud environments adopts the Zero Trust approach, which explicitly positions identity as the primary boundary for access decisions. Microsoft states that in modern, distributed environments, “the traditional network perimeter is no longer sufficient” and that identity becomes the new security perimeter for protecting access to resources across on-premises and cloud. In Zero Trust, access is granted based on who the user or workload is, the risk of the sign-in, the device health, and the context of the session. Microsoft summarizes this shift as: “Identity is the control plane,” emphasizing that authentication, authorization, and continuous evaluation of trust are enforced through identity-centric controls such as Conditional Access, multifactor authentication, Privileged Identity Management, device compliance, and session controls.
While tools like firewalls and services such as Microsoft Defender for Cloud remain important layers in a defense-in-depth strategy, they are not the primary perimeter in a hybrid model. Because users, devices, and applications operate from anywhere, identity is the consistent, verifiable layer through which policy is enforced for both on-premises and cloud resources. Therefore, in an environment that spans on-premises and cloud, Microsoft recommends treating identity as the primary security perimeter, applying continuous verification and least-privilege access through identity-driven policies.
What can you use to provide threat detection for Azure SQL Managed Instance?
Options:
Microsoft Secure Score
application security groups
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Azure Bastion
Answer:
CExplanation:
For Azure data services such as Azure SQL Managed Instance, Microsoft provides threat detection and protection through Microsoft Defender for Cloud (via Microsoft Defender for SQL). Microsoft documentation states that Defender for Cloud “provides advanced threat protection for your SQL resources,” including Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance, by “continuously monitoring for anomalous activities and potential SQL injection, brute force, and exploitation attempts.” When enabled, the plan “generates security alerts when suspicious activities are detected,” and these alerts can be surfaced in Defender for Cloud, forwarded to Microsoft Sentinel, or integrated with workflows for response. Microsoft Secure Score is a security posture metric, application security groups are for network segmentation in Azure, and Azure Bastion provides secure RDP/SSH over TLS—none of these deliver database-specific threat detection. Therefore, to provide threat detection for Azure SQL Managed Instance, you use Microsoft Defender for Cloud (Defender for SQL).
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity guidance, Microsoft Defender for Identity (formerly Azure ATP) is explicitly described as “a cloud-based security solution that leverages your on-premises Active Directory signals to identify, detect, and investigate advanced threats.” The service deploys lightweight sensors on domain controllers to collect and analyze Active Directory (AD) authentication and activity data. Using behavioral analytics and built-in detections, it helps security teams surface indicators of compromised identities, lateral movement, pass-the-ticket/NTLM relay, and other identity-driven attack techniques. Documentation further explains that Defender for Identity “profiles and learns entity behavior,” correlates events, and raises security alerts with investigation timelines and evidence to accelerate incident response in hybrid environments.
This precisely matches the sentence in the prompt: the only Microsoft security product whose core purpose is to use on-premises AD signals to identify, detect, and investigate advanced threats is Defender for Identity. By contrast, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint focuses on endpoint prevention and EDR; Microsoft Defender for Office 365 protects email and collaboration workloads from phishing and malware; and Microsoft Cloud App Security (now Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps) operates as a CASB for app discovery, control, and session monitoring. Therefore, aligning with SCI study guides and product descriptions, the correct completion is Microsoft Defender for Identity.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
Explanation:
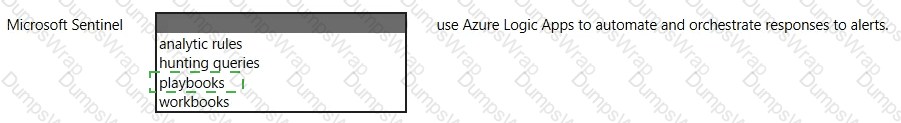
In Microsoft Sentinel, playbooks are the feature that integrates with Azure Logic Apps to automate response. Microsoft’s documentation describes them as “collections of procedures that can be run from Microsoft Sentinel in response to an alert” and clarifies that “playbooks are built on Azure Logic Apps” providing a workflow engine and a gallery of connectors to other Microsoft and third-party services. Playbooks can be triggered automatically from analytics rules or manually from incidents and alerts, enabling orchestration such as assigning owners, creating tickets, disabling accounts, blocking IPs, or posting to collaboration channels. The platform emphasizes that the Logic Apps foundation gives security teams a visual designer, managed connectors, and run history to track execution and outcomes. In short, Sentinel uses playbooks to “automate and orchestrate responses to alerts and incidents”, reducing mean-time-to-respond and standardizing actions across your SOC. Other Sentinel components serve different purposes: analytic rules detect threats, hunting queries aid proactive investigation, and workbooks provide dashboards and visualizations. Therefore, the correct completion is: Microsoft Sentinel playbooks use Azure Logic Apps to automate and orchestrate responses to alerts.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
Explanation:

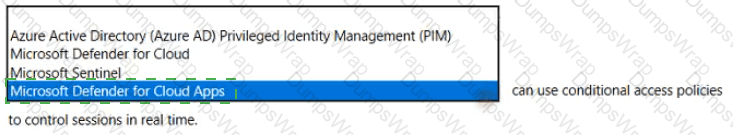
In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity portfolio, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps (formerly Microsoft Cloud App Security) integrates directly with Microsoft Entra Conditional Access to provide Conditional Access App Control—Microsoft’s real-time session control. Microsoft’s documentation describes this capability as enabling organizations to “monitor and control user sessions in real time” and to “protect downloads, restrict uploads, block copy/paste and print, and apply access or session policies” for sanctioned and unsanctioned applications. The enforcement is achieved through a reverse-proxy session that is invoked by Conditional Access policy decisions, allowing continuous inspection and dynamic controls after authentication.
By contrast, other options in the list do not offer real-time session enforcement via Conditional Access. Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) focuses on just-in-time role activation, approval workflows, and access reviews for privileged accounts—not session control of app usage. Microsoft Defender for Cloud provides cloud security posture management and workload protection across Azure, multicloud, and hybrid resources—again, not Conditional Access–based user session governance. Microsoft Sentinel is a SIEM/SOAR solution used for ingestion, detection, investigation, and response; it does not apply Conditional Access policies to control user sessions. Therefore, the service that can use Conditional Access policies to control sessions in real time is Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps through Conditional Access App Control.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Box 1: Yes
Azure Defender provides security alerts and advanced threat protection for virtual machines, SQL databases, containers, web applications, your network, your storage, and more
Box 2: Yes
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) is available for free to all Azure users.
Box 3: Yes
Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of your data centers, and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud - whether they're in Azure or not - as well as on premises.
Match the types of compliance score actions to the appropriate tasks.
To answer. drag the appropriate action type from the column on the left to its task on the right. Each type may be used once. more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager, improvement actions are categorized by control type to reflect how they reduce risk and contribute to your compliance score. Microsoft’s SCI guidance explains that preventative controls are safeguards that “prevent a security or compliance incident from occurring by enforcing protections in advance (for example, enforcing encryption of data at rest and in transit, access restrictions, and configuration baselines).” This directly aligns with the task “Use encryption to protect data at rest”, which is a classic prevention mechanism intended to stop unauthorized disclosure before it can happen.
The guidance also states that detective controls are measures that “identify, log, and surface anomalous or non-compliant activities so they can be investigated and addressed (for example, continuous monitoring, alerting, audit logging, and analytics).” This maps to “Actively monitor systems to identify irregularities that might represent risks”, because the goal is to detect suspicious behavior or drift as it occurs.
By comparison, corrective controls are used to “remediate issues and restore a desired state after a problem is discovered (for example, patching, incident response, or configuration correction).” No corrective action is described in the two listed tasks, so Corrective is not selected. This mapping reflects how Compliance Manager classifies actions that contribute points to the compliance score based on their risk-reducing impact.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft’s Conditional Access (part of Microsoft Entra ID) evaluates multiple signals to make access decisions. The official description lists typical signals such as “user or group membership, IP location information, device state, application, and real-time risk.” The device state element explicitly refers to conditions like “compliant or hybrid Azure AD joined devices,” allowing policies that grant or block access—or require extra controls—based on whether a device meets compliance/registration requirements.
Regarding evaluation timing, Microsoft’s guidance states that Conditional Access “policies are enforced after the first-factor authentication is completed.” This means the engine needs the user’s primary sign-in context (who the user is and how they authenticated) to evaluate the conditions and then decide whether to allow, block, or require additional controls. Therefore, the statement that policies apply before first factor is not correct.
Finally, Conditional Access includes grant controls such as “Require multi-factor authentication,” and policies can be scoped to specific cloud apps or actions. As a result, you can target a particular application and require MFA when a user attempts to access it, satisfying application-specific risk mitigation while preserving user productivity.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Azure DDoS Protection Standard is a platform-native service designed to mitigate distributed denial of service attacks against Azure-hosted workloads that expose public IP addresses. Microsoft’s guidance explains that DDoS Protection Standard is “enabled on a virtual network” and, once enabled, “automatically protects resources within the virtual network with public IP addresses” (for example, Application Gateway, Azure Load Balancer, and virtual machines). The service is “tuned to the traffic patterns of the protected resources” and provides adaptive real-time mitigation with telemetry and attack analytics.
Critically, the scope of enablement is at the virtual network (VNet) level, not at the resource group level, and it does not apply to Azure Active Directory (Microsoft Entra ID) users or applications, which are identity services rather than network resources. Microsoft’s materials emphasize that by associating a DDoS protection plan to a VNet, you “protect all public IPs assigned to resources in that VNet”, giving layered protection alongside Azure’s always-on basic protections.
Therefore, the only option that correctly completes the sentence is virtual networks, because Azure DDoS Protection Standard is configured on, and provides coverage for, resources inside a VNet that have public endpoints—exactly matching Microsoft’s SCI/Azure security documentation.
Which three authentication methods can Microsoft Entra users use to reset their password? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Options:
text message to a phone
certificate
mobile app notification
security questions
picture password
Answer:
A, C, DExplanation:
Microsoft Entra self-service password reset (SSPR) supports multiple verification methods that users can register and use to prove their identity during a reset. Microsoft’s documentation lists the SSPR methods as: “Mobile app notification,” “Mobile app code,” “Email,” “Mobile phone (text message or call),” “Office phone,” and “Security questions.” Administrators choose which of these are allowed and how many methods are required. During the reset flow, SSPR “prompts the user to verify with the registered methods” before permitting a password change. Notably, certificates and picture passwords are not SSPR verification methods in Microsoft Entra ID. Therefore, among the options provided: a text message to a phone (mobile phone), a mobile app notification (Microsoft Authenticator), and security questions are valid SSPR authentication methods; certificate and picture password are not supported for SSPR. This aligns with SCI learning content that positions SSPR as a user-empowering capability to securely restore access using admin-approved methods without help-desk intervention.
What is an example of encryption at rest?
Options:
encrypting communications by using a site-to-site VPN
encrypting a virtual machine disk
accessing a website by using an encrypted HTTPS connection
sending an encrypted email
Answer:
BExplanation:
In Microsoft’s SCI guidance, encryption at rest is defined as protecting data when it is stored on a disk or other persistent media. Microsoft describes it as controls that “help safeguard your data to meet your organizational security and compliance commitments by encrypting data when it is persisted,” distinguishing it from protections for data in transit. Within Azure and Microsoft 365, examples include Azure Disk Encryption for IaaS VMs (using BitLocker for Windows and DM-Crypt for Linux), server-side encryption for storage accounts, and Transparent Data Encryption for databases. A virtual machine’s OS and data disks encrypted with BitLocker or DM-Crypt are canonical cases of at-rest encryption because the encryption keys protect the physical media; the data becomes unreadable if the disks are accessed outside the authorized context. By contrast, site-to-site VPN, HTTPS web sessions, and encrypted email protect data in transit—they secure network communications but do not encrypt the data where it is stored. Therefore, among the options provided, encrypting a virtual machine disk is the correct example of encryption at rest in Microsoft’s security model.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point

Options:
Answer:
Explanation:
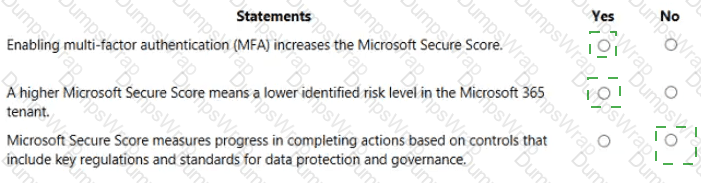
Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) increases the Microsoft Secure Score. Yes
A higher Microsoft Secure Score means a lower identified risk level in the Microsoft 365 tenant. Yes
Microsoft Secure Score measures progress in completing actions based on controls that include key regulations and standards for data protection and governance. No
Microsoft Secure Score is a measurement of an organization’s security posture in Microsoft 365. The SCI materials explain that Secure Score is calculated from improvement actions such as requiring multi-factor authentication for users, especially administrators. When you configure and enforce MFA, you complete one of these recommended actions, and Secure Score awards points, so enabling MFA directly increases Microsoft Secure Score.
The documentation further states that Secure Score reflects how many recommended security controls you have implemented. A higher score indicates that more recommended controls are in place, which reduces exposure to common threats and therefore represents a lower residual risk level in the tenant. While it is not an absolute guarantee of security, it is an indicator that risk has been reduced compared to a lower score.
The third statement, however, describes the purpose of Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager and its compliance score, which tracks progress against controls mapped to regulations and standards for data protection and governance. Secure Score does not measure alignment with regulatory frameworks; it is focused on technical security configurations and behaviors in Microsoft 365. Therefore, that statement is No.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
YES YES YES
Microsoft Entra Conditional Access is explicitly described by Microsoft as a system of policies that act as if-then statements: if a user wants to access a resource, then certain controls must be satisfied. These are called Conditional Access policies, and they combine assignments and access controls to enforce organizational requirements.
Among the configurable conditions in a policy is Device platforms. The documentation explains that Conditional Access identifies the device platform (Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux) from the user agent and notes that this condition is typically used with grant controls such as block access or in combination with other controls. This allows administrators to block or allow access based specifically on the operating system of the user’s device.
For scoping, the Users and groups assignment lets you include or exclude groups instead of individual users. Microsoft’s Entra groups overview states that you can create a Conditional Access policy that applies to a group, and that Entra supports both security groups and Microsoft 365 groups, while another architecture article notes that either a security group or a Microsoft 365 Group can be used in Conditional Access policies.
What feature supports email as a method of authenticating users?
Options:
Microsoft Entra ID Protection
Microsoft Entra Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
self-service password reset (SSPR)
Microsoft Entra Password Protection
Answer:
CExplanation:
In Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), self-service password reset (SSPR) is the feature that explicitly supports email as an authentication method when users need to verify their identity to reset or unlock their password.
According to Microsoft’s identity and access documentation and the SCI learning content, SSPR lets administrators choose which verification methods are available to users, such as mobile phone, office phone, mobile app, security questions, and email. When email is enabled, a verification code can be sent to a registered alternate email address. The user proves their identity by entering this code, which is treated as an authentication step in the SSPR process.
By contrast:
Microsoft Entra Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) does not support email as an MFA method; it focuses on methods like authenticator apps, phone calls, and text messages.
Microsoft Entra ID Protection detects and responds to risky sign-ins and users but does not provide email-based authentication.
Microsoft Entra Password Protection deals with banned and compromised passwords, not with email verification.
Therefore, the only option in the list that uses email as a supported authentication method is self-service password reset (SSPR).
To which type of resource can Azure Bastion provide secure access?
Options:
Azure Files
Azure SQL Managed Instances
Azure virtual machines
Azure App Service
Answer:
CExplanation:
Azure Bastion is a managed PaaS service that provides secure and seamless RDP/SSH connectivity to your Azure virtual machines directly from the Azure portal over TLS/HTTPS. SCI and Azure security documentation summarize it as eliminating public IP exposure on VMs by using a fully managed bastion host deployed inside your virtual network. Users connect through their browser and the service brokers the RDP or SSH session, which “protects your VMs from exposing RDP/SSH to the Internet.” Bastion does not provide access to Azure Files, SQL Managed Instance, or App Service; it is specifically built to secure management access to VMs without requiring a VPN or public endpoints. Therefore, the resource type Azure Bastion securely connects to is Azure virtual machines.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity learning content for Microsoft Defender for Cloud, the service is described as providing ongoing posture management and threat protection. The official description states that Defender for Cloud “continuously assesses your resources to identify security misconfigurations and weaknesses” and “continuously discovers and evaluates resources” across your subscriptions. The recommendations and secure-score updates are produced as the platform “continuously analyzes your environment using security policies and analytics,” surfacing issues the moment they’re detected and mapping them to remediation guidance. This continuous assessment model underpins Defender for Cloud’s cloud security posture management (CSPM) capability and ensures that newly created or modified resources are evaluated without waiting for a scheduled job. By design, there is no fixed interval (such as hourly, every 15 minutes, or daily) required to trigger assessments—policy-driven evaluation and data collection run as changes occur and signals are received. Therefore, the sentence “Microsoft Defender for Cloud assesses Azure resources ____ for security issues” is correctly completed with continuously, reflecting Microsoft’s emphasis on persistent, real-time security posture evaluation rather than periodic scans.
Which Microsoft Purview feature allows users to identify content that should be protected?
Options:
Sensitivity Labels
Insider Risks
Data Loss prevention
eDiscovery
Answer:
AExplanation:
In Microsoft Purview, Sensitivity labels are the feature designed to let users identify and classify content that should be protected. Microsoft’s guidance explains that sensitivity labels “enable you to classify and protect your organization's data while ensuring that user productivity and collaboration aren't hindered.” Users can manually choose a label in Office apps and services to indicate the data’s sensitivity; as Microsoft notes, labels “can be applied by users or automatically,” and the label “persists with the content in its metadata.” Once identified with a label, protection settings can be enforced, including “encryption, content marking (headers, footers, watermarks), and access restrictions based on the label.”
By comparison, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) focuses on “monitoring and blocking the unintentional sharing of sensitive information” based on policy—DLP enforces handling rules after data is identified, rather than providing the user-centric classification mechanism. Insider Risk addresses “risky user activities and insider data security scenarios,” and eDiscovery is used to “find, preserve, collect, and review content for investigations or litigation.” Therefore, the feature that explicitly allows users to identify content that should be protected—by selecting and applying a classification that then drives protection—is Sensitivity labels.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:
Explanation:

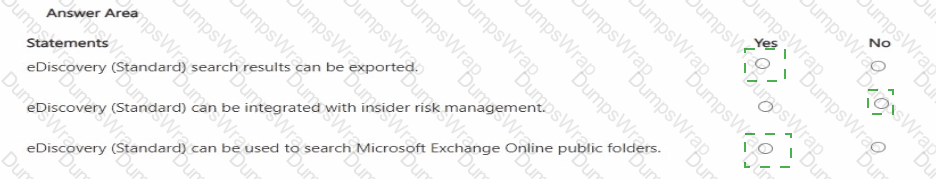
In Microsoft Purview, eDiscovery (Standard) (formerly Core eDiscovery) provides case management, holds, searches, and export. Microsoft describes that eDiscovery (Standard) lets investigators “search across Microsoft 365 data sources and export the results,” including options to export native files, email to PST, and CSV reports for further review. It uses the same Content search engine and supports selecting locations such as **Exchange Online mailboxes, Microsoft 365 Groups, Teams, SharePoint sites, OneDrive accounts, and Exchange public folders,” enabling organization-wide discovery that includes public folders.
Integration for end-to-end legal review from Microsoft Purview Insider Risk Management is specifically aligned to eDiscovery (Premium) (formerly Advanced eDiscovery). Insider Risk cases provide actions like “Send to eDiscovery (Premium)” to create a review set and apply advanced processing, analytics, and review workflows. Those advanced integrations (review sets, analytics, legal hold communications) are not features of eDiscovery (Standard). Therefore: exporting results (Yes), Insider Risk integration (No, as it targets eDiscovery Premium), and searching Exchange Online public folders (Yes) are the correct evaluations based on the Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity study materials for Purview eDiscovery capabilities.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:
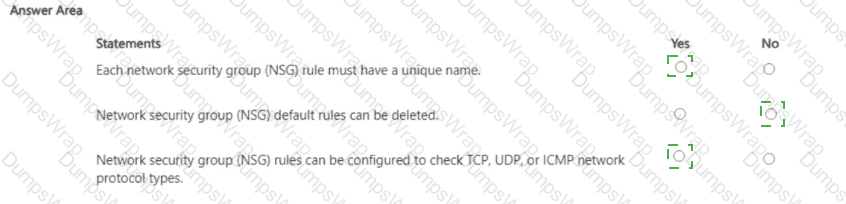
Explanation:

In Microsoft Azure, an NSG consists of ordered security rules evaluated by priority. The Azure documentation specifies that every rule includes identifying metadata and must be uniquely named within the NSG: “Each security rule has a name that is unique within the network security group.” Rule evaluation is deterministic: “Security rules are processed in priority order… once a rule matches traffic, processing stops.”
Azure creates several default security rules in every NSG to provide a safe baseline. These defaults are protected: “You can’t remove the default security rules, but you can override them by creating rules with a higher priority.” This means deletion of default rules is not allowed; administrators add custom rules with lower priority numbers to supersede the defaults as needed.
Regarding protocols, NSG rules can target specific L4/L3 protocols. The platform guidance states that the rule Protocol field supports TCP, UDP, ICMP, or Any: “For Protocol, specify TCP, UDP, ICMP, or Any.” Therefore, configuring rules to check TCP, UDP, or ICMP traffic types is fully supported.
Putting this together: (1) unique rule names are required (Yes), (2) default rules cannot be deleted (No), and (3) NSG rules can indeed be configured for TCP/UDP/ICMP (Yes). These behaviors align with Azure’s prescribed NSG design and management model used across Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity learning content.
Which Microsoft Purview data classification type supports the use of regular expressions?
Options:
exact data match (EDM)
fingerprint classifier
sensitive information types (SlTs)
trainable classifier
Answer:
CExplanation:
Sensitive Information Types (SITs) support regular expressions (regex), which allow for custom pattern matching to detect sensitive content like credit card numbers, social security numbers, or custom identifiers. Regex is fundamental to the detection logic within SITs.
SCI Extract: "Sensitive information types use pattern matching techniques, including regular expressions, keyword matches, and checksums to identify sensitive data."
What can you use to deploy Azure resources across multiple subscriptions in a consistent manner?
Options:
Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Azure Policy
Azure Blueprints
Answer:
DExplanation:
Microsoft guidance describes Azure Blueprints as the native way to stamp out governed environments consistently across tenants and subscriptions. Microsoft states: “Azure Blueprints enables cloud architects and central information technology groups to define a repeatable set of Azure resources that implements and adheres to an organization’s standards, patterns, and requirements.” It further explains that “Blueprints make it possible to package artifacts, such as role assignments, policy assignments, ARM templates, and resource groups, into a single blueprint definition that can be assigned to your subscriptions.” This is precisely what’s required when you need to deploy Azure resources across multiple subscriptions in a consistent manner—you define a blueprint (with policies, RBAC, templates, and resource groups) and assign it to one or more subscriptions to get uniform, compliant deployments. While services like Microsoft Defender for Cloud and Azure Policy help assess and enforce security and compliance, Blueprints orchestrate multi-artifact deployment and governance at scale from day one of an environment’s lifecycle, ensuring standardization and repeatability across subscriptions.
What Microsoft Purview feature can use machine learning algorithms to detect and automatically protect sensitive items?
Options:
eDiscovery
Data loss prevention
Information risks
Communication compliance
Answer:
BExplanation:
Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is designed to “detect and protect sensitive items” across Microsoft 365 locations, endpoints, and cloud apps. Microsoft explains that Purview DLP policies use sensitive information types, exact data match (EDM), and machine learning–based trainable classifiers to identify content, and then automatically apply protective actions such as blocking or restricting sharing, notifying users with policy tips, auditing, or auto-quarantining/justifying activities. This fulfills the description “use machine learning algorithms to detect and automatically protect sensitive items.” While eDiscovery focuses on legal hold and content discovery, and Communication compliance monitors communications for policy violations (ethics/regulatory scenarios), they are not positioned to broadly and automatically protect sensitive data across services. “Information risks” is not a distinct Purview solution category. Therefore, the Purview capability that leverages machine learning classifiers and automatically enforces protections on sensitive data is Data loss prevention (DLP).
What are three uses of Microsoft Cloud App Security? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Options:
to discover and control the use of shadow IT
to provide secure connections to Azure virtual machines
to protect sensitive information hosted anywhere in the cloud
to provide pass-through authentication to on-premises applications
to prevent data leaks to noncompliant apps and limit access to regulated data
Answer:
A, C, EExplanation:
Microsoft Cloud App Security (now Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps) is Microsoft’s CASB that “discovers and controls shadow IT,” integrates with identity and endpoint signals, and enforces data protection in SaaS and custom apps. SCI materials describe three core use cases relevant here: (1) Discovery and control of shadow IT by analyzing network logs and app usage, rating risk, and applying governance—matching A. (2) Protect sensitive information hosted anywhere in the cloud via policies such as DLP, information protection label awareness, and integration with apps through API connectors—matching C. (3) Prevent data leaks to noncompliant apps and limit access to regulated data using Conditional Access App Control and session controls that can block download, apply protections, or monitor in real time—matching E. In contrast, secure connections to Azure virtual machines are provided by Azure Bastion, not the CASB (eliminating B), and pass-through authentication to on-premises apps is delivered by Azure AD features such as Azure AD Application Proxy or PTA (not Cloud App Security), eliminating D.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:
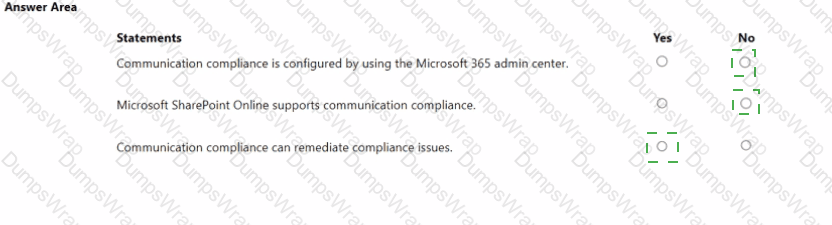
Explanation:
No
No
Yes
Microsoft states that Communication Compliance is administered in Microsoft Purview, not the Microsoft 365 admin center. The Learn article shows configuration and policy templates “in the Microsoft Purview portal” and directs admins to “configure Communication Compliance” there, confirming the management plane is the Purview compliance portal, not the M365 admin center.
Regarding supported locations, Microsoft lists the communication channels that policies can inspect: “Microsoft Teams… Exchange Online… Viva Engage… [and] Third-party sources.” SharePoint Online is not listed among supported channels, so SharePoint content isn’t monitored by Communication Compliance policies.
Finally, Communication Compliance includes built-in workflows to address findings. The Learn page explicitly provides a Remediate step: “Remediate Communication Compliance issues you investigate by using the following options:” such as “Notify the user” and “Escalate to another reviewer.” These actions demonstrate that the solution does more than detect; it supports remediation within the Purview portal workflow.
Exact extracts (selected):
“You can choose from the following policy templates in the Microsoft Purview portal.”
“Communication Compliance policies check… Microsoft Teams… Exchange Online… Viva Engage… Third-party sources.”
“Remediate Communication Compliance issues you investigate by using the following options: Notify the user… Escalate to another reviewer.”
You have an Azure subscription.
You need to implement approval-based, tiProme-bound role activation.
What should you use?
Options:
Windows Hello for Business
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Identity Protection
access reviews in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Answer:
DExplanation:
In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity guidance, Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is the service used to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in Azure and Microsoft 365. The documentation explains that PIM enables “just-in-time” and “time-bound” activation of privileged roles, requiring users to elevate only when needed and for a limited duration. PIM policies can require approval before a role is activated, enforce multifactor authentication, capture business justification, send notifications, and maintain detailed auditing and access review records. These controls are designed to reduce the risk associated with standing administrative privileges by ensuring that elevation is temporary, approved, and tracked.
By contrast, Windows Hello for Business provides strong, device-bound authentication; Azure AD Identity Protection focuses on detecting and remediating risky sign-ins and users; and Azure AD Access Reviews periodically reattest existing assignments but do not provide the on-demand, approval-based, time-limited activation of roles. Therefore, when the requirement is approval-based, time-bound role activation, Microsoft’s prescribed capability is Azure AD PIM, which delivers just-in-time elevation with approvers, duration limits, and audit/logging to support least privilege and Zero Trust operational practices.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:
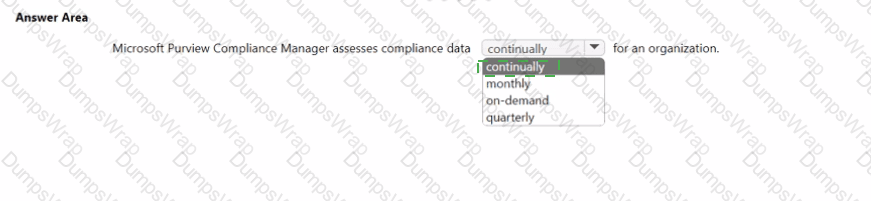
Explanation:

Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager is designed to give organizations a continuous view of their compliance posture. In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity guidance, Compliance Manager is described as a capability that assesses your compliance posture against regulatory standards and data protection baselines and updates the compliance score as you implement or fail controls. The platform aggregates signals from assessments, controls, and improvement actions, then recalculates your compliance score as evidence is collected and actions are marked complete or tested. Because these evaluations are tied to live improvement actions and mapped controls (such as access, data protection, and governance controls), your organization’s status isn’t limited to a fixed reporting cycle; rather, it reflects ongoing progress and gaps across supported regulations and standards.
SCI study materials also emphasize that the score is not a one-time audit: it’s a running indicator of risk reduction and control implementation. As you address recommendations, add or update evidence, or connect automated tests where available, the score and related dashboards refresh to show the latest compliance state. This makes Compliance Manager suitable for continuous assessment, enabling organizations to monitor posture, prioritize work, and demonstrate incremental improvements over time—hence, it assesses compliance data continually for an organization.
What can you use to provision Azure resources across multiple subscriptions in a consistent manner?
Options:
Azure Defender
Azure Blueprints
Azure Sentinel
Azure Policy
Answer:
BExplanation:
Azure Blueprints allow cloud architects and central IT to define a repeatable set of Azure resources and governance artifacts—including Azure Policy assignments, role assignments (RBAC), resource groups, and ARM/Bicep templates—and then deploy them consistently across subscriptions. Microsoft’s guidance describes Blueprints as a way to “orchestrate the deployment of various resource templates and other artifacts” to establish standards, patterns, and compliance for environments at scale. This is distinct from Azure Policy, which evaluates and enforces configuration but does not package multi-artifact environments; Microsoft Sentinel and Defender are security analytics/protection services rather than provisioning frameworks. Thus, for consistent provisioning across multiple subscriptions, the prescribed solution is Azure Blueprints.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Conditional access policies always enforce MFA = NoMicrosoft Entra Conditional Access policies are flexible and do not always require MFA. MFA is one possible control, but policies can enforce other access controls such as requiring a compliant device, blocking access entirely, requiring Terms of Use acceptance, or enforcing session controls.
SCI Extract: “Conditional Access is the tool used by Azure AD to bring signals together, to make decisions, and enforce organizational policies. These policies can require MFA, but it is not mandatory for all policies.”
Block access based on location = YesConditional Access supports location-based conditions using named locations (such as country or IP ranges). Policies can block or allow access based on where the user is signing in from.
SCI Extract: “Administrators can use Conditional Access policies to block or grant access based on user location, using named locations to define trusted or risky areas.”
Only affects Entra joined devices = NoConditional Access applies to all users and devices, including:
Entra-joined,
Hybrid Entra-joined,
Registered devices (via Microsoft Intune or Azure AD),
And even unmanaged (BYOD) devices depending on configuration.
SCI Extract: “Conditional Access policies apply to all users and devices based on selected conditions, not only Microsoft Entra joined devices.”
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft defines hybrid identity as enabling a common identity across on-premises and cloud by integrating your directory services. Microsoft Learn states: “Hybrid identity is achieved by integrating your on-premises Active Directory with Azure Active Directory.” This integration is delivered through the synchronization and optional federation capabilities that connect AD DS to Azure AD so users can access both on-premises and cloud resources with one identity.
To implement this integration, Microsoft’s tooling is explicit: “Azure AD Connect is the Microsoft tool designed to meet and accomplish your hybrid identity goals.” Azure AD Connect (now Microsoft Entra Connect) synchronizes users, groups, and optionally passwords or hashes to Azure AD, providing the foundation for hybrid scenarios such as single sign-on and seamless sign-in.
Regarding tenants, Microsoft’s identity platform clarifies that “A Microsoft 365 organization is associated with a single Azure AD tenant.” Therefore, a hybrid identity deployment does not require two Microsoft 365 tenants; it typically links a single Azure AD (Microsoft Entra ID) tenant with one or more on-premises AD DS forests. In summary, Azure AD Connect enables hybrid identity, hybrid identity is the synchronization/integration of AD DS with Azure AD, and it does not necessitate multiple Microsoft 365 tenants.
You need to keep a copy of all files in a Microsoft SharePoint site for one year, even if users delete the files from the site. What should you apply to the site?
Options:
a data loss prevention (DLP) policy
a retention policy
an insider risk policy
a sensitivity label policy
Answer:
BExplanation:
In Microsoft Purview (Microsoft 365 compliance), a retention policy applied to a SharePoint site keeps content for the specified period (e.g., 1 year) even if users delete it. Items are retained and recoverable until the retention period expires, meeting your preservation requirement.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
Compliance Manager tracks only customer-managed controls. No
Compliance Manager provides predefined templates for creating assessments. Yes
Compliance Manager can help you assess whether data adheres to specific data protection standards. No
Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager is described as a feature that “helps you manage your organization’s compliance requirements” by giving you assessments, improvement actions, and a compliance score that “measures your progress in completing recommended actions” aligned to regulations and standards. The service does not track only customer-managed controls; Microsoft’s documentation clarifies that Compliance Manager includes “Microsoft-managed controls and customer-managed controls,” and it tracks both within each assessment to show overall posture. It also provides prebuilt (predefined) assessment templates for common regulations and industry standards so organizations can “create assessments from templates” such as GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and the Data Protection Baseline.
Importantly, Compliance Manager evaluates control implementation and improvement actions mapped to requirements; it does not scan or classify individual data to determine whether specific data items “adhere” to a standard. Instead, it helps you assess organizational compliance posture by tracking the status of controls, assigning actions, and recording evidence. Thus:
“Tracks only customer-managed controls” → No (it tracks Microsoft-managed and customer-managed).
“Provides predefined templates for creating assessments” → Yes (prebuilt templates are a core feature).
“Helps you assess whether data adheres to specific data protection standards” → No (it measures control/compliance posture, not data-level adherence).
Box 1: No
Compliance Manager tracks Microsoft managed controls, customer-managed controls, and shared controls. Box 2: Yes
Box 3: Yes
Which feature is included in Microsoft Entra ID Governance?
Options:
Verifiable credentials
Permissions Management
Identity Protection
Privileged Identity Management
Answer:
DExplanation:
Microsoft defines Microsoft Entra ID Governance as the capability to manage “the identity lifecycle, access lifecycle, and privileged access” so organizations can ensure “the right people have the right access to the right resources at the right time.” The product family explicitly lists the following core features: “Lifecycle workflows, Entitlement management, Access reviews, and Privileged Identity Management (PIM).” Microsoft further explains that PIM helps you “manage, control, and monitor access within your organization,” enabling just-in-time elevation, approval workflows, MFA/justification on activation, and detailed auditing for privileged roles. By contrast, the other options are separate Microsoft Entra offerings outside ID Governance: Verifiable credentials (Microsoft Entra Verified ID) issues and validates digital credentials; Permissions Management (Microsoft Entra Permissions Management) provides CIEM for multi-cloud permissions; and Identity Protection offers risk-based detection and policies for sign-ins and users. Therefore, among the choices, the feature that is included in Microsoft Entra ID Governance is Privileged Identity Management (PIM), which is specifically called out by Microsoft as a pillar of ID Governance and is used to govern privileged access with policy-based controls, time-bound assignments, approvals, and comprehensive auditability.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft’s identity guidance classifies social identity services (e.g., GitHub, Google, Facebook) as cloud-based identity providers that can be used for external identities with Microsoft Entra ID. In this model, GitHub functions as an IdP using OAuth/OpenID Connect to authenticate users and issue tokens that applications or Entra ID can accept. Federation in Microsoft terms is the trust relationship that allows SSO across organizational boundaries and with multiple identity providers, such as Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), SAML, or OpenID Connect providers, so users can authenticate once and access multiple apps without repeated sign-ins.
Crucially, SCI materials distinguish roles: an identity provider primarily handles authentication (proving who the user is and issuing claims/tokens). Authorization—deciding what the user can do—is enforced by the application or resource (often using roles/claims from the IdP). Auditing spans multiple planes: the IdP provides sign-in and audit logs, while applications and other services maintain their own activity logs. Therefore, it is incorrect to say a central IdP “manages all modern authentication services” including authorization and auditing; those responsibilities are shared across the identity platform and the relying applications/resources.
Which Microsoft portal provides information about how Microsoft manages privacy, compliance, and security?
Options:
Microsoft Service Trust Portal
Compliance Manager
Microsoft 365 compliance center
Microsoft Support
Answer:
AExplanation:
The Service Trust Portal is Microsoft’s public-facing portal that centralizes how Microsoft manages privacy, compliance, and security for its cloud services. It provides independent audit reports, compliance guides, data protection resources, and details on Microsoft’s internal controls and practices. It’s the authoritative place to learn how Microsoft meets global, regional, and industry standards.
Which Microsoft portal provides information about how Microsoft cloud services comply with regulatory standard, such as International Organization for Standardization (ISO)?
Options:
the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center
Azure Cost Management + Billing
Microsoft Service Trust Portal
the Azure Active Directory admin center
Answer:
CExplanation:
The Microsoft Service Trust Portal contains details about Microsoft's implementation of controls and processes that protect our cloud services and the customer data therein.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is designed to collect and aggregate security data from multiple sources—such as servers, devices, applications, and security appliances—across an organization. It then analyzes the data for anomalies, correlations, and patterns that could indicate potential threats or breaches.
From the SCI certification learning paths, especially SC-200 (Microsoft Security Operations Analyst), Microsoft defines SIEM as follows:
“SIEM tools collect and analyze activity from multiple resources across your IT infrastructure. Microsoft Sentinel is Microsoft’s cloud-native SIEM that provides intelligent security analytics and threat intelligence to help detect and respond to security threats.”
A SIEM system:
Ingests large volumes of data (logs, events).
Uses built-in rules, AI, and analytics to identify threats.
Correlates alerts from various sources to form incidents.
Generates alerts and dashboards for security analysts.
Microsoft Sentinel, as Microsoft’s SIEM solution, embodies all of these capabilities.
Other options in the dropdown (incorrect for this context):
SOAR is focused on automating responses after SIEM alerts.
TAXII is a threat intel transport protocol, not a detection system.
ASR (Attack Surface Reduction) refers to endpoint hardening, not centralized event analysis.
✅ Therefore, the correct and Microsoft-verified term is: A security information and event management (SIEM).
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

Microsoft defines Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) as “a cloud-based identity and access management (IAM) service” that “helps your employees sign in and access resources.” In SCI learning paths, Entra ID is positioned as the tenant’s identity provider (IdP) that authenticates users and issues tokens for applications using standards such as OpenID Connect, OAuth 2.0, and SAML, which applications then use to authorize access based on roles/claims. Microsoft further explains that Entra ID provides single sign-on, Conditional Access, MFA, and token-based authorization—all core IdP capabilities that govern who can access what across Microsoft 365, Azure, and thousands of SaaS apps.
By contrast, an extended detection and response (XDR) system refers to Microsoft Defender XDR, which focuses on incident detection, correlation, and response—not identity provisioning or token issuance. A security information and event management (SIEM) system refers to Microsoft Sentinel, which aggregates and analyzes logs and alerts—not primary authentication. An Azure management group is a governance scope used to organize subscriptions and apply policy/RBAC at scale; it is not an authentication/authorization service. Therefore, within Microsoft’s SCI scope, Microsoft Entra ID is an identity provider used to perform authentication (verifying identity and issuing tokens) and to enable authorization in applications and resources that consume those tokens.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity materials, Azure AD B2B collaboration is the feature designed for working with external organizations. Microsoft describes it as follows: “Azure AD B2B collaboration allows you to securely share your company’s applications and services with guest users from any other organization, while maintaining control over your own corporate data. Guest users sign in with their own work, school, or social identities, and appear as guest users in your directory.” This directly matches the sentence in the prompt—enabling collaboration with suppliers, partners, and vendors while ensuring that external users appear as guest users in the tenant.
By contrast, Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is an on-premises directory service for Windows domain joined resources and does not provide cloud guest user collaboration. Active Directory forest trusts establish trust relationships between AD DS forests for resource access, not modern cloud guest access using Conditional Access, MFA, or entitlement processes. Azure AD B2C is for consumer/retail scenarios where you build customer-facing apps, managing their identities in a separate customer directory; it is not intended for partner collaboration within your enterprise tenant. Therefore, the capability that fits the statement—external partner collaboration with users appearing as guest accounts—is Azure AD B2B.
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft’s Security, Compliance, and Identity guidance, multi-factor authentication (MFA) is based on combining independent categories of credentials to verify a user. Microsoft describes the three factor types as: something you know (knowledge), something you have (possession), and something you are (inherence). A password is explicitly categorized as “something you know,” because it relies on a secret the user memorizes and types during sign-in. MFA improves security by requiring two or more of these distinct factors—e.g., a password (know) plus a phone approval or hardware token (have), or a biometric like Windows Hello (are). Using factors from different categories mitigates common attacks such as password spray, credential stuffing, and phishing, because compromising one factor (for example, the password) does not grant access without the second, unrelated factor. Microsoft recommends enabling MFA broadly and pairing passwords with stronger possession or inherence methods to achieve a measurable reduction in account compromise risk. Therefore, in the MFA model used by Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD), a password is considered something you know.
Match the Microsoft Defender for Office 365 feature to the correct description.
To answer, drag the appropriate feature from the column on the left to its description on the right. Each feature may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:

In Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Threat Trackers (also known as threat analytics in the security portal) surface curated intelligence on prevailing and emerging cyberthreats, giving security teams insight into current campaigns, affected regions, and recommended actions. Threat Explorer (Explorer/Real-time detections) is the investigation workspace that provides near real-time visibility into detected phishing, malware, and other malicious email content, allowing analysts to identify, filter, and analyze recent threats and take remediation actions (e.g., purge messages). Anti-phishing protection is configured via anti-phishing policies and uses machine learning and impersonation settings (user and domain impersonation) to detect and block impersonation attempts and other phishing techniques in Exchange Online. Together, these capabilities map directly to the statements: Trackers = intelligence on active threats, Explorer = real-time analysis and reporting, and Anti-phishing = detection of impersonation.
What can you use to provide a user with a two-hour window to complete an administrative task in Azure?
Options:
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Identity Protection
conditional access policies
Answer:
DExplanation:
Privileged Identity Management provides time-based and approval-based role activation to mitigate the risks of excessive, unnecessary, or misused access permissions on resources that you care about. Here are some of the key features of Privileged Identity Management: Provide just-in-time privileged access to Azure AD and Azure resources Assign time-bound access to resources using start and end dates Require approval to activate privileged roles Enforce multi-factor authentication to activate any role Use justification to understand why users activate Get notifications when privileged roles are activated Conduct access reviews to ensure users still need roles Download audit history for internal or external audit Prevents removal of the last active Global Administrator role assignment
Select the answer that correctly completes the sentence.

Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
access
In Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), dynamic groups are a key feature used to automate the access lifecycle for users and devices. SCI learning material on identity governance explains that organizations can automate the access lifecycle process through technologies such as dynamic groups, alongside automated user provisioning. These resources describe the access lifecycle as managing a user’s access to resources from the moment they join the organization, through role or department changes, until they leave. Dynamic groups help with this by using attribute-based rules (for example, department, job title, location, or device platform) to automatically add or remove identities from groups as their attributes change.
Because group membership typically controls access to applications, SharePoint sites, Teams, and licenses, this automatic membership update keeps access aligned with the user’s current role without manual intervention. When a user changes departments, the dynamic rules reevaluate and move them into the appropriate groups, granting new access and removing old access as required. This is exactly what Microsoft refers to as automating the access lifecycle.
The other options do not match the terminology used in SCI content: “object lifecycle” is not the term used in Entra identity governance, and “privileged access” lifecycle is handled specifically by Privileged Identity Management (PIM), not by dynamic groups. Therefore, the sentence is correctly completed with access.
Which feature provides the extended detection and response (XDR) capability of Azure Sentinel?
Options:
integration with the Microsoft 365 compliance center
support for threat hunting
integration with Microsoft 365 Defender
support for Azure Monitor Workbooks
Answer:
CExplanation:
Microsoft positions Microsoft Sentinel as a cloud-native SIEM and SOAR that “collects data at cloud scale” and “detects, investigates, and responds to threats.” The extended detection and response (XDR) layer in Microsoft’s security stack is delivered by Microsoft 365 Defender, which “correlates signals across endpoints, identities, email, and apps to automatically detect, investigate, and remediate attacks.” Sentinel’s XDR capability is realized through its integration with Microsoft 365 Defender, enabling incident synchronization, alert enrichment, and bi-directional actions. Documentation explains that this integration “brings Microsoft 365 Defender incidents into Microsoft Sentinel,” unifying SIEM/SOAR analytics with the cross-domain XDR detections from Defender. Features such as automatic incident grouping, advanced hunting, and entity behavior flow from Microsoft 365 Defender to Sentinel, giving analysts an end-to-end XDR view. By contrast, threat hunting and workbooks are valuable Sentinel features, and compliance center is unrelated to XDR. The specific capability that provides Sentinel’s XDR experience is its integration with Microsoft 365 Defender.
Which three authentication methods can be used by Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Options:
phone call
text message (SMS)
email verification
Microsoft Authenticator app
security question
Answer:
A, B, DExplanation:
Microsoft states that Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication “adds a second form of verification” to sign-ins and supports multiple verification methods. The documented methods include Microsoft Authenticator app notifications or verification codes, text message (SMS) codes, and phone call verification. In Microsoft’s description, users can approve a push notification in the Microsoft Authenticator app or enter a code from the app; they can receive a text message containing a verification code; or they can answer a phone call to complete the challenge. Email verification and security questions are not listed as supported MFA methods for Azure AD sign-ins and are not valid second factors in Azure AD MFA. Consequently, the correct methods from the options provided are Phone call, Text message (SMS), and Microsoft Authenticator app. These align with Azure AD’s core MFA capabilities used in Conditional Access and per-user MFA to strengthen authentication beyond the password and to meet compliance and security requirements for strong user verification.
What feature in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides the first line of defense against cyberthreats by reducing the attack surface?
Options:
automated remediation
automated investigation
advanced hunting
network protection
Answer:
DExplanation:
In Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, attack surface reduction (ASR) is described as the first defensive layer in the protection stack, and Network protection is a core ASR capability. Microsoft’s documentation states that “Attack surface reduction provides the first line of defense in the stack.” It further explains that these capabilities are designed to reduce opportunities for compromise before malware can run or persistence can be established. Within ASR, Microsoft specifically defines Network protection as a feature that “helps reduce the attack surface of your devices from Internet-based events.” Microsoft also clarifies how it works: “It prevents employees from using any application to access dangerous domains that may host phishing scams, exploits, and other malicious content on the Internet.”
Because the question asks for the feature in Defender for Endpoint that delivers the first line of defense by reducing the attack surface, the applicable ASR capability is Network protection. It proactively blocks access to known malicious IPs, domains, and URLs, shrinking the exploitable surface area and thereby reducing risk before an attack can execute. By contrast, automated investigation and automated remediation act after detections to contain and fix issues, and advanced hunting is an analyst-driven, query-based detection and investigation tool—not an attack-surface–reduction control. Hence, Network protection is the correct choice.
What can you use to scan email attachments and forward the attachments to recipients only if the attachments are free from malware?
Options:
Microsoft Defender for Office 365
Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender for Identity
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Answer:
AExplanation:
Microsoft Defender for Office 365 includes Safe Attachments, a protection that “checks attachments in a secure, virtual environment to detect malicious behavior.” In Microsoft’s guidance, Safe Attachments is described as part of the anti-malware pipeline that “routes messages with attachments to a detonation chamber; if no suspicious activity is detected, the message is released to the recipient, and if malicious behavior is found, the attachment is blocked or removed.” Administrators can choose Block, Replace, Dynamic Delivery, or Monitor actions. The Dynamic Delivery option specifically supports the use case in the question: the email body is delivered while the attachment is scanned, and “the attachment is automatically reattached and forwarded to the recipient only when it is determined to be safe.” This capability is unique to Defender for Office 365’s Safe Attachments, not to be confused with endpoint antivirus or identity tools. Defender Antivirus protects Windows devices, Defender for Identity secures on-premises identities, and Defender for Endpoint focuses on endpoint detection and response. Therefore, the Microsoft service you use to scan email attachments and forward them only when clean is Microsoft Defender for Office 365 (Safe Attachments).

