Operational Risk Manager (ORM) Exam Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT true in respect of bilateral close out netting:
Which of the following is not a measure of risk sensitivity of some kind?
Which of the following steps are required for computing the aggregate distribution for a UoM for operational risk once loss frequency and severity curves have been estimated:
I. Simulate number of losses based on the frequency distribution
II. Simulate the dollar value of the losses from the severity distribution
III. Simulate random number from the copula used to model dependence between the UoMs
IV. Compute dependent losses from aggregate distribution curves
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Credit risk and counterparty risk are synonymous
II. Counterparty risk is the contingent risk from a counterparty's default in derivative transactions
III. Counterparty risk is the risk of a loan default or the risk from moneys lent directly
IV. The exposure at default is difficult to estimate for credit risk as it depends upon market movements
Under the internal ratings based approach for risk weighted assets, for which of the following parameters must each institution make internal estimates (as opposed to relying upon values determined by a national supervisor):
If the loss given default is denoted by L, and the recovery rate by R, then which of the following represents the relationship between loss given default and the recovery rate?
For a group of assets known to be positively correlated, what is the impact on economic capital calculations if we assume the assets to be independent (or uncorrelated)?
Which of the following decisions need to be made as part of laying down a system for calculating VaR:
I. How returns are calculated, eg absoluted returns, log returns or relative/percentage returns
II. Whether VaR is calculated based on historical simulation, Monte Carlo, or is computed parametrically
III. Whether binary/digital options are included in the portfolio positions
IV. How volatility is estimated
Which of the following measures can be used to reduce settlement risks:
Which of the following credit risk models considers debt as including a put option on the firm's assets toassess credit risk?
Which loss event type is the loss of personally identifiableclient information classified as under the Basel II framework?
An assumption regarding the absence of ratings momentum is referred to as:
When compared to a medium severity medium frequency risk, the operational risk capital requirement for a high severity very low frequency risk is likely to be:
Which of the following is not one of the 'three pillars' specified in the Basel accord:
When compared to a low severity high frequency risk, the operational risk capital requirement for a medium severity medium frequency risk is likely to be:
A financial institution is considering shedding a business unit to reduce its economic capital requirements. Which of the following is an appropriate measure of theresulting reduction in capital requirements?
Which of the following statements are correct in relation to the financial system just prior to the current financial crisis:
I. The system was robustagainst small random shocks, but not against large scale disturbances to key hubs in the network
II. Financial innovation helped reduce the complexity of the financial network
III. Knightian uncertainty refers to risk that can be quantified and measured
IV. Feedback effects under stress accentuated liquidity problems
Credit exposure for derivatives is measured using
Which of the following are valid criticisms of value at risk:
I. There are many risks that a VaR framework cannot model
II. VaR does not considerliquidity risk
III. VaR does not account for historical market movements
IV. VaR does not consider the risk of contagion
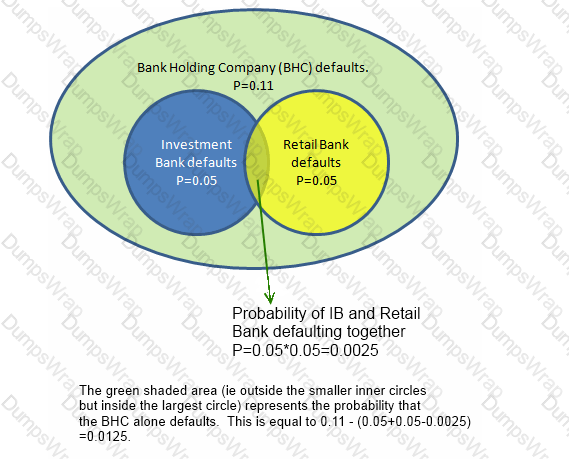
A Bank Holding Company (BHC) is invested in an investment bank and a retail bank. The BHC defaults for certain if either the investment bank or the retail bank defaults. However, the BHC can also default on its own without either the investment bank or the retail bank defaulting. The investment bank and the retail bank's defaults are independent of each other, with a probability of default of 0.05 each. The BHC's probability of default is 0.11.
What is the probabilityof default of both the BHC and the investment bank? What is the probability of the BHC's default provided both the investment bank and the retail bank survive?
Which of the following distributions is generally not used for frequency modeling for operational risk
The VaR of a portfolio at the 99% confidence level is $250,000 when mean return is assumed to be zero. If the assumption of zero returns is changed to an assumption of returns of $10,000, what is the revised VaR?
According to the Basel framework, shareholders' equity and reserves are considered a part of:
Which of the following techniques is used to generate multivariate normal random numbers that are correlated?
The frequency distribution for operational risk loss events can be modeled by which of the following distributions:
I. The binomial distribution
II. The Poisson distribution
III. The negative binomial distribution
IV. The omega distribution
When modeling severity of operational risk losses using extreme value theory (EVT), practitioners often use which of the following distributions to model loss severity:
I. The 'Peaks-over-threshold' (POT) model
II. Generalized Pareto distributions
III. Lognormal mixtures
IV. Generalized hyperbolic distributions
The loss severity distribution for operational risk loss events is generally modeled by which of the following distributions:
I. the lognormal distribution
II. The gamma density function
III. Generalized hyperbolic distributions
IV. Lognormal mixtures
A risk analyst peforming PCA wishes to explain80% of the variance. The first orthogonal factor has a volatility of 100, and the second 40, and the third 30. Assume there are no other factors. Which of the factors will be included in the final analysis?
A stock that follows the Weiner process has its future price determined by:
Which of the following event types is hacking damage classified under Basel II operational risk classifications?
If the odds of default are 1:5, what is the probability of default?
Which of the following cannot be used as an internal credit rating model to assess an individual borrower:
Which of the following belong to the family of generalized extreme value distributions:
I. Frechet
II. Gumbel
III. Weibull
IV. Exponential
A bank's detailed portfolio data on positions held in a particular security across the bank does not agree with the aggregate total position for that security for the bank. What data quality attribute is missing in this situation?
What would be the consequences of a model of economic risk capital calculation that weighs all loans equallyregardless of the credit rating of the counterparty?
I. Create an incentive to lend to the riskiest borrowers
II. Create an incentive to lend to the safest borrowers
III. Overstate economic capital requirements
IV. Understate economic capitalrequirements
Which of the following are valid approaches to leveraging external loss data for modeling operational risks:
I. Both internal and external losses can be fitted with distributions,and a weighted average approach using these distributions is relied upon for capital calculations.
II. External loss data is used to inform scenario modeling.
III. External loss data is combined with internal loss data points, and distributions fitted to the combined data set.
IV. External loss data is used to replace internal loss data points to create a higher quality data set to fit distributions.